Overview
This article delves into the essential steps and principles of Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) and Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) specifically tailored for pharmaceutical applications. These techniques are crucial in ensuring product quality, characterizing biologics, and refining drug formulations.
The article details the necessary setup and execution processes to achieve reliable and accurate analytical results, underscoring their significance in the pharmaceutical landscape. By understanding these methodologies, professionals can enhance their analytical capabilities and ensure the integrity of their products.
Introduction
GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography) and SEC (Size Exclusion Chromatography) stand as indispensable techniques within the pharmaceutical landscape, facilitating the precise separation of molecules based on size. These methodologies not only enhance our understanding of molecular characteristics but also play a critical role in ensuring the quality and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
However, the complexities involved in their application prompt inquiries regarding their limitations and the best practices for optimization. How can researchers effectively navigate these challenges to leverage GPC and SEC in advancing drug development and formulation?
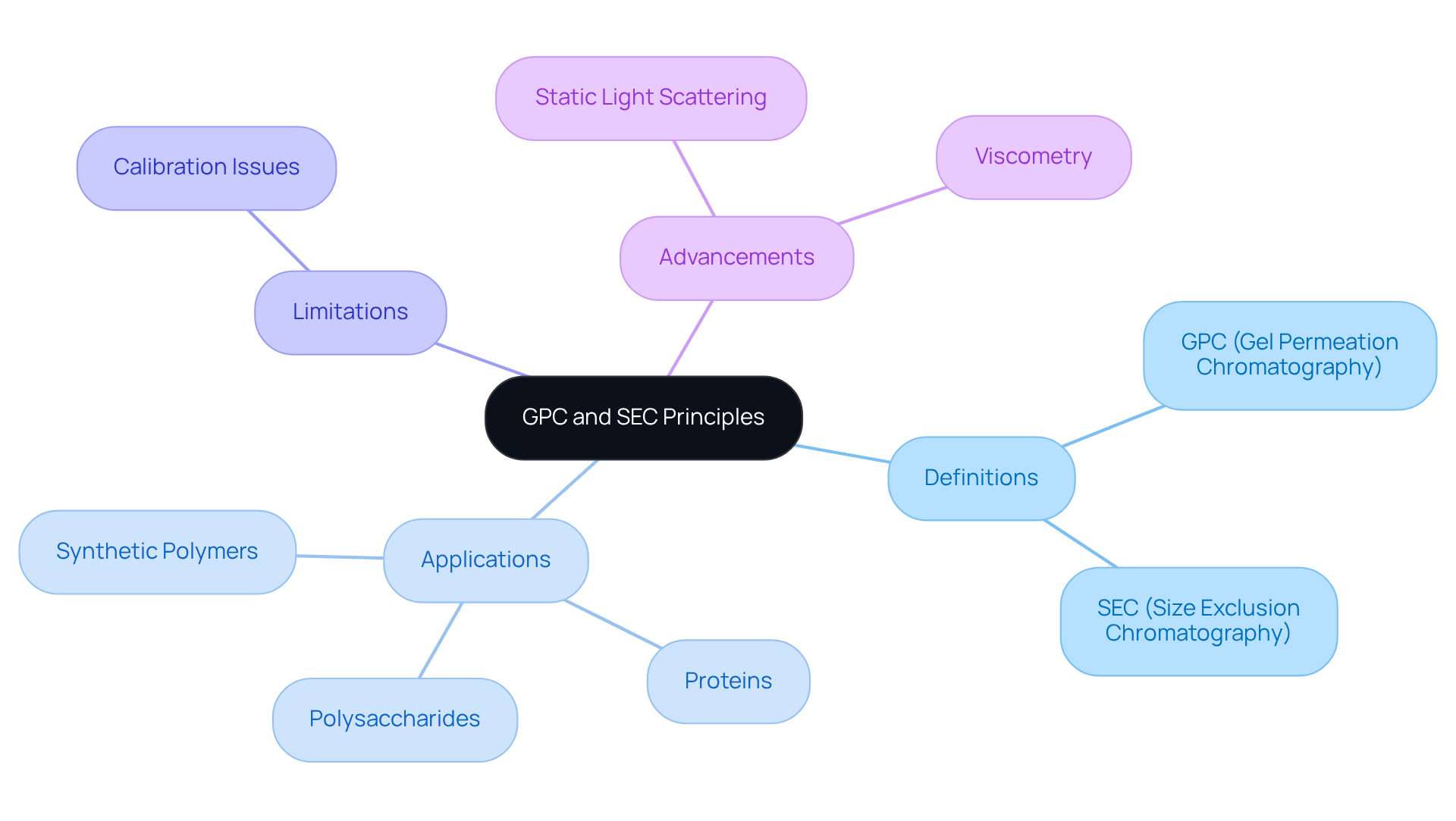
Clarify GPC and SEC Principles
GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography) and SEC (Size Exclusion Chromatography) are essential chromatographic techniques known collectively as gpc/sec, which are utilized to separate molecules based on their size in solution. GPC is primarily associated with the examination of synthetic polymers, whereas SEC encompasses a broader spectrum of macromolecules, including proteins and polysaccharides. The separation process occurs within a column packed with porous beads, allowing smaller molecules to navigate through the pores while larger molecules are excluded, resulting in their elution at distinct times. This fundamental understanding is crucial for optimizing analytical conditions and accurately interpreting results in pharmaceutical applications.
The significance of GPC and SEC in pharmaceutical examination cannot be overstated. These techniques provide vital insights into the distribution of mass and structural features of compounds, which are essential for maintaining product consistency and effectiveness. A case study involving the analysis of dextran samples using an OMNISEC system exemplifies this, demonstrating the ability to achieve precise molecular weight measurements across a range from 1 kDa to 1000 kDa, underscoring the technique's effectiveness in characterizing polymers.
However, traditional GPC/SEC techniques do have limitations, particularly when the calibration standard varies in chemical structure from the sample, potentially leading to inaccuracies. The integration of advanced detection methods, such as static light scattering and viscometry, enhances the sensitivity and productivity of gpc/sec. These techniques facilitate the identification of slight variations in mass and structure, which is particularly crucial during the initial phases of drug development. Accurate distribution data of molecules is vital for polysaccharide characterization, and employing these methods enables laboratories to refine extraction processes and maintain product uniformity within strict tolerances. Moreover, calibration with established standards is essential for obtaining precise measurements of compounds, ensuring the reliability of analytical outcomes. Ultimately, these advancements contribute significantly to .
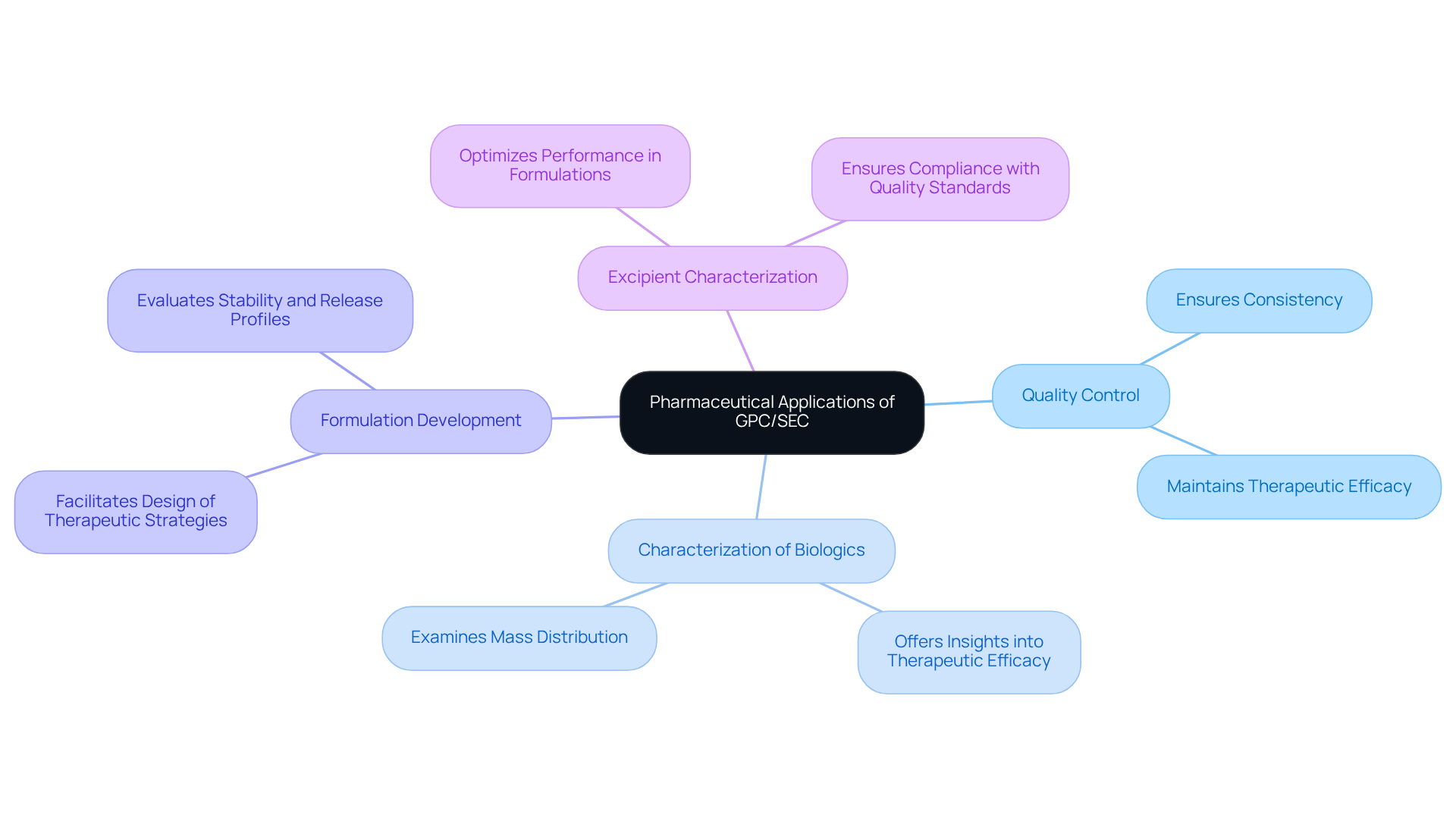
Explore Pharmaceutical Applications of GPC/SEC
The role of gpc/sec is pivotal in the pharmaceutical industry, serving various essential functions.
- Quality Control: It ensures the consistency and quality of polymer excipients used in drug formulations, which is vital for maintaining therapeutic efficacy and safety.
- Characterization of Biologics: This method is essential in examining the mass distribution of proteins and peptides, offering insights into their therapeutic efficacy and stability. Malvern systems measure properties such as molecular weight, size, and shape, which are crucial for understanding biologics.
- Formulation Development: The evaluation of stability and release profiles of drug delivery systems, including nanoparticles and liposomes, facilitates the design of effective therapeutic strategies. Recent advancements in chromatography technology, such as enhanced sensitivity, allow for the detection of subtle differences in feedstocks, ensuring product consistency.
- Excipient Characterization: By evaluating the properties of excipients, the technique optimizes their performance in drug formulations, ensuring that they meet stringent quality standards. As Stephen Ball from Malvern Instruments mentions, "Precise distribution data and structural details are crucial for effective polysaccharide characterization."
These applications emphasize the essential role of gpc/sec in maintaining high standards in pharmaceutical development, particularly regarding drug formulation quality control. For instance, case studies illustrate how this technology allows accurate assessment of mass distribution and structural traits, which are essential for the efficient characterization of polysaccharides and other excipients. This capability not only aids in but also ensures product consistency, ultimately impacting the performance of finished pharmaceutical products.
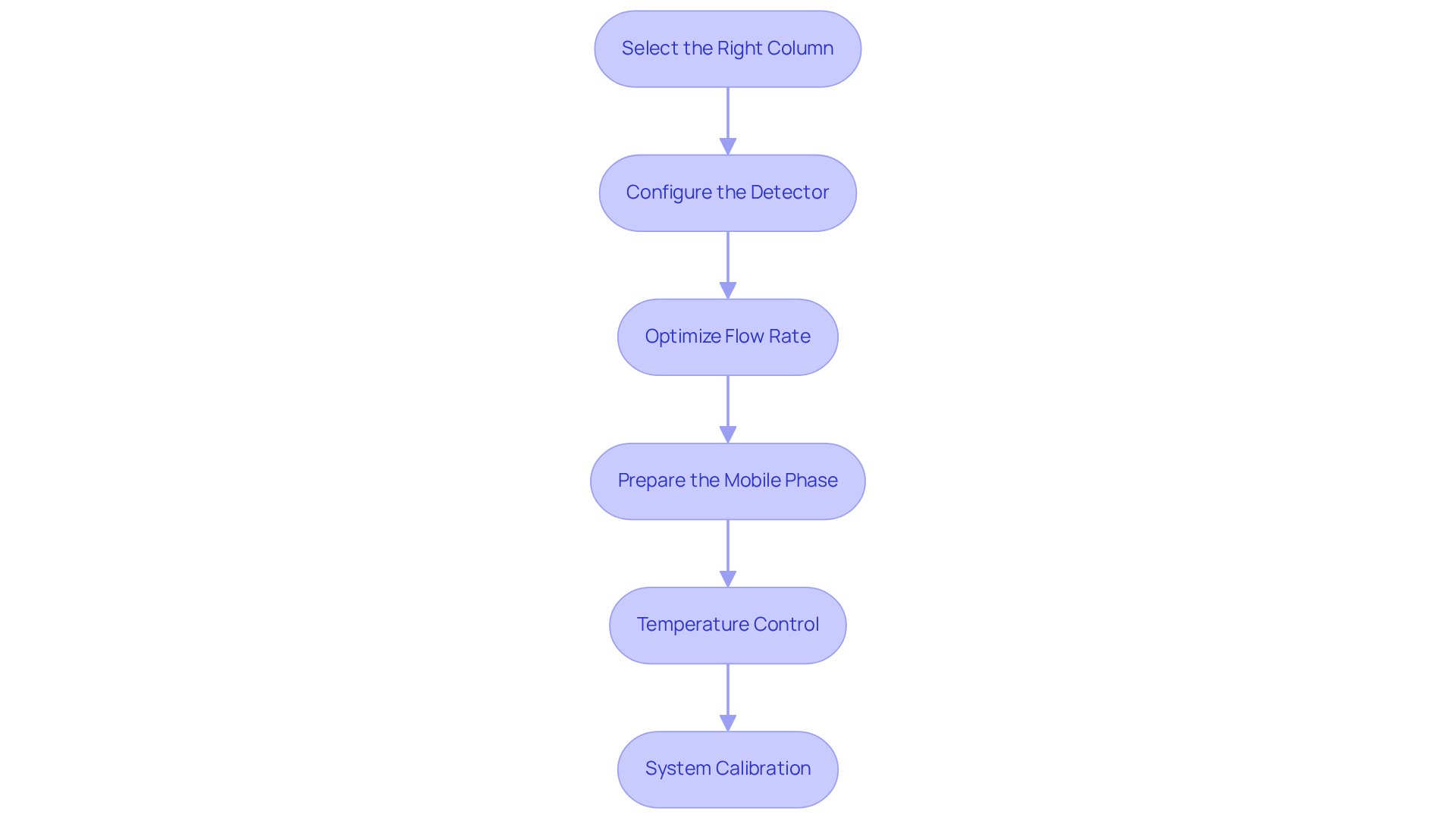
Set Up GPC/SEC Instrumentation and Parameters
Setting up the gpc/sec instrumentation involves several critical steps to ensure optimal performance and accurate results.
- Select the Right Column: Begin by choosing a column with appropriate pore size and dimensions tailored for the range of the analytes' mass. This selection is vital for effective separation, as JM Science is recognized for its , which can significantly enhance the separation process.
- Configure the Detector: Next, utilize common detectors such as refractive index (RI) and UV detectors. Ensure they are calibrated specifically for the analytes being measured to enhance detection sensitivity. Calibration is crucial, as highlighted by studies in polymer characterization, which emphasize the importance of using narrow molecular weight standards for accurate results in gpc/sec.
- Optimize Flow Rate: Adjust the flow rate according to the column specifications, typically ranging from 0.5 to 1.0 mL/min for analytical columns. This parameter is essential for attaining optimal resolution and evaluation time, conforming to best practices in the field.
- Prepare the Mobile Phase: Select a solvent that is compatible with both the analytes and the column material. Common choices include THF and DMF, which facilitate effective elution of the target compounds. The selection of solvent can significantly influence the examination, as highlighted in various studies.
- Temperature Control: Maintain a consistent temperature throughout the evaluation to ensure reproducibility. Most size-exclusion chromatography assessments are performed at ambient temperature, which aids in reducing variability in gpc/sec measurements. As emphasized in expert literature, temperature stability is essential for reliable results.
- System Calibration: Finally, calibrate the system using narrow molecular weight standards to guarantee accurate results. This calibration is essential for obtaining reliable data, particularly in pharmaceutical applications where precision is paramount. JM Science's commitment to quality and customer support ensures that laboratories have access to reliable instrumentation for these critical processes.
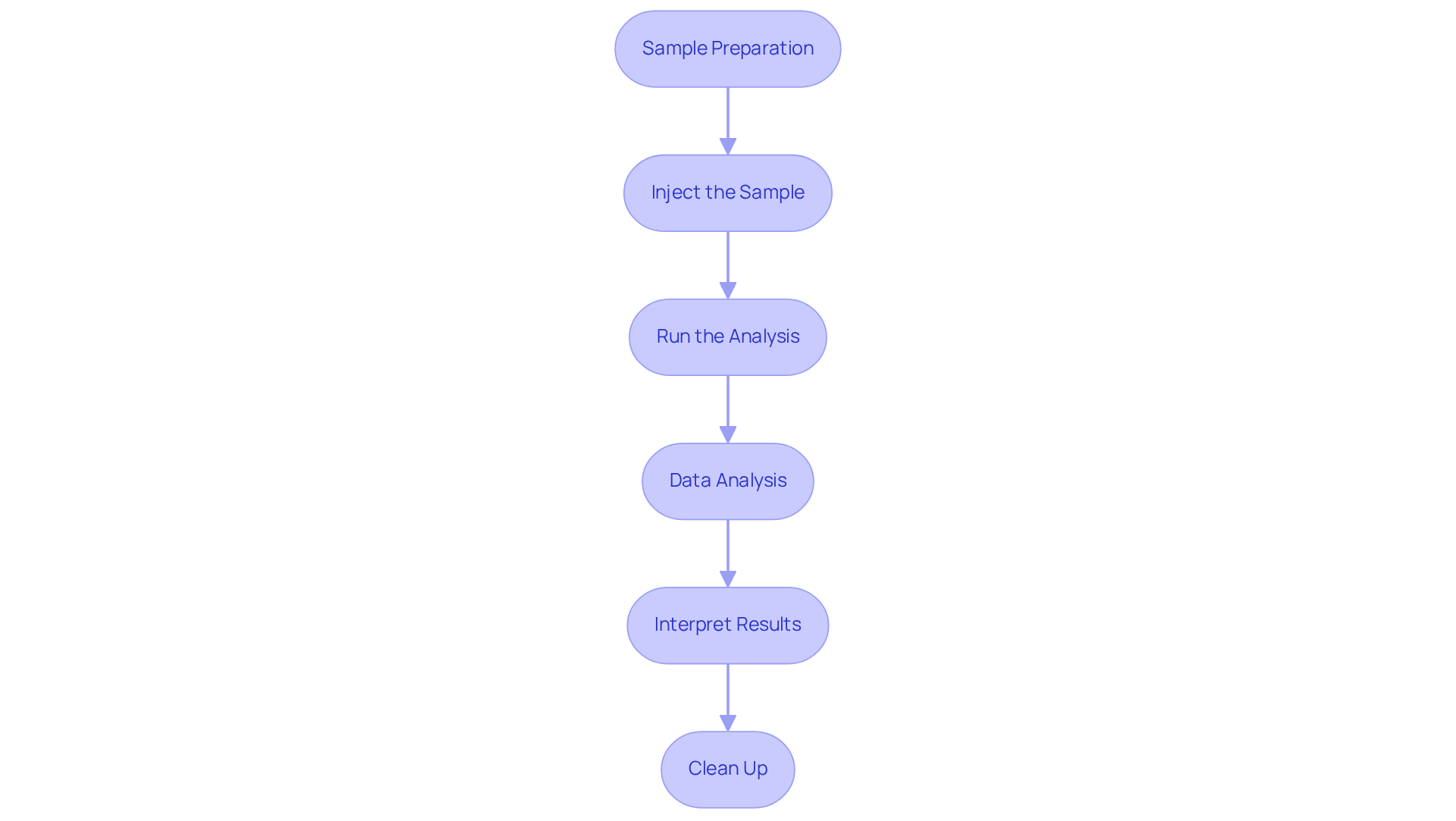
Execute GPC/SEC Analysis: Step-by-Step Guide
To execute a successful GPC/SEC analysis, it is essential to follow these steps:
- Sample Preparation: Start by dissolving the sample in an appropriate solvent, ensuring complete solubility. It is crucial to strain the solution to eliminate any particulates that could impede the evaluation.
- Inject the Sample: Use an autosampler or manual injector to introduce the sample into the system. Consistency in injection volume is vital to meet method requirements and ensure reliable results.
- Run the Analysis: Initiate the chromatography run while closely monitoring the system for any irregularities. Document elution times and detector responses meticulously to enable precise data evaluation. In GPC/SEC, , as they cannot enter the pores of the separation column; this understanding is fundamental to the analysis process.
- Data Analysis: Utilize suitable software to analyze the chromatograms. Determine average masses and distributions based on the calibration curve created during system adjustment, which is crucial for precise characterization. Ensure that the concentration detector and viscometer are calibrated with a standard of known concentration, intrinsic viscosity, and molecular weight to guarantee accurate results.
- Interpret Results: Compare the obtained results against established quality standards and specifications. Record any deviations and investigate possible causes to uphold the integrity of the evaluation. As Prof. Stepan Podzimek notes, understanding the structure-property connections is vital in polymer evaluation, aiding in the avoidance of common mistakes in gel permeation chromatography/size exclusion chromatography.
- Clean Up: After completing the evaluation, flush the system with the mobile phase to prevent contamination and maintain the integrity of the columns for future assessments.
By adhering to these steps, you will ensure a successful GPC/SEC analysis, particularly tailored for pharmaceutical applications, thereby enhancing the reliability and accuracy of your results.
Conclusion
Mastering GPC and SEC techniques is essential for pharmaceutical applications, as these methods facilitate the effective separation and characterization of compounds based on size. A thorough understanding of Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) and Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) not only enhances analytical accuracy but also plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality and consistency of pharmaceutical products.
The significance of GPC and SEC spans various pharmaceutical functions, including:
- Quality control
- Characterization of biologics
- Formulation development
- Excipient optimization
Advanced detection methods and meticulous calibration are vital to overcoming traditional limitations, ensuring precise measurements that are critical during drug development. By adhering to a structured setup and analysis process, laboratories can achieve reliable results that accurately reflect the true nature of the compounds under investigation.
Ultimately, the integration of GPC and SEC techniques in pharmaceutical research is indispensable. As the industry continues to evolve, leveraging these methodologies will not only enhance product quality but also improve patient safety and therapeutic outcomes. Engaging with the latest advancements in GPC and SEC empowers professionals to push the boundaries of drug development, ensuring that every product meets the highest standards of efficacy and safety.




