Overview
The article primarily aims to deliver a comprehensive step-by-step guide for selecting the appropriate Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) column, particularly within pharmaceutical applications. It delineates critical criteria including:
- Molecular weight range
- Pore dimensions
- System compatibility
Emphasizing that meticulous selection based on these parameters is vital, the article asserts that such diligence is essential for obtaining accurate and reliable analytical results in drug development.
Introduction
The realm of pharmaceuticals is fundamentally anchored in precise analytical techniques, with Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) emerging as a pivotal method for the separation of molecules based on size. The selection of an appropriate GPC column transcends mere technicality; it has profound implications for the efficacy and safety of drug formulations, particularly in terms of accurate molecular weight determination. Yet, with a plethora of options and criteria to navigate, how does one effectively tackle the intricacies of GPC column selection to ensure reliable outcomes? This guide offers a thorough, step-by-step approach to discerning the optimal GPC column, addressing prevalent challenges and providing insights that can significantly enhance analytical performance within pharmaceutical applications.
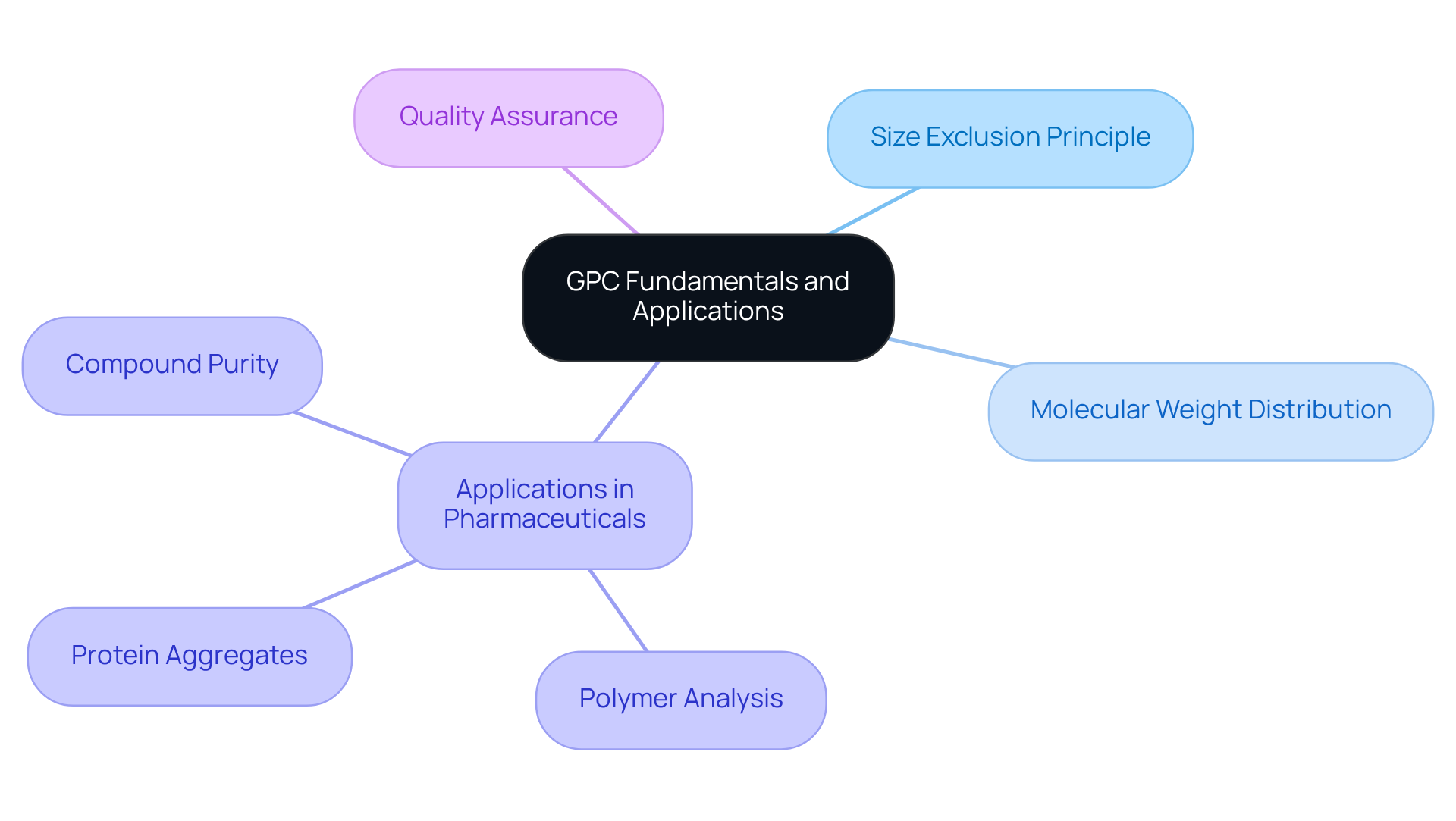
Understand GPC Fundamentals and Applications in Pharmaceuticals
The gpc column is a pivotal method in Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) for separating molecules by their dimensions, playing a particularly significant role in the pharmaceutical sector for the analysis of polymers and proteins. By operating on the principle of size exclusion, the gpc column enables smaller molecules to traverse through the pores of a stationary phase, while larger molecules are effectively excluded. This mechanism facilitates precise separation, which is essential for understanding molecular weight distribution—a crucial factor in pharmaceuticals that directly influences drug efficacy and safety. For example, the accurate determination of polymer molecular weight is vital for ensuring the stability and effectiveness of drug formulations.
The assessment of protein aggregates and the evaluation of pharmaceutical compound purity extensively utilize the GPC column, both of which are critical for regulatory compliance and product quality. Industry leaders assert that the GPC column plays a vital role in quality assurance by providing critical data on the molecular weight distribution of polymers and other materials. Familiarizing yourself with these foundational principles will enhance your ability to select the appropriate GPC option tailored to your specific analytical needs, ultimately leading to improved outcomes in drug development.
Identify Key Selection Criteria for GPC Columns
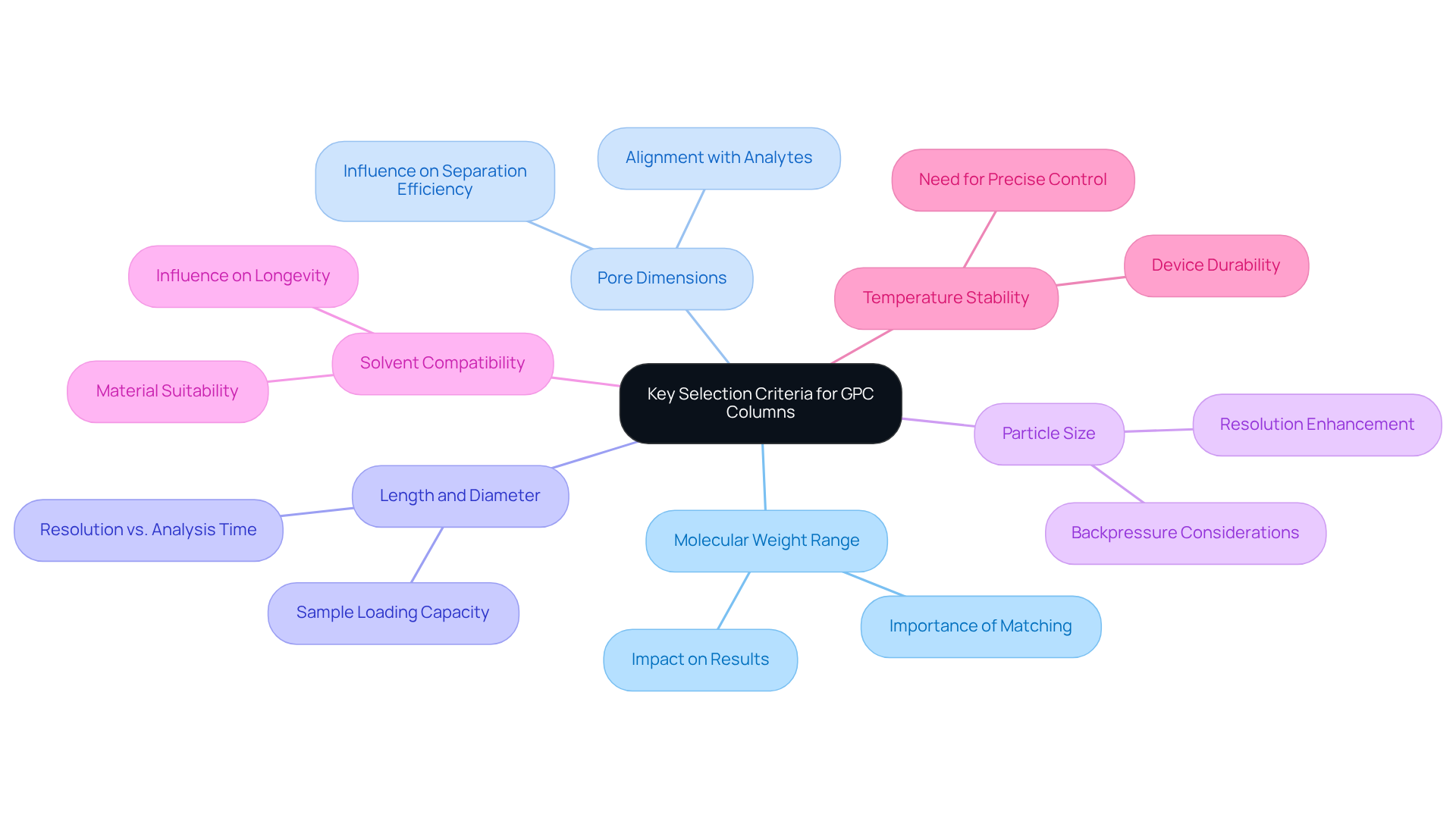
When selecting a GPC column, several key criteria must be considered to ensure optimal analytical performance:
-
Molecular Weight Range: It is essential to select an apparatus that is appropriate for the molecular weight of your specimens. Each column has a specific range it can effectively separate. Research indicates that the molecular weight ranges for pharmaceutical samples are critical for accurate analysis, as improper selection can lead to misleading results.
-
Pore Dimensions: The pore dimensions of the stationary phase significantly influence separation efficiency. Choosing a pore dimension that corresponds with the dimensions of the analytes is crucial for achieving optimal resolution. As chromatography specialist Daniela Held points out, "Proper selection aids in measuring accurate results," underscoring the importance of aligning pore size with the characteristics of the material.
-
Length and Diameter of Columns: Longer columns can offer improved resolution but may require extended analysis durations. The diameter affects the sample loading capacity, necessitating a careful balance between resolution and throughput.
-
Particle Size: Smaller particles can enhance resolution but may also increase backpressure. It is vital to balance resolution with system compatibility to ensure accurate and reliable results, as emphasized by ResolveMass.
-
Solvent Compatibility: Ensure that the material of the columnar structure is suitable for the solvents you intend to utilize, as this can greatly influence both longevity and performance.
-
Temperature Stability: Some applications may require precise temperature control; therefore, it is essential to ensure that the device can withstand the necessary conditions.
Calibration standards are indispensable in the GPC column for converting elution times into molecular weights. Utilizing the correct standards guarantees accurate molecular weight determination and maintains the reliability of the GPC system.
By thoroughly assessing these criteria, you can select a GPC column that satisfies your analytical needs. Case studies have demonstrated that appropriate pairing of columns and detectors results in high-quality, interpretable data, which is crucial for dependable decision-making in research and quality control.
Follow a Step-by-Step Process to Choose Your GPC Column
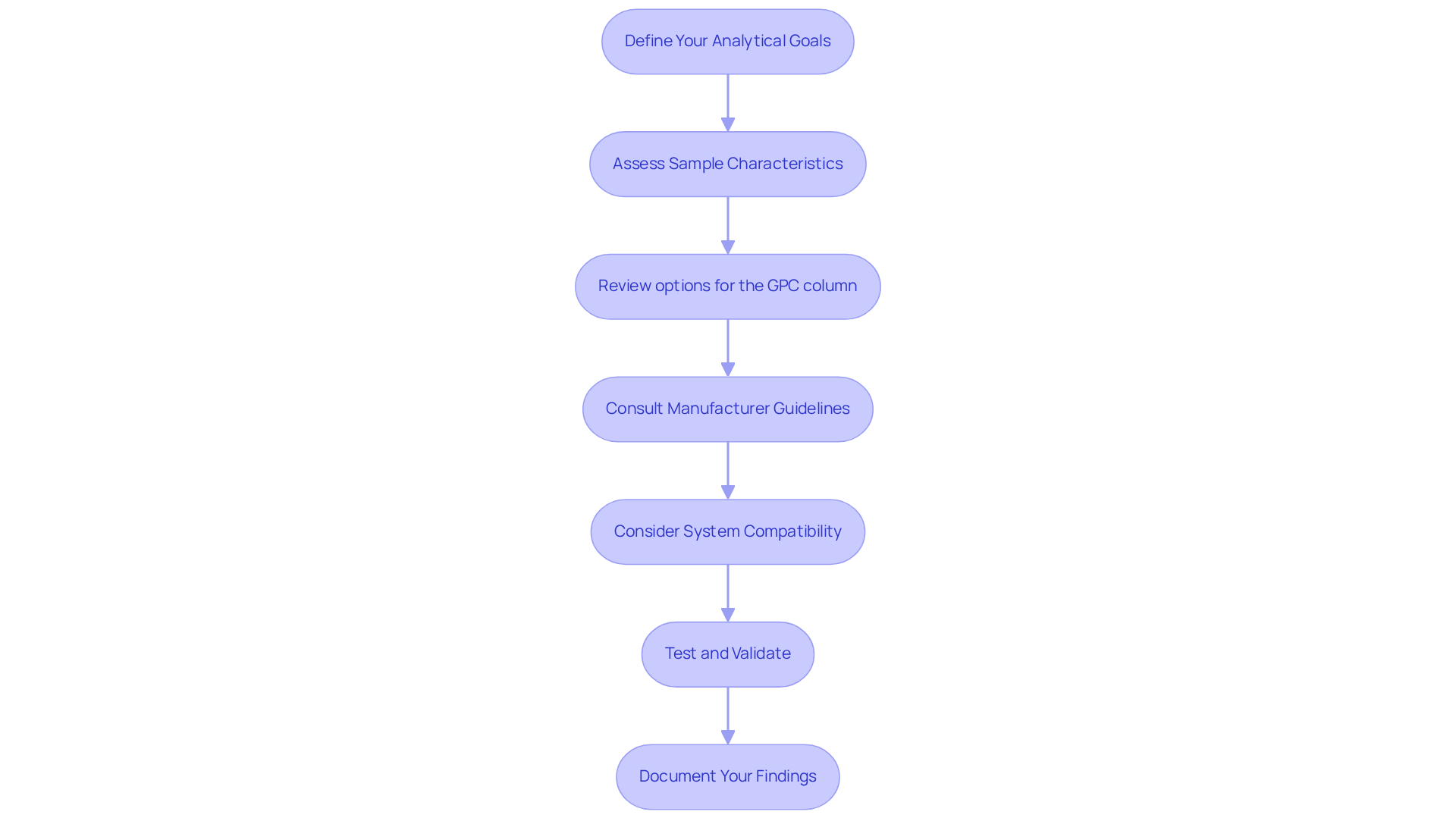
To select the appropriate GPC column, adhere to the following steps:
- Define Your Analytical Goals: Begin by determining your analysis requirements, such as the type of samples (e.g., polymers, proteins) and the necessary resolution.
- Assess Sample Characteristics: Evaluate the molecular weight and dimensions of your samples to identify the suitable specification parameters. This includes pore dimensions, which are essential for effective analysis using a GPC column based on the molecular weight of the samples.
- Review options for the GPC column: Investigate the available GPC selections that align with your criteria. Focus on aspects such as pore size, particle size, and compatibility with your solvents.
- Consult Manufacturer Guidelines: Refer to manufacturer resources, including selection guides and technical notes, to gain insights into the performance characteristics of various supports.
- Consider System Compatibility: Ensure that the chosen element is compatible with your existing GPC system. This encompasses pump pressure limits and detector types. Selecting a suitable GPC column within a GPC/SEC system is vital to prevent unnecessary repairs and downtime, as many HPLC instruments are not designed for GPC applications.
- Test and Validate: After selecting a section, conduct initial tests to verify its performance with your samples. Adjust parameters as necessary to optimize results. Be aware that improper handling of GPC/SEC systems can result in irreproducible outcomes and reduced instrument lifespan.
- Document Your Findings: Maintain comprehensive records of your selection process and results to inform future analyses and decisions. GPC materials typically endure for 500 to 1000 runs, making performance tracking essential.
By following these steps, you can systematically choose a GPC column that aligns with your analytical needs. As Wolfgang Radke, Head of the PSS contract analysis department, emphasizes, 'Regularly monitoring performance metrics is a suggestion for GPC/SEC users, and it is also required by national and international standards.
Troubleshoot Common Issues in GPC Column Selection
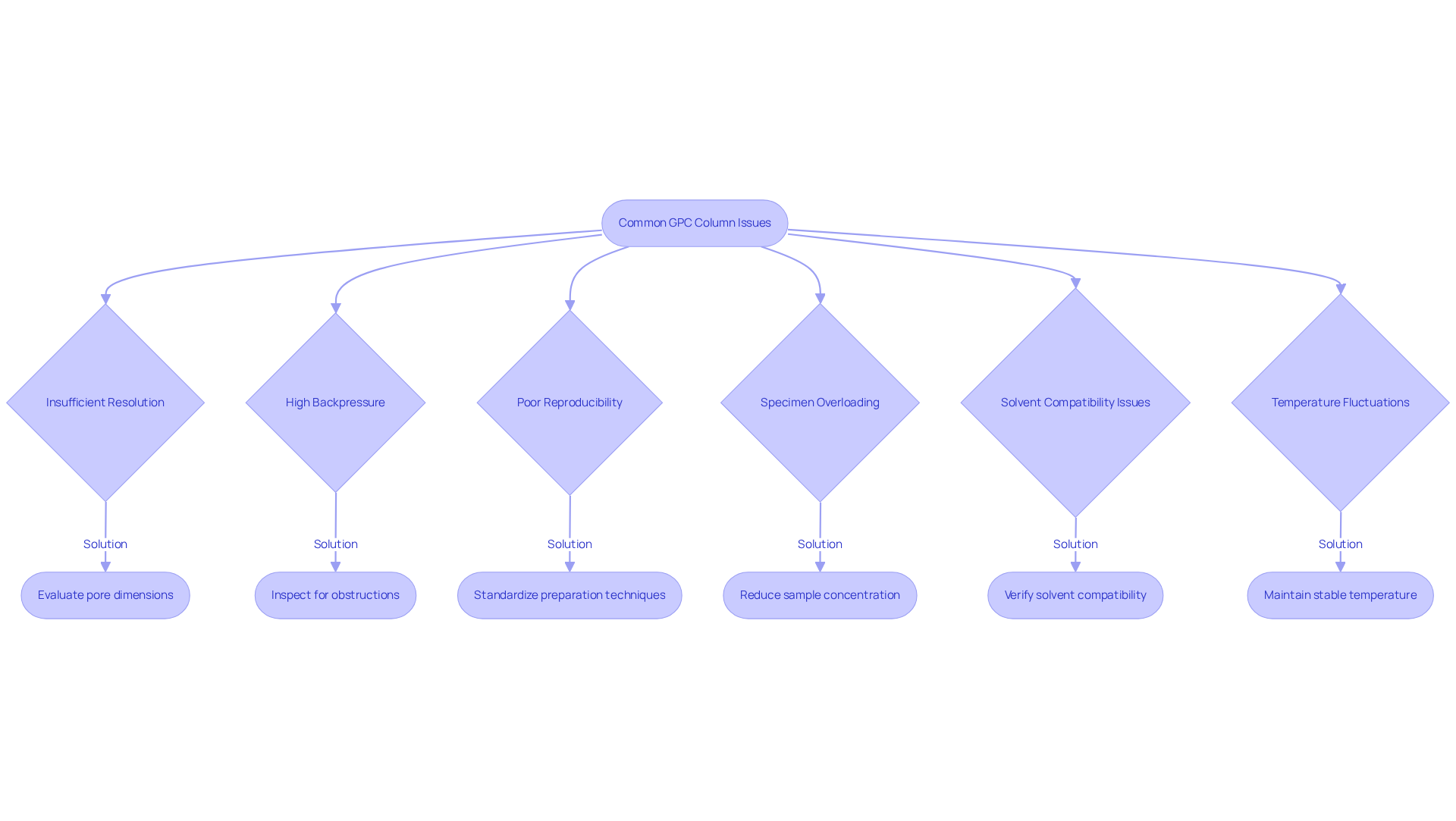
When selecting a gpc column, there are several common issues that may arise and impact your analysis.
-
Insufficient Resolution: If the support fails to deliver the anticipated resolution, it is essential to evaluate whether the pore dimensions align with your sample's molecular weight. Transitioning to a section with more suitable pore dimensions can significantly enhance separation efficiency. As Sarah Lee states, "The selection of GPC phase depends on the type of polymer being analyzed, the desired molecular weight range, and the solvent used."
-
High Backpressure: Excessive backpressure often signifies that the particle dimensions are too small for your system or that the tubing may be obstructed. Regularly inspect for obstructions and consider utilizing a configuration with larger particle sizes to alleviate pressure issues. Daniela Held notes, "A pressure change can be an indicator of a problem."
-
Poor Reproducibility: Variability in results can stem from inconsistent material preparation or degradation of the chromatography medium. To ensure uniformity, standardize your preparation techniques and replace the tube if signs of wear are evident. Research indicates that poor reproducibility is a widespread challenge in pharmaceutical analyses, underscoring the necessity for consistent practices.
-
Specimen Overloading: Distorted peaks may suggest specimen overloading. Reducing the sample concentration or opting for a tube with a larger internal diameter can help mitigate this issue and improve peak shape.
-
Solvent Compatibility Issues: Incompatibility between materials and solvents can lead to degradation. Always verify solvent compatibility before use to prevent damage to the apparatus.
-
Temperature Fluctuations: Maintaining a consistent temperature is vital for accurate results. Ensure that the section is kept at a stable temperature to avoid fluctuations that could compromise your analysis.
By recognizing these common challenges and implementing the suggested solutions, you can enhance the reliability of your analytical results and optimize your selection process for the GPC column. Statistics indicate that resolution challenges are prevalent in pharmaceutical samples, with numerous labs reporting difficulties in achieving the desired separation efficiency. Effectively addressing these issues is crucial for successful GPC analyses involving a GPC column.
Conclusion
Choosing the right GPC column is a pivotal step that can profoundly influence the success of analytical processes within the pharmaceutical industry. A solid understanding of Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) and its specific applications empowers professionals to make informed decisions that enhance the quality and reliability of drug development efforts. The meticulous selection of a GPC column, tailored to the unique characteristics of the samples, ensures accurate molecular weight determination and effective separation—both of which are essential for maintaining the efficacy and safety of pharmaceutical products.
In this article, we have thoroughly examined the key criteria for selecting a GPC column. Factors such as:
- Molecular weight range
- Pore dimensions
- Column length and diameter
- Particle size
- Solvent compatibility
- Temperature stability
are all critical in optimizing analytical performance. By adhering to a systematic step-by-step process—from defining analytical goals to troubleshooting common issues—professionals can avoid pitfalls and enhance the reliability of their results. The importance of calibration standards and regular performance monitoring further emphasizes the necessity for meticulous attention to detail throughout the selection process.
Ultimately, the significance of choosing the right GPC column transcends mere technicalities; it directly impacts the overall quality of pharmaceutical research and product development. By applying the insights and guidelines presented here, professionals can elevate their analytical capabilities and contribute to the advancement of safe and effective drug formulations. The pursuit of excellence in GPC column selection is not solely about meeting regulatory standards; it embodies a commitment to ensuring the highest quality in pharmaceutical care and innovation.




