Overview
This article delves into the critical role of alpha acids in brewing, emphasizing their importance in shaping the bitterness and flavor balance of beer. Alpha acids are fundamental to achieving the desired sharpness and complexity in beer, a process that occurs through isomerization during boiling. Brewers can influence this outcome by carefully selecting hop varieties and adjusting their brewing techniques. Understanding the manipulation of alpha acids is essential for any brewer aiming to craft high-quality beer.
Introduction
Alpha acids are fundamental to the brewing process, serving as the backbone of beer's flavor and bitterness. These vital compounds, derived from hops, not only impart sharpness but also balance the sweetness of malt, culminating in a harmonious flavor profile. Yet, the transition from hop cone to the ideal brew is not without its challenges—how can brewers effectively harness these acids to realize their desired taste? This article delves into the complexities of alpha acids, examining their chemical properties, formation, and practical applications in brewing. By doing so, it empowers both novice and seasoned brewers to elevate their craft.
Define Alpha Acids and Their Importance in Brewing
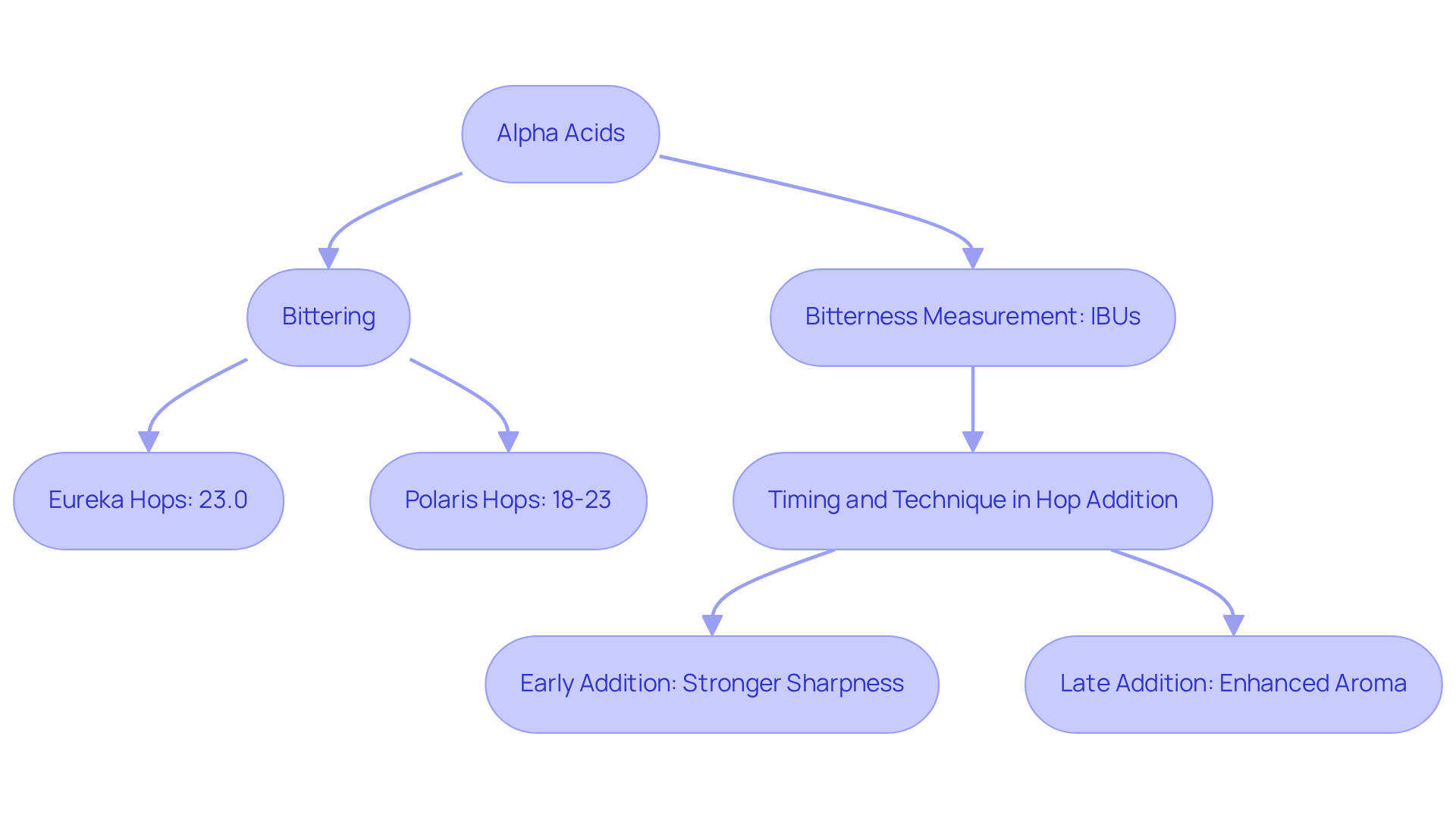
Alpha acids are crucial chemical substances found in the resin of hop cones, serving as the primary contributors to the sharp flavor of beer. This sharpness is vital for balancing the sweetness of malt, thereby enhancing the overall flavor profile of the brew. The intensity of sharpness imparted by hop compounds is quantified in International Bitterness Units (IBUs), a key metric that allows brewers to fine-tune their recipes to achieve the desired flavor. For instance, hops like Eureka can reach bittering compound percentages of up to 23.0%, while Polaris hops have a bittering compound range of 18-23%. This significant variation influences both the sharpness and flavor complexity of the beer.
Understanding the role of bitter compounds is essential for both homebrewers and commercial brewers, as these compounds directly impact the quality and character of the final product. A well-balanced beer typically exhibits a harmonious interaction between bittering and flavor compounds, with the latter enhancing aroma rather than sharpness. Most bittering hops maintain alpha-to-beta compound ratios of 3:1 or greater, which helps preserve a desirable bitterness profile while allowing for aromatic depth.
Without a solid understanding of hop compounds, brewers may struggle to create balanced and enjoyable beers. The transformation of primary compounds into iso-primary compounds during the brewing process, particularly through isomerization, is a critical factor in achieving the distinctive bitter taste. This process underscores the importance of timing and technique in hop addition; early additions during boiling yield stronger sharpness, while late additions enhance aroma.
In conclusion, alpha acids are not merely the foundation of beer sharpness; they are integral to crafting a balanced flavor profile that appeals to a diverse range of tastes. As one expert aptly noted, 'Alpha acids are the foundation of beer sharpness and play a vital role in its flavor profile.
Explore the Chemical Properties and Formation of Alpha Acids
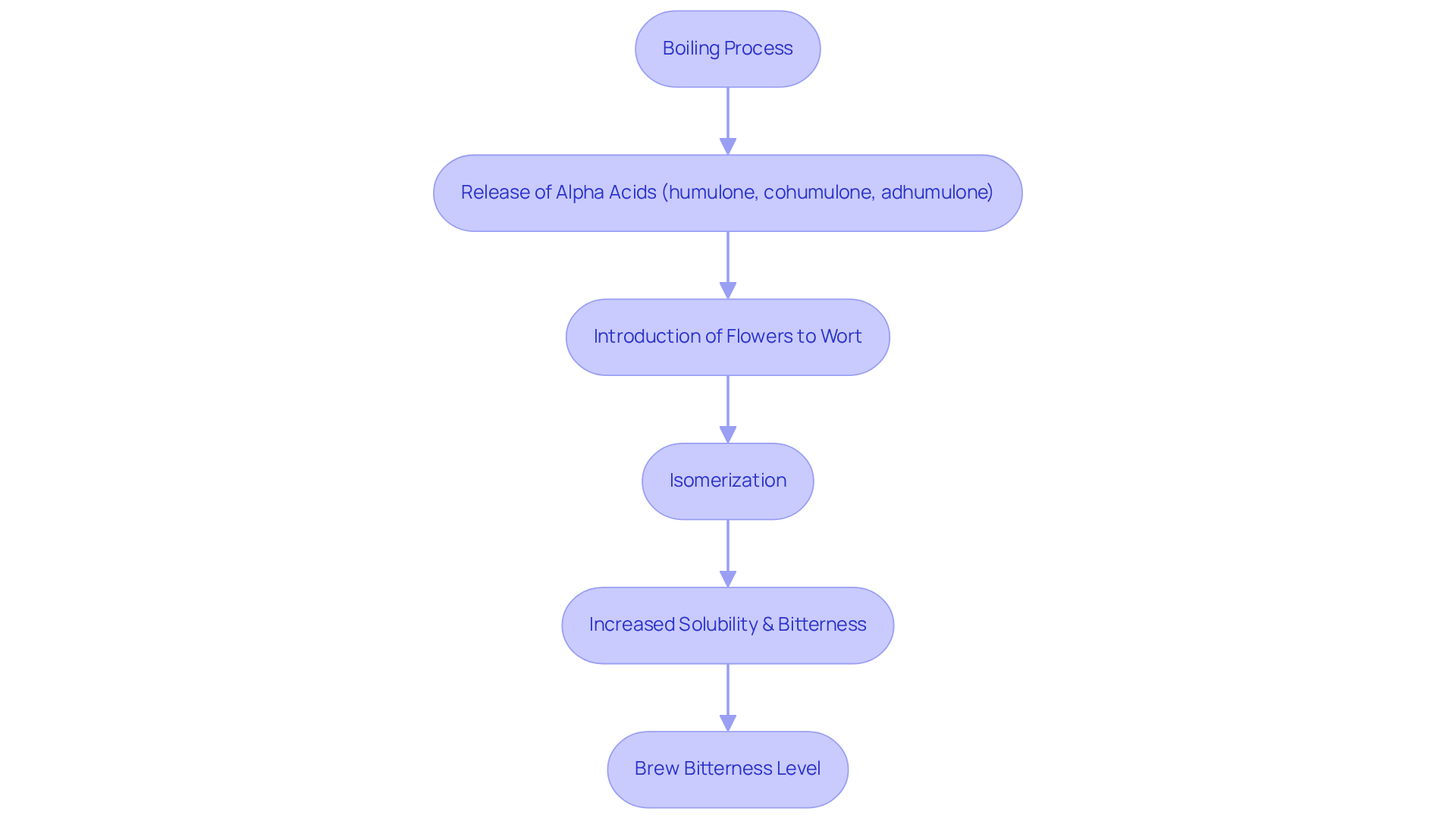
During the boiling process, alpha acids, primarily consisting of humulone, cohumulone, and adhumulone, are released from the plant. When flowers are introduced to boiling wort, these compounds undergo isomerization, transforming into iso-compounds that exhibit greater solubility and significantly enhance the beer's sharpness. This transformation is crucial, as the degree of isomerization directly affects the final bitterness level of the brew.
The concentration of bitter compounds varies among different plant varieties, typically ranging from 3% to 20%. For instance, commercial varieties often show an average content of 9.15 g/100 g DW, while an average of 4.1 g of bitter compounds is necessary per hectoliter of beer.
Understanding these chemical characteristics empowers brewers to strategically select ingredients and adjust boiling durations to effectively control the bitterness of their beers. Furthermore, proper storage techniques are essential for preserving hop quality, as factors such as light, temperature, and oxygen exposure can significantly alter their chemical composition.
As emphasized by experts in the field, the variability in bitter compound content across different hop types underscores the importance of selecting the right hops to achieve desired flavor profiles.
Apply Knowledge of Alpha Acids in Brewing Practices
To effectively leverage alpha acids in brewing, brewers must adopt specific practices that enhance the flavor and quality of their beer.
-
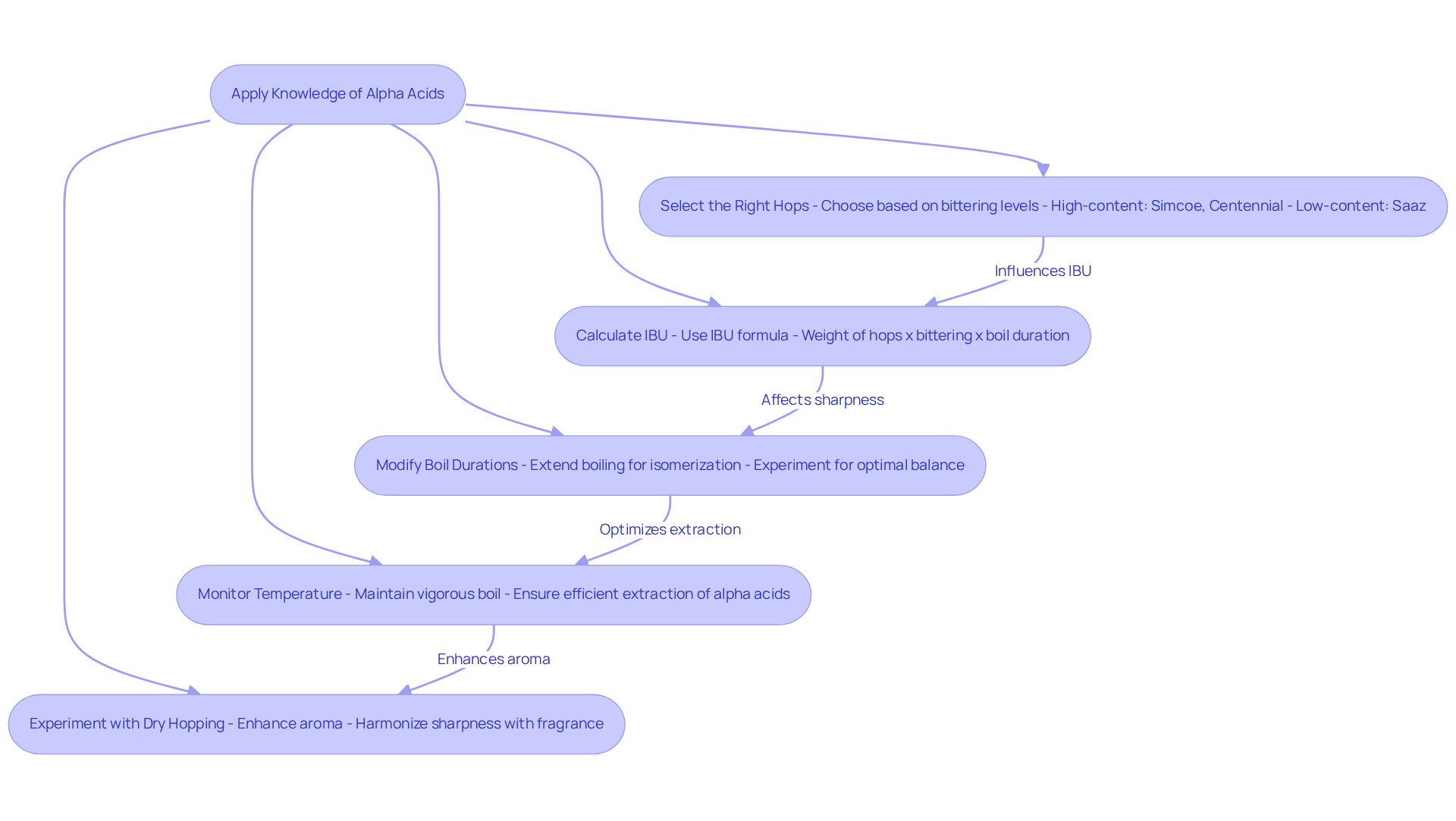
Select the Right Hops: It is essential to choose hop types based on their bittering component levels to achieve the desired sharpness in the beer. High-content varieties such as Simcoe and Centennial, which can range from 10% to 15% in composition, are excellent for adding sharpness. In contrast, lower content types like Saaz, with levels around 3% to 6%, are better suited for imparting fragrance. Notably, low-alpha aroma hop types typically possess acid levels of 2.5% to 6%.
-
Calculate IBU: Utilizing the IBU calculation formula is critical for quantifying the bitterness contribution from the hops. This involves multiplying the weight of the hops (in ounces) by their bittering percentage and the boil duration (in minutes), followed by applying a specific factor to convert this into IBUs. For instance, a 4 oz. (approximately 113 grams) sample can yield an IBU value that varies significantly based on the hop variety and usage. Historically, the IBU was established in the 1950s and 1960s to assess the mixture of isomerized bitter compounds (IAAs) and supplementary bittering substances (ABCs).
-
Modify Boil Durations: Extending boiling durations enhances the isomerization of specific compounds, leading to increased sharpness. By experimenting with various boil durations, brewers can discover the optimal balance for their recipes, as longer boils can elevate IBU values considerably.
-
Monitor Temperature: The wort's temperature during boiling is crucial for the efficient extraction of alpha acids. Maintaining a vigorous rolling boil is vital for optimal extraction and isomerization of alpha acids, ensuring that the sharpness is effectively developed.
-
Experiment with Dry Hopping: While dry hopping does not significantly contribute to sharpness, it can greatly enhance the beer's aroma. Understanding the role of primary compounds allows brewers to harmonize sharpness with fragrant attributes, resulting in a richer flavor profile. For example, adding dry hops with floral and citrus characteristics can amplify the sharpness obtained from high-content hops used earlier in the brewing process. Additionally, it is important to note that approximately 10% of available alpha acids oxidize quickly in boiling wort, producing oxidized alpha acids (oAAs), which can influence perceived bitterness.
Conclusion
Alpha acids serve as the cornerstone of beer's flavor complexity, fundamentally shaping the balance between bitterness and sweetness in brews. Their pivotal role in the brewing process cannot be overstated, as they influence not only the sharpness of the beer but also its overall character and appeal. By mastering the use of alpha acids, brewers elevate their craft, creating beers that resonate with a wide range of palates.
Throughout this article, we have explored several key insights, including:
- The chemical properties of alpha acids
- Their transformation during brewing
- The strategic practices that enhance their impact
From selecting the right hop varieties to understanding the significance of isomerization and proper boiling techniques, each element plays a crucial part in achieving the desired flavor profile. Furthermore, the importance of International Bitterness Units (IBUs) as a measurement tool emphasizes the need for precision in brewing practices.
Ultimately, the mastery of alpha acids not only enhances the quality of beer but also empowers brewers to innovate and experiment with their recipes. As the brewing landscape continues to evolve, embracing the science behind alpha acids will ensure that brewers consistently produce exceptional beers that captivate and satisfy their audience.




