Overview
This article serves as a comprehensive guide on selecting the appropriate analytical column for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC). It outlines essential criteria and a systematic selection process that underscores the importance of understanding key factors such as:
- Stationary phase chemistry
- Particle size
- Sample properties
These elements collectively influence both the performance and suitability of the chosen column for specific analytical objectives. By following the outlined steps, readers can ensure they make informed decisions that enhance their analytical outcomes.
Introduction
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) serves as a cornerstone in analytical chemistry, facilitating the precise separation and identification of complex mixtures. Selecting the appropriate analytical column is critical for optimizing this powerful technique; the right choice can significantly influence resolution, efficiency, and overall outcomes.
However, with a multitude of column types and specifications available, how can one effectively navigate this intricate selection process to ensure optimal results for specific applications?
This guide explores essential criteria and step-by-step strategies designed to empower researchers and analysts in making informed decisions regarding their HPLC columns.
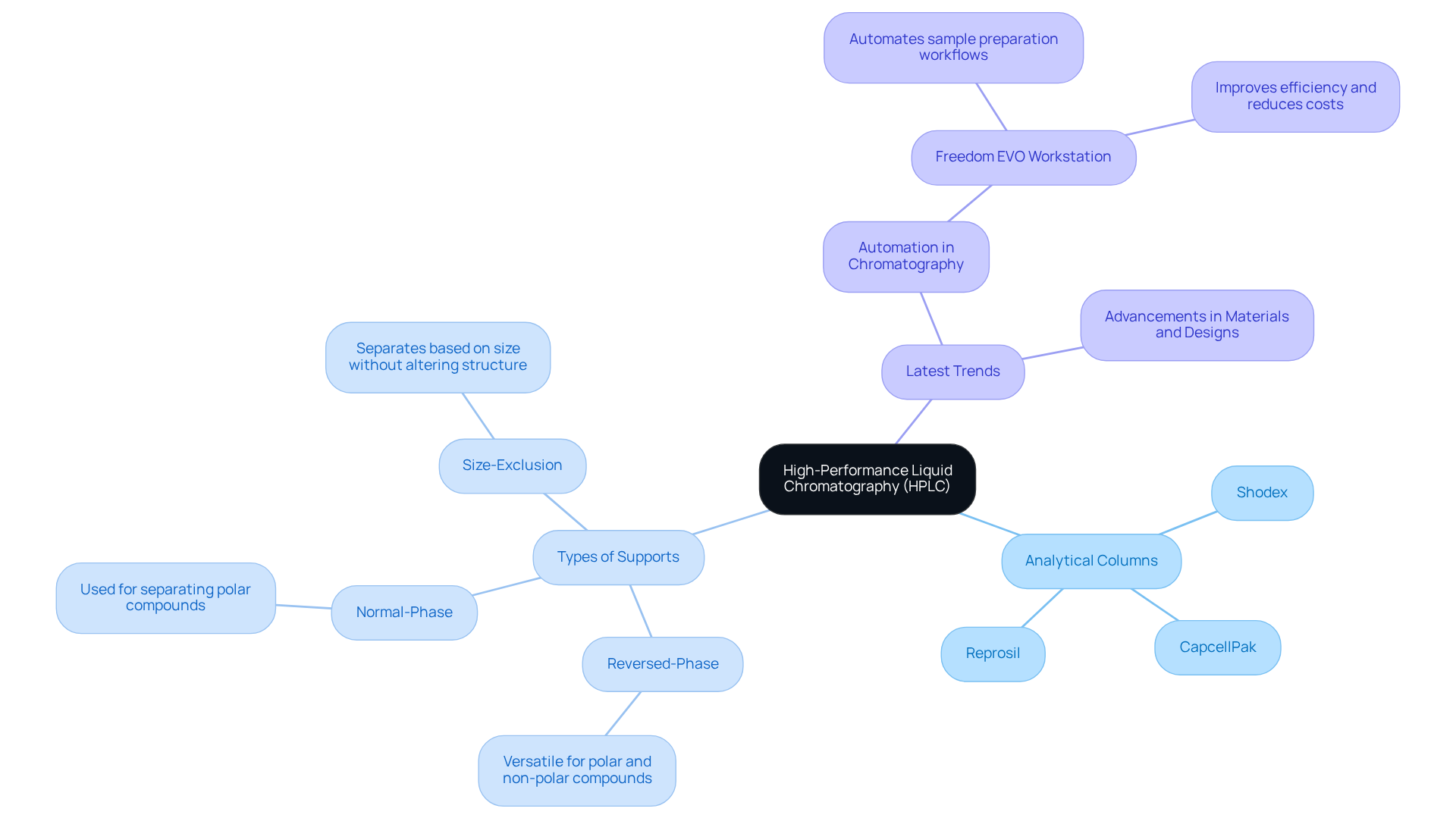
Understand the Basics of HPLC and Analytical Columns
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is an essential method that utilizes an analytical column HPLC for the separation, identification, and quantification of constituents within complex mixtures. At the heart of this method is the analytical tube, which houses a stationary phase that interacts with sample components as they pass through.
JM Science Inc. offers a comprehensive range of high-quality liquid chromatography tubes, including:
- Shodex
- CapcellPak
- Reprosil
These are vital for selecting the right tube for your specific applications. Understanding the various types of supports available, such as:
- reversed-phase
- normal-phase
- size-exclusion
is crucial for optimizing the analytical column HPLC processes. Each type has distinct characteristics that influence separation efficiency, resolution, and analysis duration. For example, reversed-phase materials are widely favored for their versatility in separating polar and non-polar compounds, while size-exclusion media excel in separating molecules based on size without altering their chemical structure.
Additionally, JM Science provides titrators and Karl Fischer reagents, which enhance chromatography solutions and bolster laboratory capabilities. Staying updated on the latest trends in analytical techniques for 2025, including advancements in materials and designs, can significantly improve laboratory performance. By familiarizing yourself with these fundamental concepts and recent developments, such as the integration of automation systems like the Freedom EVO, you will be better equipped to navigate the selection process and enhance your chromatography applications.
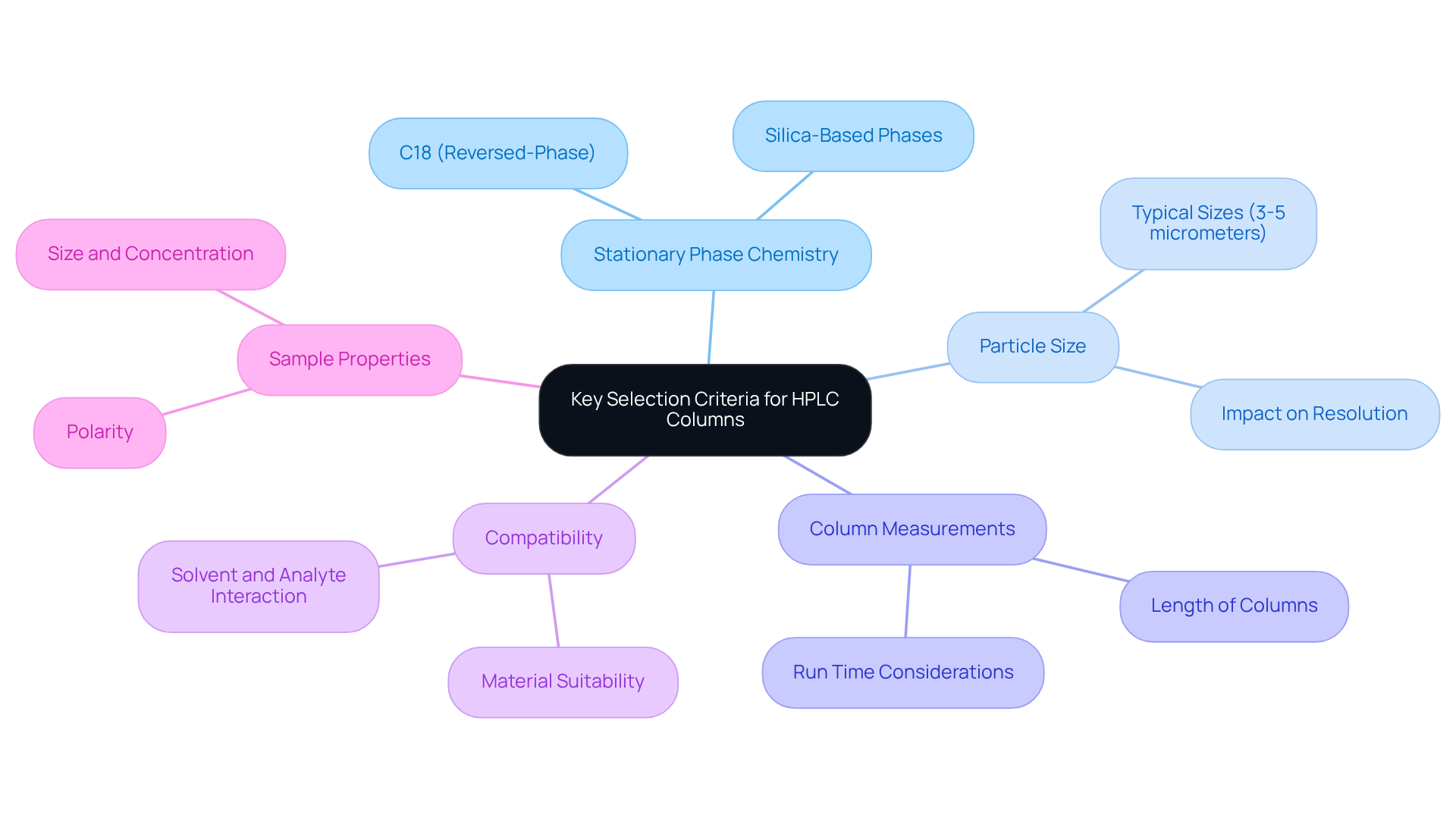
Identify Key Selection Criteria for HPLC Columns
When selecting an analytical column HPLC, several key criteria warrant careful consideration to ensure optimal performance in your analytical endeavors.
-
Stationary Phase Chemistry is paramount; the chemical characteristics of the stationary phase significantly influence how various compounds interact with the medium. Common types, such as C18 (reversed-phase) and silica-based phases, offer distinct advantages depending on the nature of your analysis.
-
Particle Size also plays a critical role. Smaller particles generally provide enhanced resolution, although they may necessitate higher pressure. Typical sizes range from 3 to 5 micrometers, and understanding this can help you achieve the desired analytical results.
-
Column Measurements further affect efficiency and analysis duration. Longer columns typically yield better separation, yet they also increase run time, a trade-off that must be carefully evaluated based on your specific requirements.
-
Compatibility is another essential factor. Ensure that the material of the column is suitable for the solvents and analytes employed in your analysis to prevent any adverse reactions that could compromise results.
-
Lastly, consider the Sample Properties. The nature of the samples being analyzed, including their polarity, size, and concentration, will influence your choice of stationary phase. By taking these factors into account, you can make a well-informed decision that enhances the reliability and accuracy of your analytical column HPLC results.
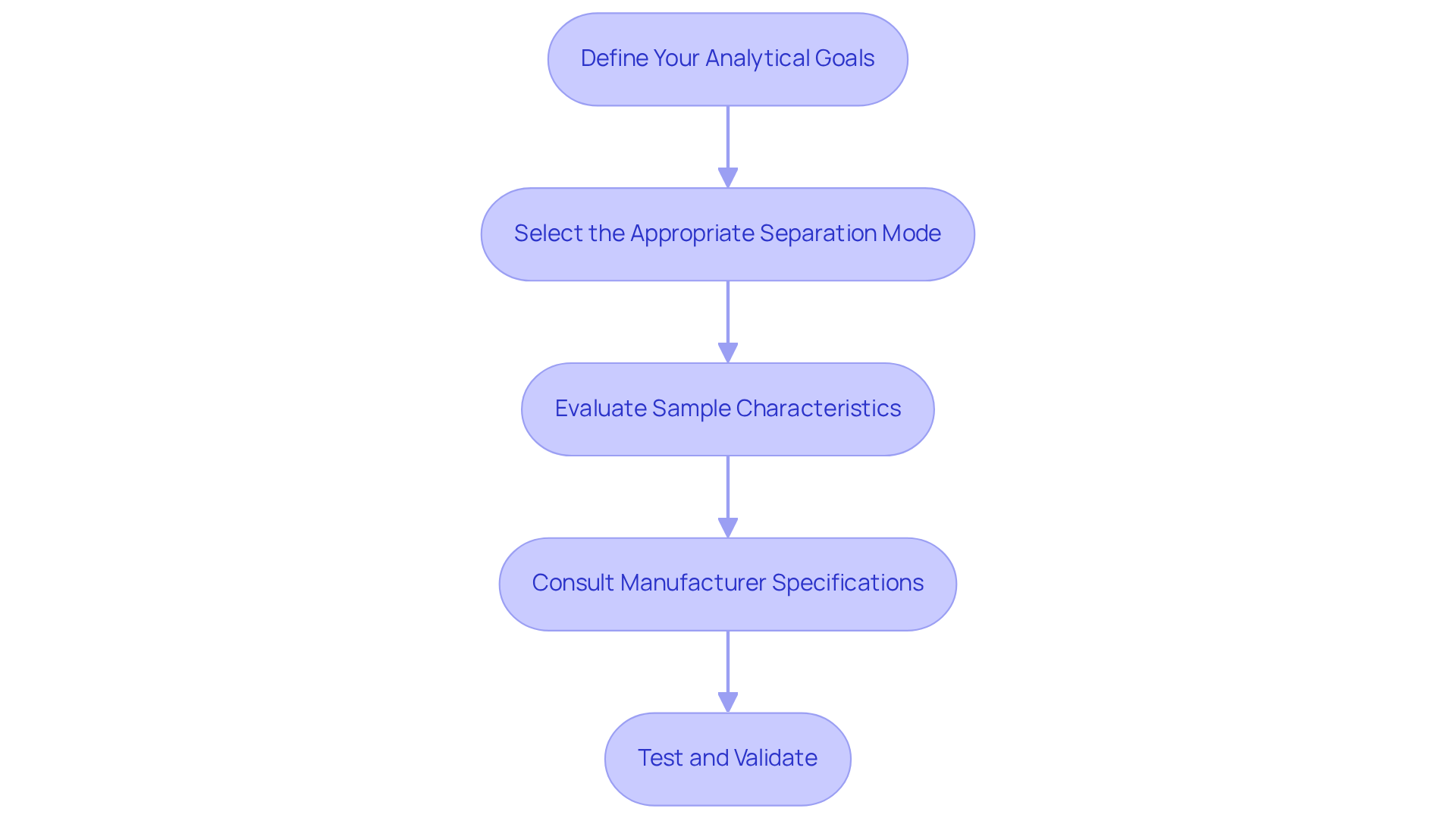
Follow a Step-by-Step Process to Choose the Right Column
To select the right HPLC column, follow these essential steps:
- Define Your Analytical Goals: Begin by determining what you aim to achieve with your analysis. Consider factors such as resolution efficiency, speed, and sensitivity, as these will guide your subsequent decisions.
- Select the Appropriate Separation Mode: Based on your defined goals, decide whether you require reversed-phase, normal-phase, or another type of separation. This choice is crucial for effective analysis.
- Evaluate Sample Characteristics: Analyze the properties of your samples, including polarity and molecular weight. Understanding these characteristics will assist you in selecting the most suitable chromatographic medium.
- Consult Manufacturer Specifications: Review the specifications provided by manufacturers. This step is vital to identify options that align with your criteria and analytical needs.
- Test and Validate: After selecting a column, conduct preliminary tests to validate its performance with your specific samples. Be prepared to adjust your choice based on the results to ensure optimal analysis outcomes.
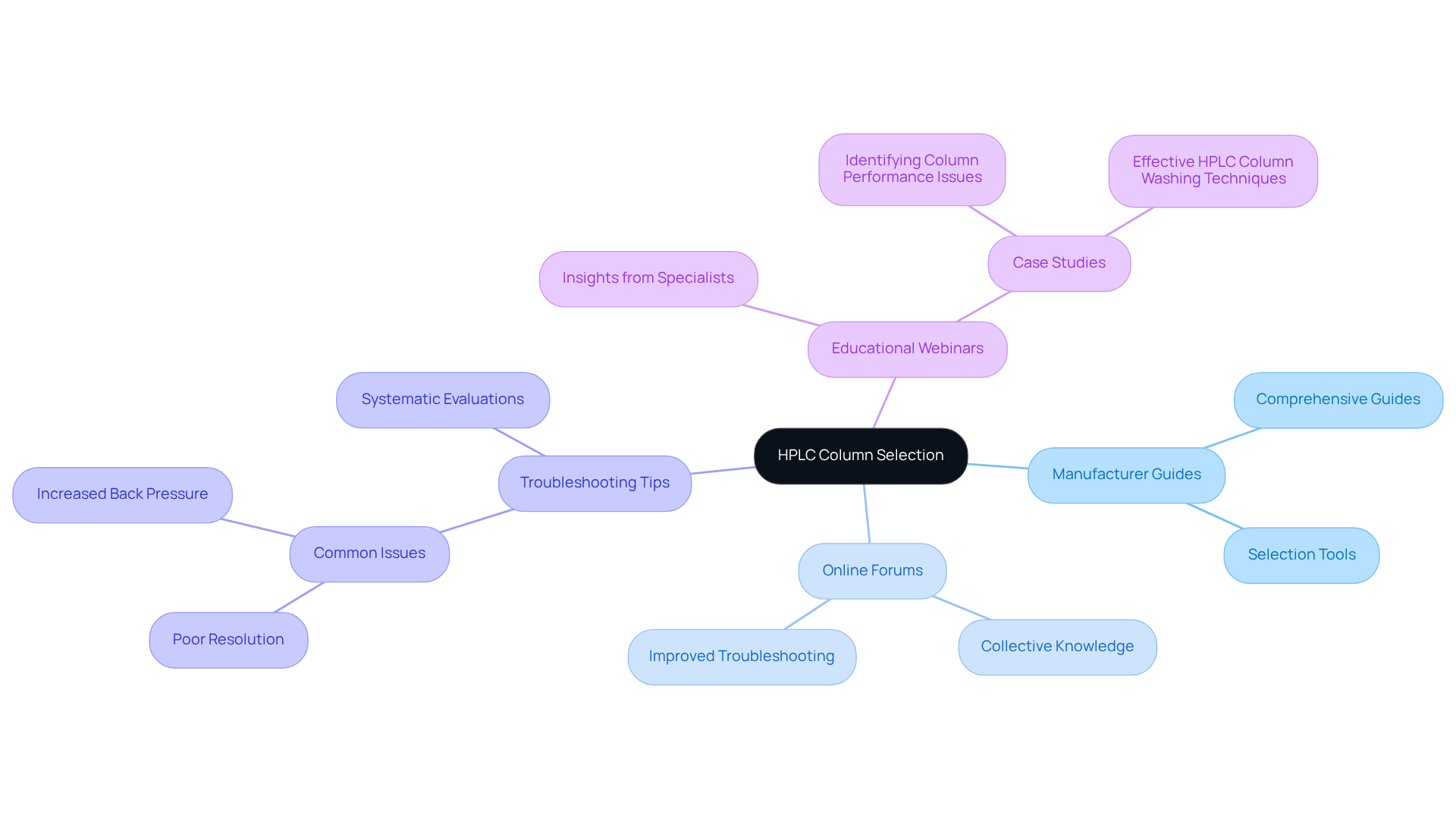
Access Resources and Troubleshooting Tips for HPLC Column Selection
To enhance your HPLC column selection process, it is essential to utilize a variety of resources and troubleshooting strategies.
-
Manufacturer Guides: Many manufacturers provide comprehensive guides and selection tools on their websites, specifically tailored to various applications. These resources can significantly streamline your decision-making process, ensuring you choose the right column for your needs.
-
Online Forums and Communities: Engaging in chromatography forums allows you to tap into the collective knowledge of experienced users who have navigated similar challenges. This collaborative environment fosters effective problem-solving. Statistics indicate that active participation in these forums often leads to improved troubleshooting outcomes, as users share valuable insights and solutions based on their experiences.
-
Troubleshooting Tips: Should you encounter issues like poor resolution or increased back pressure, it is crucial to examine typical causes such as obstructions in the phase or inappropriate mobile phase compositions. For instance, flushing the system with a strong organic solvent can effectively eliminate contaminants, while extending equilibration times can enhance performance. Regular maintenance and vigilant management of supports are vital to minimizing potential issues.
-
Educational Webinars: Attending webinars led by industry specialists can provide valuable insights into effective column selection and troubleshooting methods, thereby enhancing your understanding and application of chromatography technology. A pertinent case study, such as 'Identifying Column Performance Issues,' illustrates how systematic evaluations can aid in pinpointing and addressing common performance challenges.
By leveraging these resources, you can significantly improve your HPLC operations and ensure optimal performance in your analytical column HPLC processes.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate analytical column for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a critical step that significantly impacts the quality and efficiency of analytical results. A solid understanding of HPLC fundamentals and the various types of columns available empowers users to make informed decisions tailored to their specific applications, ultimately enhancing the reliability of their analyses.
Key factors in this selection process include:
- The chemistry of the stationary phase
- Particle size
- Compatibility with sample properties
By following a systematic approach—defining analytical goals, evaluating sample characteristics, and consulting manufacturer specifications—users can navigate the complexities of column selection more effectively. Utilizing available resources, such as manufacturer guides and online forums, further enriches this process by providing valuable insights and troubleshooting strategies.
In conclusion, making the right choice in HPLC column selection transcends mere technical specifications; it involves staying informed about emerging trends and advancements in chromatography. By harnessing the knowledge and resources outlined in this guide, users can optimize their HPLC applications, leading to improved analytical outcomes and greater success in their laboratory endeavors. Embracing this systematic approach ensures that analytical processes remain robust, efficient, and capable of meeting the demands of modern scientific research.




