Overview
The article centers on the vital steps for calibrating pH probes, a process essential for ensuring precise pH measurements in laboratory environments, particularly within the pharmaceutical industry. Calibration is not merely a procedural task; it is fundamental in maintaining drug stability and efficacy. This article meticulously outlines the necessary tools and provides step-by-step procedures, along with strategies for troubleshooting common issues. Such guidance is crucial for enhancing the reliability of pH measurements, ultimately ensuring that laboratory practices meet the highest standards of accuracy.
Introduction
Accurate pH measurement is crucial across various scientific domains, particularly in pharmaceuticals. Here, even the slightest deviation can have profound implications for drug stability and efficacy. This article explores the essential steps for pH probe calibration, equipping lab managers with the knowledge and tools necessary to ensure precision in their measurements. Yet, with numerous challenges and potential pitfalls in the calibration process, one must ask: how can we guarantee that our pH readings remain reliable and compliant with regulatory standards?
Understand the Importance of pH Meter Calibration
The pH probe calibration of devices is paramount, as even minor deviations in pH readings can result in significant alterations in chemical properties and reactions. Accurate pH measurement is especially critical in pharmaceuticals, where precise formulations are essential for ensuring drug stability and efficacy. Routine adjustments not only ensure that the pH meter accurately reflects the current attributes of the electrode but also address drift over time. This practice bolsters the reliability of results and supports compliance with regulatory standards, which is vital for successful research outcomes and product development.
In a pharmaceutical laboratory, a slight error in pH measurement can jeopardize the stability of a drug formulation, potentially leading to safety issues. Research indicates that incorrect pH levels can profoundly affect drug solubility and dissolution, thereby impacting bioavailability and overall effectiveness. To achieve precise pH measurements, pH probe calibration requires a minimum of three standards to create a calibration curve. The integration of advanced titration methods, such as Multi-Point Calibration, facilitates pH probe calibration at three or more pH values, ensuring that formulations remain within acceptable pH ranges to maximize safety and efficacy. Moreover, the Hiranuma Aquacounter AQV-300 Volumetric and AQ-300 Coulometric Karl Fischer titrators enhance the precision of moisture content analysis in drug formulations, ensuring compliance with the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. As Michael Luo asserts, "Accurate pH measurements are essential for ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products.
Gather Essential Tools for Calibration
To effectively calibrate a pH meter, it is crucial to gather the following essential tools:
-
pH Buffer Mixtures: Secure at least two standard buffer mixtures, typically pH 4.00 and pH 7.00, to cover the expected pH range of your samples. It is imperative to use fresh mixtures, as opened measuring liquids lose precision after 20 minutes. For applications requiring high accuracy, consider adding pH 10.00 as well. Calibration preparations for pH 4.00, 7.00, and 10.00 can be acquired for $23.99.
-
Distilled Water: Employ distilled water for rinsing the pH probe between adjustments. This practice prevents contamination and ensures accurate readings.
-
Clean Containers: Prepare sanitized containers for storing the liquid mixtures and rinsing the probe. Contamination can significantly impact adjustment results. Only pour a small quantity of solution into a separate container for use to avoid contamination.
-
Calibration Log: Keep a logbook to document calibration dates, buffer lot numbers, and any observations made during the calibration process. This practice aids in monitoring the performance of your pH device over time. As a general guideline, conduct pH probe calibration before each use to ensure accuracy.
-
pH Device: Confirm that your pH device is functioning correctly and is equipped with a compatible electrode. Regular checks on the electrode's condition are essential; dirty or dried-out electrodes can lead to inaccurate readings. If the pH meter reads greater than 0.05 pH from the buffer solution, it is recommended to perform a pH probe calibration.
By preparing these tools, you can streamline the adjustment process and enhance the precision of your pH measurements, a critical aspect for ensuring quality control in pharmaceutical applications.
Follow Step-by-Step Calibration Procedures
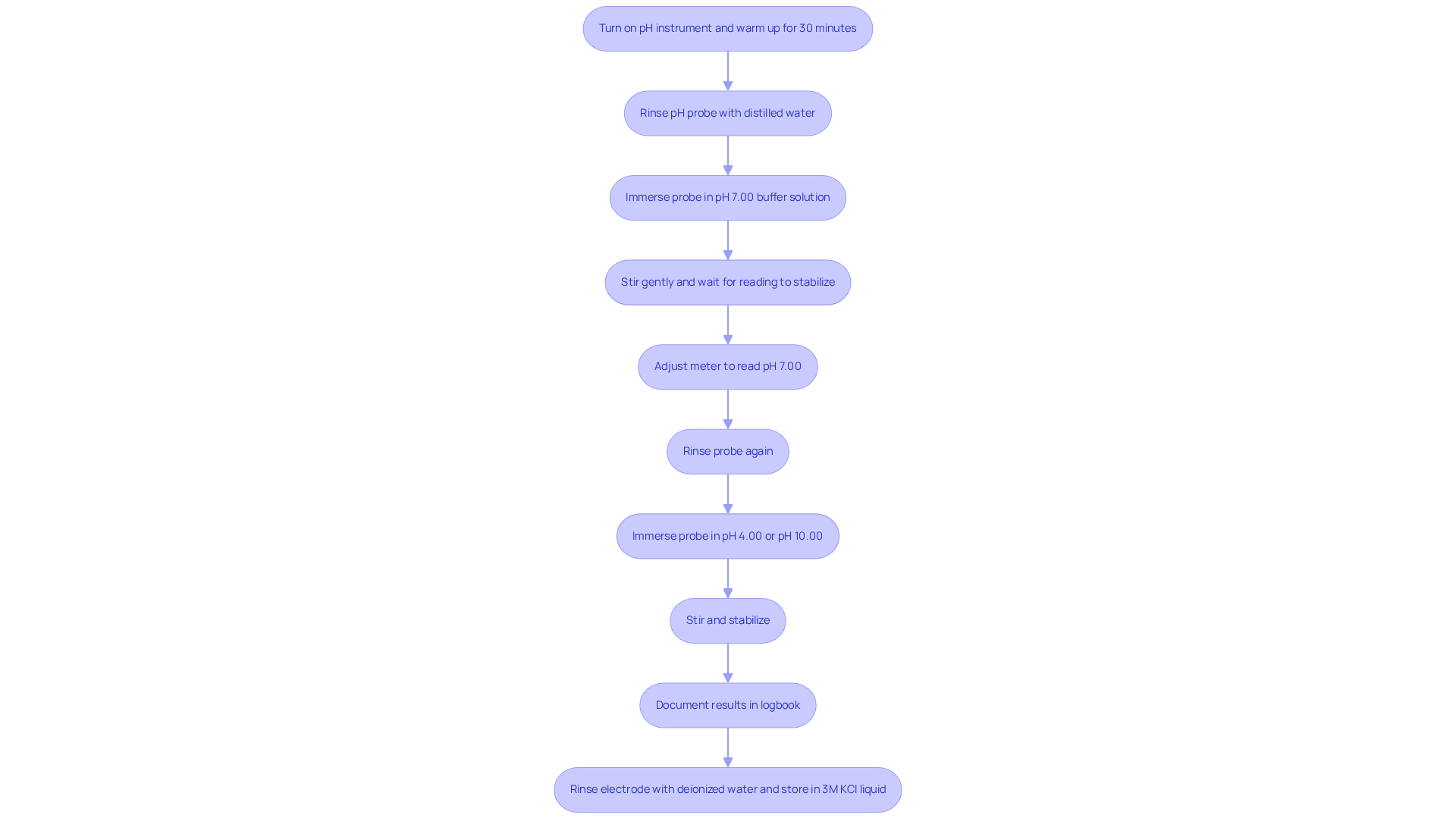
To ensure accurate pH measurements, it is essential to perform pH probe calibration by following detailed procedures for your pH meter. Begin by preparing the device: turn on the pH instrument and allow it to warm up according to the manufacturer's instructions, typically for about 30 minutes to ensure stability. Next, rinse the pH probe with distilled water to eliminate any contaminants from previous measurements, as these can affect accuracy.
The next step is to carry out the pH probe calibration using a pH 7.00 buffer solution. Immerse the probe in the solution, stir gently, and wait for the reading to stabilize, which should ideally occur within a few seconds. If necessary, modify the meter to display pH 7.00, which is essential during pH probe calibration, ensuring that the deviation remains within the acceptable range of ±0.1 pH, a common procedure in standardization. After this, rinse the probe again with distilled water to prevent cross-contamination before proceeding to the next calibration point.
Depending on your anticipated measurement range, you should conduct the pH probe calibration by immersing the probe in either a pH 4.00 or pH 10.00 liquid. Stir gently and wait for stabilization, then adjust the instrument to read the corresponding pH value accurately. Following this, perform a final rinse of the probe with distilled water to maintain cleanliness. It is also crucial to document the adjustment results in your logbook, noting the date, buffer solutions used, and any modifications made. This practice not only ensures adherence but also assists in monitoring the performance of your pH device over time.
By adhering to these steps, you will significantly enhance the reliability of your pH measurements, which is crucial for pharmaceutical applications. Regular adjustment, preferably at least twice a month or daily for high-frequency use, is vital to ensure measurement precision and extend the lifespan of your pH meter. Furthermore, after use, rinse the electrode with deionized water and keep it in a 3M KCl liquid to maintain sensitivity. For improved precision, consider conducting a third-point calibration using an extra liquid.
Troubleshoot Common Calibration Issues
Calibration issues can arise for various reasons, particularly related to pH probe calibration, impacting the accuracy of pH measurements. Understanding these common problems and their solutions is crucial for maintaining reliable laboratory outcomes.
-
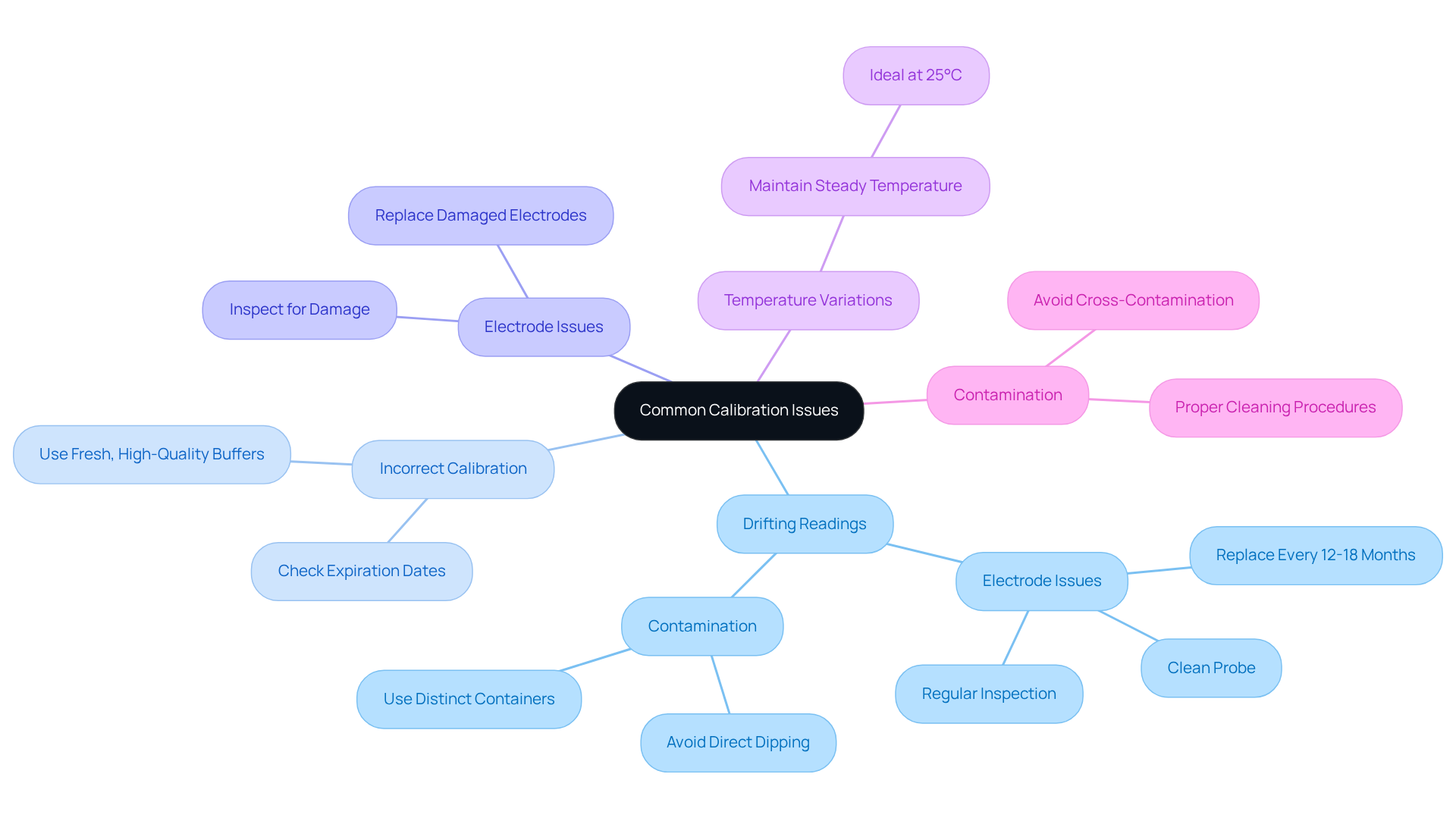
Drifting Readings: Fluctuating pH gauge readings often indicate electrode issues. Ensuring the probe is clean and performing pH probe calibration by rinsing it thoroughly before use is essential. Regular inspection for contamination or wear is vital, as aging electrodes can lead to slow response times and inaccurate measurements. A well-maintained electrode is crucial for consistent performance, with replacements typically needed every 12-18 months.
-
Incorrect Calibration: If the meter fails to read the reference liquids accurately, checking the expiration dates of the substances is necessary. Utilizing outdated or tainted solutions can result in measurement inaccuracies. It is advisable to conduct pH probe calibration using new, high-quality mixtures to ensure reliable readings. As emphasized by Water Test Systems, employing fresh, high-quality standard pH reference liquids is essential for effective pH probe calibration.
-
Electrode Issues: Old or damaged electrodes may require replacement. Regular inspection for cracks or signs of wear is recommended, as these can significantly affect measurement accuracy.
-
Temperature Variations: pH readings can be sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Ensuring that both the solution mixtures and samples are at a steady temperature during adjustment—ideally around 25°C—is critical to prevent fluctuations in measurements. This temperature consistency is essential for precise adjustment, as highlighted in numerous studies.
-
Contamination: To prevent contamination, it is important to avoid dipping the probe directly into solution containers. Always use distinct containers for standard mixtures to help maintain the integrity of the buffers and ensure accurate pH probe calibration.
By being aware of these common issues and their solutions, lab managers can effectively maintain the accuracy and reliability of their pH measurements, ultimately supporting better laboratory outcomes.
Conclusion
Accurate pH probe calibration stands as a critical component in laboratory environments, particularly within the pharmaceutical sector, where even minor deviations in pH readings can precipitate significant consequences. Ensuring precise measurements not only enhances the reliability of research outcomes but also supports compliance with stringent regulatory standards. The calibration process is essential for maintaining the integrity of drug formulations, ensuring their safety and efficacy.
Key steps for effective pH calibration involve:
- Gathering essential tools, including high-quality buffer solutions and distilled water.
- Maintaining a meticulous calibration log.
- Adhering to a structured calibration procedure.
- Remaining vigilant about common calibration issues.
These steps can greatly improve the accuracy of pH measurements. The insights shared in this article underscore the importance of regular maintenance and troubleshooting to address potential problems, thus ensuring that all laboratory results remain reliable and valid.
Ultimately, the significance of pH probe calibration cannot be overstated. By prioritizing accurate pH measurements, laboratory managers can safeguard the quality of their products and uphold the standards necessary for successful pharmaceutical development. Embracing these practices fosters a culture of precision and drives advancements in research and product safety. It is imperative to commit to these essential calibration techniques to ensure that laboratory work consistently meets the highest standards of excellence.




