Overview
This article presents a comprehensive four-step process for mastering HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC). It emphasizes:
- Understanding the fundamental principles
- Gathering the necessary equipment
- Executing the process effectively
- Troubleshooting common issues
Each step is underpinned by specific guidelines and best practices, highlighting the critical importance of:
- Thorough preparation
- Meticulous sample handling
- Proactive problem-solving
These elements are essential for achieving reliable and reproducible results in biomolecule analysis, reinforcing the significance of high-quality scientific instruments in laboratory settings.
Introduction
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is a cornerstone of analytical techniques, expertly separating biomolecules based on size and providing critical insights into their behavior and functionality. As advancements in HPLC technology facilitate faster and more precise evaluations, comprehending the principles and processes behind SEC becomes essential for researchers seeking to optimize their analyses.
However, navigating the complexities of this technique presents significant challenges. What are the key steps to mastering HPLC size exclusion chromatography? How can common pitfalls be avoided to ensure reliable results? Understanding these aspects is crucial for achieving success in this vital area of research.
Understand HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography Principles
Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), also known as hplc size exclusion chromatography, is a formidable analytical technique adept at separating molecules based on size through a setup filled with porous beads. In this configuration, larger molecules cannot penetrate the beads' pores, resulting in their early elution, while smaller molecules linger longer as they navigate into the pores. The hplc size exclusion chromatography technique for size-based separation proves particularly advantageous for the analysis of biomolecules such as proteins, polysaccharides, and nucleic acids, where size variations significantly influence their behavior and functionality.
Recent advancements in HPLC size exclusion chromatography technology have heralded the emergence of ultra-high-performance SEC (UHP SEC) systems, which utilize columns packed with sub-2-μm particles. These innovations not only enhance resolution but also reduce evaluation times by an impressive 30-50% compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, the integration of hplc size exclusion chromatography with advanced detection systems, including mass spectrometry and charge detection mass spectrometry, has expanded its applications in characterizing complex biomolecules, such as monoclonal antibodies and gene therapies.
As we approach 2025, the SEC market is witnessing a notable shift toward specialized solutions tailored for biopharmaceutical applications, driven by the escalating demand for high-resolution evaluations of biologics. This trend is particularly pronounced in regions like North America and Asia-Pacific, where substantial investments in biotechnology are accelerating the adoption of advanced SEC technologies. Understanding the principles of HPLC size exclusion chromatography and remaining informed about these developments is essential for and achieving reliable results in biomolecule analysis.

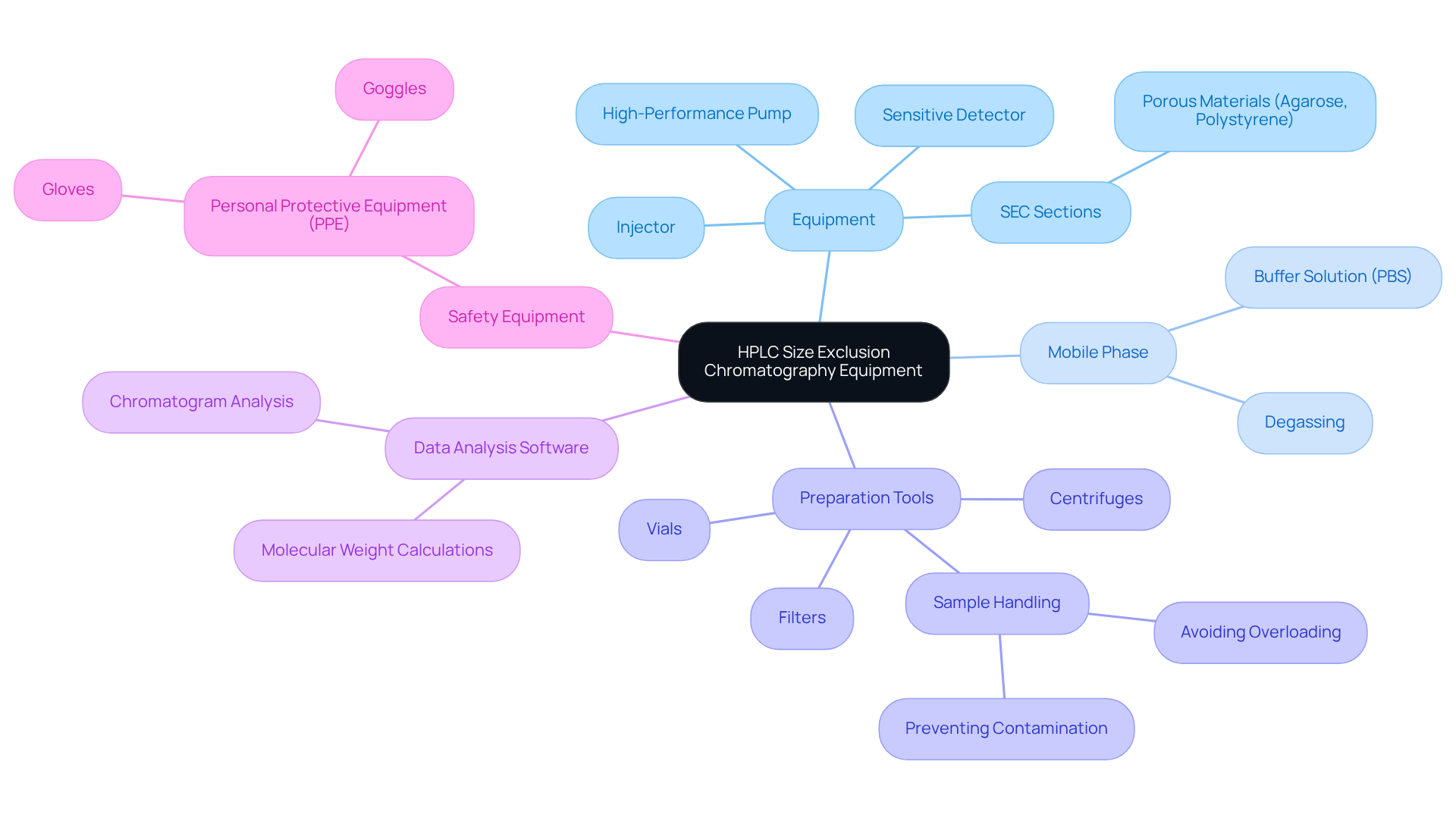
Gather Essential Equipment and Materials
To effectively conduct HPLC size exclusion chromatography, it is essential to gather the following equipment and materials.
Ensure your HPLC size exclusion chromatography system is equipped with a high-performance pump, injector, and a sensitive detector suitable for SEC applications. This foundational component is critical for achieving reliable results.
- SEC Sections: Choose sections specifically designed for size exclusion, such as those with pore sizes tailored to your analytes. This ensures optimal separation based on molecular size through HPLC size exclusion chromatography. Common types of SEC supports include those filled with porous materials like agarose or polystyrene, which enhance the efficiency of the separation process.
- Mobile Phase: Prepare a buffer solution, commonly phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) or a similar formulation. This maintains the stability of the specimen and enhances resolution during analysis. It is also vital to degas the mobile phase to eliminate air bubbles, which can interfere with flow and lead to inaccurate results.
- Preparation Tools: Utilize centrifuges, filters, and vials for . Ensuring that specimens are free from particulates and properly diluted prevents column overload. Be cautious of common pitfalls such as overloading the column and contamination, as these can significantly affect the quality of your results.
- Data Analysis Software: Implement robust software for analyzing chromatograms, facilitating accurate interpretation of results and molecular weight calculations. Ensure that your samples are compatible with both the stationary and mobile phases for precise separation outcomes.
- Safety Equipment: Always prioritize safety by using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and goggles when handling chemicals. This ensures a safe laboratory environment and protects personnel from potential hazards.
By assembling these essential components, laboratories can enhance their capabilities in HPLC size exclusion chromatography, leading to more reliable and reproducible results in protein analysis and other applications.
Execute the HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography Process
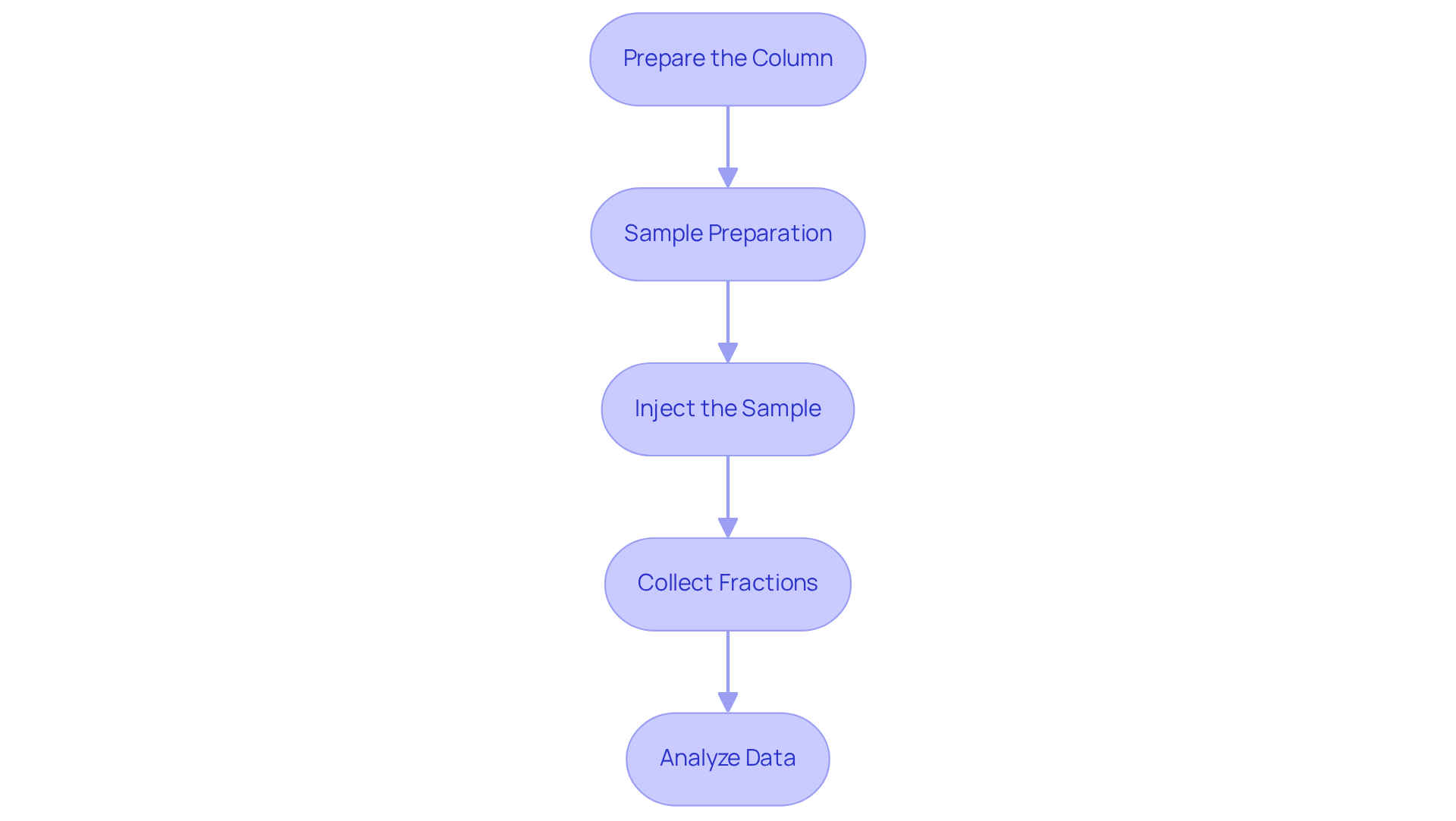
To effectively execute the HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) process, it is essential to follow these streamlined steps:
- Prepare the Column: Begin by rinsing the SEC tube with the mobile phase to equilibrate it. This vital step guarantees by stabilizing the environment of the support. For optimal performance, consider utilizing materials such as Superdex 200 for proteins under 200 kDa.
- Sample Preparation: Dilute your specimens in the mobile phase to avoid excess in the column. Ensure that the specimen volume does not surpass 30% of the bed volume, which generally improves separation efficiency and resolution. Additionally, employing centrifugation or filtration can effectively remove particulate matter before dilution.
- Inject the Sample: Utilize the HPLC injector to introduce the prepared sample into the system. It is crucial to maintain a consistent flow rate that aligns with the specifications of the structure to optimize separation. Gradually increasing the flow rate can help prevent damage to the column.
- Collect Fractions: As the extract elutes, collect fractions at regular intervals. Employ the detector to monitor the elution profile, allowing for the identification of peaks corresponding to different analytes. Ensure that the collection timing aligns with the expected elution times of your target molecules.
- Analyze Data: After the run, utilize data evaluation software to interpret the chromatograms, determining the size distribution of the analytes. This examination is crucial for comprehending the molecular weight distribution and evaluating specimen quality. Remember to calculate the optimal injection volume using the formula
V_inj = (V_column * C_sample) / C_columnto ensure effective analysis.
By adhering to these best practices, including appropriate preparation methods such as dilution and monitoring flow rates, dependable and consistent results in HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography can be attained. Furthermore, consider expert advice for simplifying and accelerating protein purification, while remaining vigilant about potential issues such as overload or inadequate detection sensitivity.
Troubleshoot Common HPLC Size Exclusion Issues
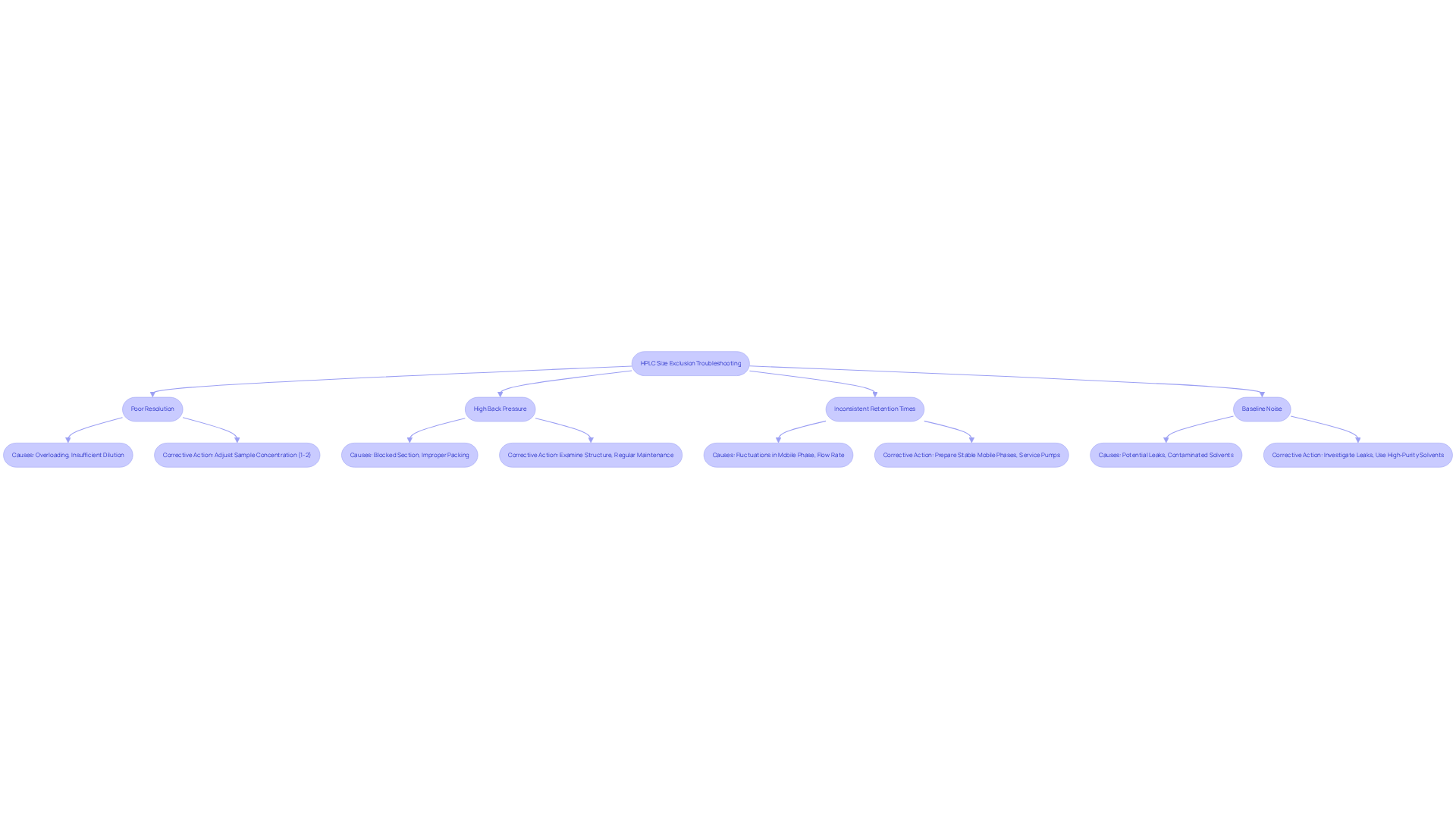
Common issues in HPLC size exclusion chromatography can significantly impact analytical results. Addressing these challenges is crucial for enhancing the reliability of laboratory analyses.
- Poor Resolution: When peaks lack clarity, it often arises from the overloading of the system or insufficient dilution of the substance. To correct this, modify the sample concentration, ensuring it remains within the ideal range of 1-2% of the total volume for concentrations around 1µg/µl. This adjustment can enhance peak clarity and resolution, leading to more accurate results.
- High Back Pressure: Increased back pressure usually signifies a blocked section or improper packing. It is essential to examine the structure for obstructions and confirm that it is filled in accordance with specifications. Regular maintenance, including flushing protocols, can prevent clogging and maintain optimal flow rates, thereby ensuring consistent performance.
- Inconsistent Retention Times: Variability in retention times can arise from fluctuations in mobile phase composition or flow rate. To ensure consistency, prepare mobile phases with stable pH and buffer concentrations, and equilibrate columns before each run. Regular servicing of pumps is also crucial to maintain steady flow rates, which is vital for reproducible results.
- Baseline Noise: High baseline noise can obscure peak detection, complicating evaluation. Investigate potential leaks in the system and ensure all connections are secure. Utilizing high-purity solvents and thoroughly degassing mobile phases can further reduce baseline noise, leading to clearer results.
By proactively addressing these common issues, laboratories can significantly enhance the performance and reliability of their HPLC size exclusion chromatography analyses. Investing in trusted equipment, such as , can further improve reliability and analytical confidence. Regular maintenance and proactive troubleshooting are essential for maximizing and ensuring high-quality analytical results.
Conclusion
Mastering HPLC Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) is crucial for accurate biomolecule analysis, especially as technology continues to evolve this analytical technique. By grasping the principles of SEC and equipping themselves with the right tools, researchers can optimize their separation processes to achieve dependable results. The transition towards ultra-high-performance systems and tailored solutions for biopharmaceutical applications emphasizes the increasing relevance of HPLC size exclusion chromatography in contemporary laboratories.
This guide has delineated the essential steps for executing HPLC SEC, from column preparation to data analysis. Critical elements such as:
- Sample preparation
- Flow rate management
- Troubleshooting common issues
are vital for ensuring peak resolution and data integrity. By following best practices and being aware of potential challenges, laboratories can enhance their analytical capabilities and produce more reproducible results.
Ultimately, the importance of mastering HPLC size exclusion chromatography transcends mere technique; it is about advancing scientific understanding and fostering innovations in biopharmaceuticals and other domains. By remaining informed and continuously refining methodologies, professionals can propel progress in their research efforts, leading to breakthroughs that significantly impact health and science.




