Overview
This article delves into the mastery of reverse phase C18 column techniques within pharmaceutical laboratories, highlighting their critical role in analytical chemistry for the effective separation of compounds based on hydrophobicity. By detailing the efficiency, reproducibility, and versatility of C18 columns, it underscores their importance in drug formulation and quality control. Furthermore, the article addresses best practices and common troubleshooting methods, providing essential insights to optimize laboratory results. Understanding these techniques is vital for any professional aiming to enhance their analytical capabilities and ensure high-quality outcomes in pharmaceutical research.
Introduction
Mastering reverse phase chromatography is vital for pharmaceutical laboratories striving for precision in their analytical processes. As the demand for effective drug development and stringent quality control escalates, a thorough understanding of the intricacies of C18 columns becomes increasingly essential. Yet, laboratories often face challenges in navigating the complexities of this technique, from maintaining optimal performance to troubleshooting common issues.
What strategies can laboratories implement to harness the full potential of reverse phase C18 columns and ensure reliable results? This inquiry not only underscores the importance of expertise in this field but also invites a deeper exploration of methods to enhance analytical precision.
Explore the Fundamentals of Reverse Phase Chromatography and C18 Columns
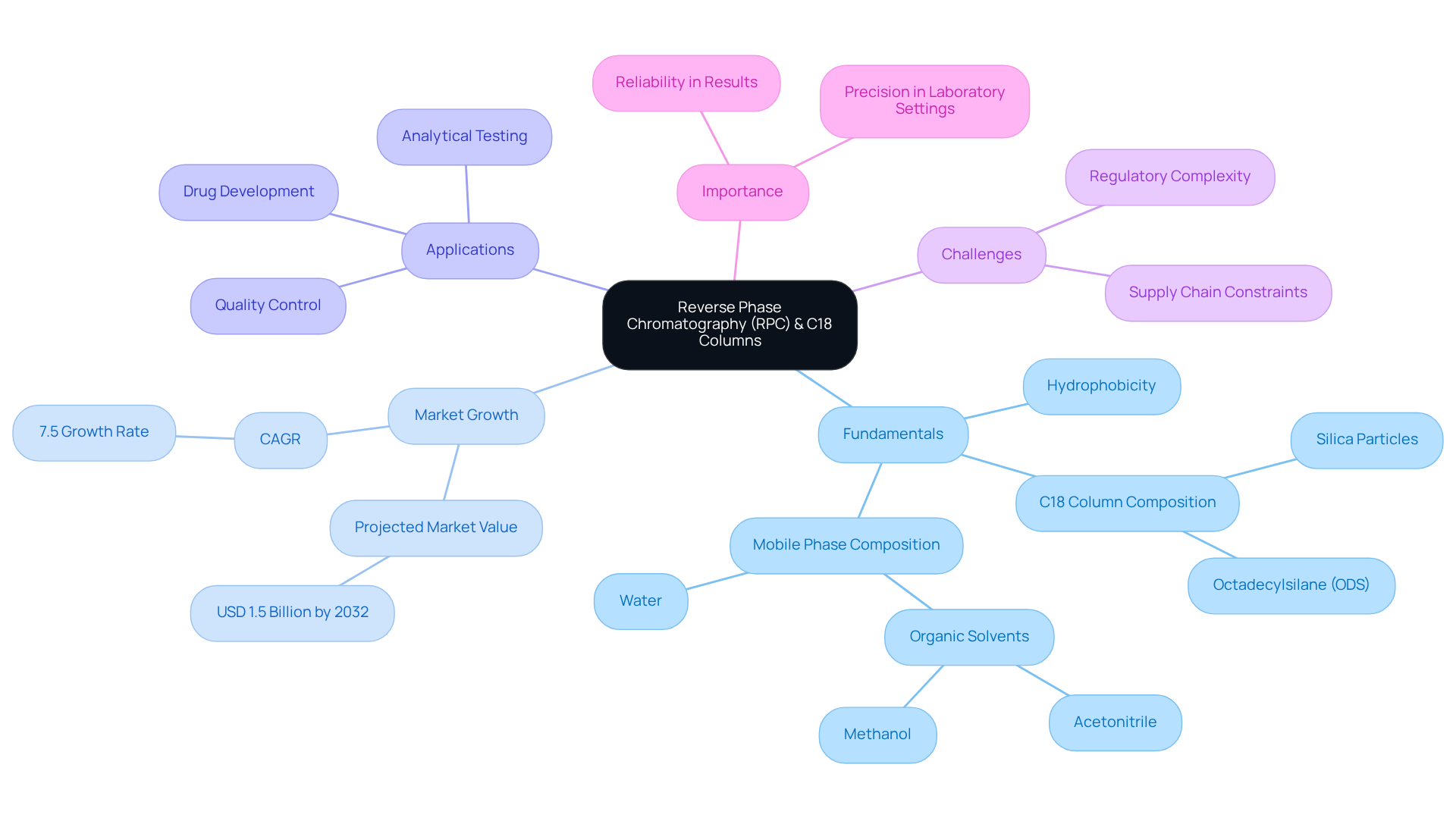
Reverse chromatography (RPC) stands as a cornerstone technique in analytical chemistry, particularly within pharmaceutical laboratories. This pivotal method distinguishes compounds based on their hydrophobicity, utilizing a [reverse phase C18 column](https://jmscience.com/products/test-capcell-pak-c-18-mg-ii-hplc-column-35x1-5mm-pore-size-100a-particle-size-3um?srsltid=AfmBOopFF9q1JI0nzl4p0Hwo6jPtl8hczf4WFToIvrd0NJI8Bm3sODP8), which is crafted from octadecylsilane (ODS) bonded to silica particles, as the primary stationary component. The hydrophobic interactions between analytes and the stationary layer are essential for achieving effective separation. In RPC, the mobile phase typically comprises a blend of water and organic solvents, such as acetonitrile or methanol, facilitating the elution of compounds according to their polarity.
Recent advancements in analytical chemistry underscore the increasing reliance on reverse phase C18 column supports, with projections indicating that the market for reverse phase C18 columns is set to reach USD 1.5 billion by 2032, expanding at a CAGR of 7.5%. These statistics not only highlight the market's growth but also demonstrate the real-world applications of RPC in drug development and quality control. Mastering RPC techniques is therefore critical for achieving reliable results in pharmaceutical analyses.
However, challenges such as regulatory complexity and supply chain constraints remain pertinent for pharmaceutical lab managers to navigate. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for and enhancing analytical outcomes. As the landscape of analytical chemistry evolves, the importance of RPC in ensuring precision and reliability in laboratory settings cannot be overstated.
Identify the Benefits of C18 Columns in Pharmaceutical Laboratories
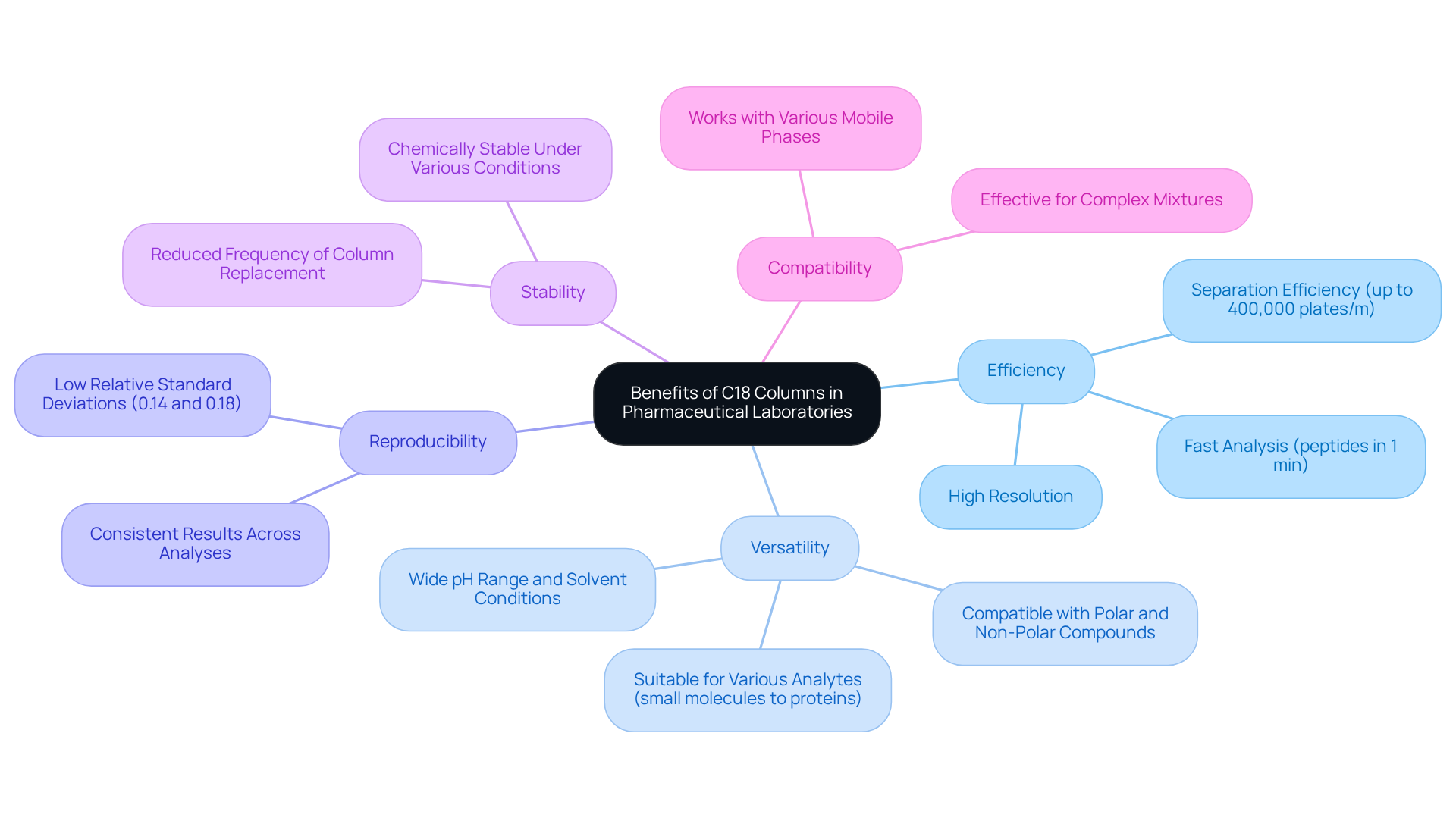
C18 materials are highly esteemed in pharmaceutical laboratories, particularly when used with a reverse phase C18 column, due to their exceptional efficiency and resolution—critical factors for separating complex mixtures in drug formulation and quality control. Their versatility facilitates the analysis of a diverse range of compounds, from small molecules to peptides and proteins, making reverse phase C18 column techniques indispensable in pharmaceutical research, where varied analytes are commonplace.
Notably, the reverse phase C18 column exhibits remarkable reproducibility and stability, ensuring consistent results across multiple analyses. Furthermore, their compatibility with various mobile phases, along with the capability to function across a wide pH range, temperature, and solvent conditions, significantly enhances their utility when utilizing a reverse phase C18 column, allowing for effective separation of both polar and non-polar compounds.
Research indicates that the reverse phase C18 column can achieve separation efficiencies of up to 400,000 plates/m, as highlighted in the study titled 'Development of Narrow-Bore C18 Medium for Fast Separation of Peptides and Proteins.' This combination of high efficiency, adaptability, and reliability positions the reverse phase C18 column as the , thereby facilitating advancements in drug formulation analysis, purity testing, and stability studies.
Implement Best Practices for Using C18 Columns in HPLC
To achieve optimal results with the in high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), it is essential to adhere to best practices that ensure reliability and accuracy in analyses.
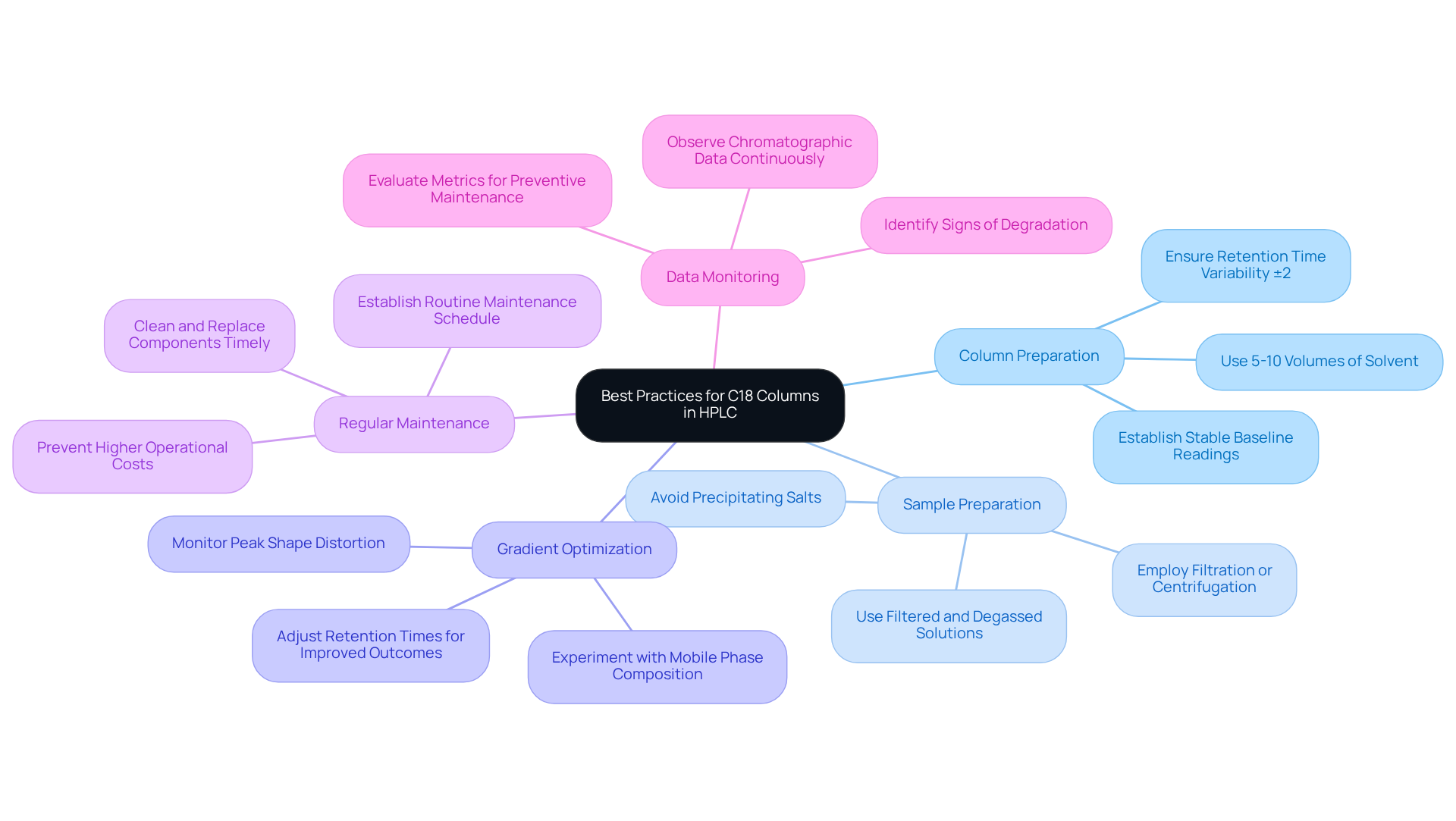
Column Preparation: Prior to use, prepare the column with approximately 5-10 volumes of the solvent. This crucial step establishes stable baseline readings and guarantees reproducibility in results, with retention time variations typically within ±2%.
Sample Preparation: Effective sample preparation is vital to prevent contamination and ensure compatibility with the apparatus. Employ techniques such as filtration or centrifugation to eliminate particulates that could interfere with analysis. Avoid adding precipitating salts to the apparatus and utilize filtered and degassed solutions to maintain integrity.
Gradient Optimization: Experimenting with gradient elution can significantly enhance separation efficiency. Adjustments to the mobile phase composition can influence retention times and peak shapes, leading to improved analytical outcomes. Monitoring early warning signs of HPLC system degradation, such as peak shape distortion, is essential to prevent critical analytical errors.
Regular Maintenance: Establishing a routine maintenance schedule that includes cleaning and timely replacement of components is crucial. This practice extends the lifespan of the reverse phase C18 column and ensures consistent performance. Neglecting maintenance can result in higher operational costs and frequent replacements.
Data Monitoring: Continuously observe chromatographic data for signs of degradation, such as increased back pressure or peak tailing. Prompt corrective actions can mitigate performance issues and ensure data integrity. Regular evaluation of these metrics aids in forecasting lifespan and planning preventive maintenance.
By implementing these best practices, laboratories can significantly enhance the reliability and accuracy of their HPLC analyses, ultimately contributing to improved research and healthcare outcomes. As Sarah Lee emphasizes, 'Proper maintenance aids in preventing contamination and blockages, preserving efficiency and resolution, and guaranteeing accurate and dependable analytical outcomes.
Troubleshoot Common Issues with C18 Columns in Laboratory Settings
Common issues faced when utilizing a reverse phase C18 column can significantly hinder analytical performance. Addressing these challenges is crucial for optimizing laboratory results. Here are some effective troubleshooting tips to enhance your analytical processes:
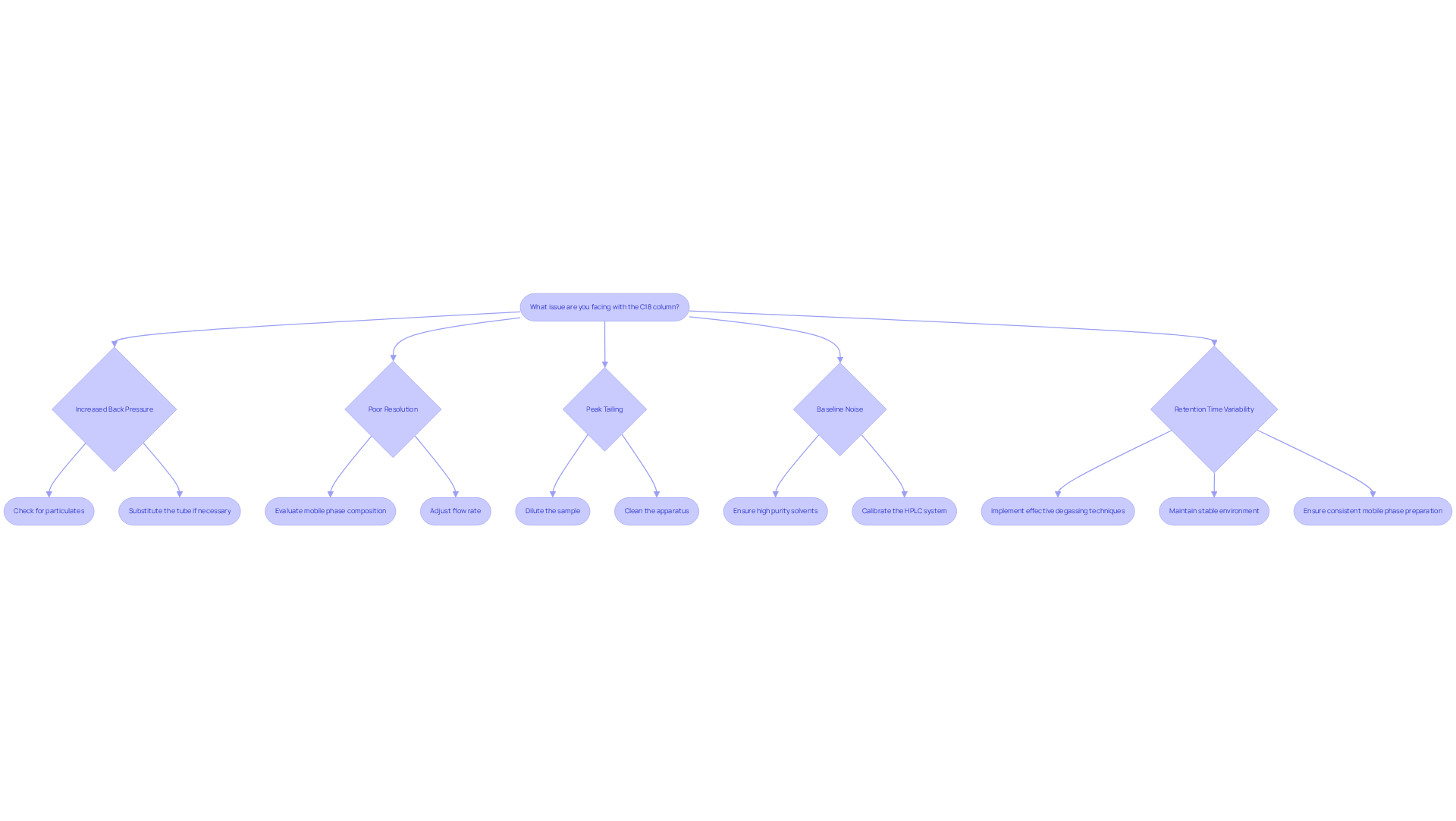
- Increased Back Pressure: This often indicates a blockage in the vertical section. It is essential to check for particulates in the sample or fluid, and consider substituting the tube if necessary. Regular checks for leaks and proper maintenance of fittings are vital to prevent pressure issues within the system. Remember, the maximum operating pressure for the SSI High Pressure Precolumn Filter is 15,000 psi; ensure that your system operates within this limit to avoid potential damage.
- Poor Resolution: When peaks are not well-resolved, it is imperative to evaluate the mobile phase composition and flow rate. Adjusting these parameters can significantly enhance separation. Utilizing high-purity solvents and ensuring proper sample preparation are effective strategies to when working with a reverse phase C18 column. As emphasized, using gradient-grade solvents is crucial for achieving accurate and reproducible results.
- Peak Tailing: This phenomenon can stem from sample overload or contamination of the material. Diluting the sample or cleaning the apparatus can help alleviate this issue. Additionally, incorporating triethylamine or acetate into the transport medium may enhance peak shape. Regular maintenance, including flushing the column with a strong solvent, is essential to prevent contamination.
- Baseline Noise: Variations in the baseline may arise from impurities in the moving solvent or equipment problems. Ensure that all solvents are of high purity and that the HPLC system is properly calibrated. Regular maintenance and cleaning of detector components can significantly enhance sensitivity, ensuring accurate detection of analytes. Implementing effective degassing techniques, such as using in-line degassers, can also stabilize baseline readings.
- Retention Time Variability: Unstable retention times can result from temperature fluctuations or alterations in the solvent composition. It is crucial to maintain a stable environment and ensure consistent mobile phase preparation. Effective degassing techniques, including the use of in-line degassers, can also help stabilize retention times. A case study on maintaining HPLC pump performance underscores the importance of routine maintenance to prevent such issues.
Conclusion
Mastering reverse phase chromatography, particularly with C18 columns, is essential for pharmaceutical laboratories striving for precision and reliability in their analyses. The significance of understanding the underlying principles, benefits, and best practices associated with C18 columns cannot be overstated; they are fundamental tools for effective separation of compounds in drug development and quality control.
Key insights discussed throughout this article include:
- The efficiency and versatility of C18 columns
- Their compatibility with various mobile phases
- The critical importance of adhering to best practices for optimal performance
Addressing common issues such as increased back pressure, poor resolution, and baseline noise underscores the necessity for meticulous attention to detail in laboratory settings. By implementing these strategies, laboratories can enhance their analytical outcomes and ensure consistent results.
In summary, mastering reverse phase C18 column techniques transcends mere technical skill; it represents a vital component in advancing pharmaceutical research and improving healthcare outcomes. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, embracing these best practices and troubleshooting methods will empower laboratories to achieve greater efficiency and reliability in their analyses. Investing time and resources into mastering these techniques is crucial for any laboratory aiming to excel in the competitive landscape of pharmaceutical analysis.




