Overview
This article focuses on essential steps and guidance for effectively utilizing a 0.22um filter syringe for sterile filtration. Proper use of this filter is critical in preventing contamination in sensitive applications, such as cell culture and vaccine production. Statistics underscore the high contamination rates associated with inadequate filtration, while expert testimonials highlight the paramount importance of maintaining sterile conditions. By adhering to these guidelines, laboratories can significantly reduce the risk of contamination and ensure the integrity of their sensitive processes.
Introduction
The significance of sterile filtration in laboratory settings is paramount, particularly in safeguarding the integrity of sensitive biological samples. A 0.22um filter syringe emerges as an indispensable tool in this endeavor, effectively eliminating bacteria and other microorganisms that could jeopardize critical research outcomes. This article explores the essential steps and best practices for utilizing a 0.22um filter syringe, equipping researchers to enhance their filtration efficiency. Yet, what occurs when unforeseen challenges arise during the filtration process? Grasping how to navigate these common issues is crucial for upholding the reliability of laboratory results.
Understand the Purpose of a 0.22um Syringe Filter
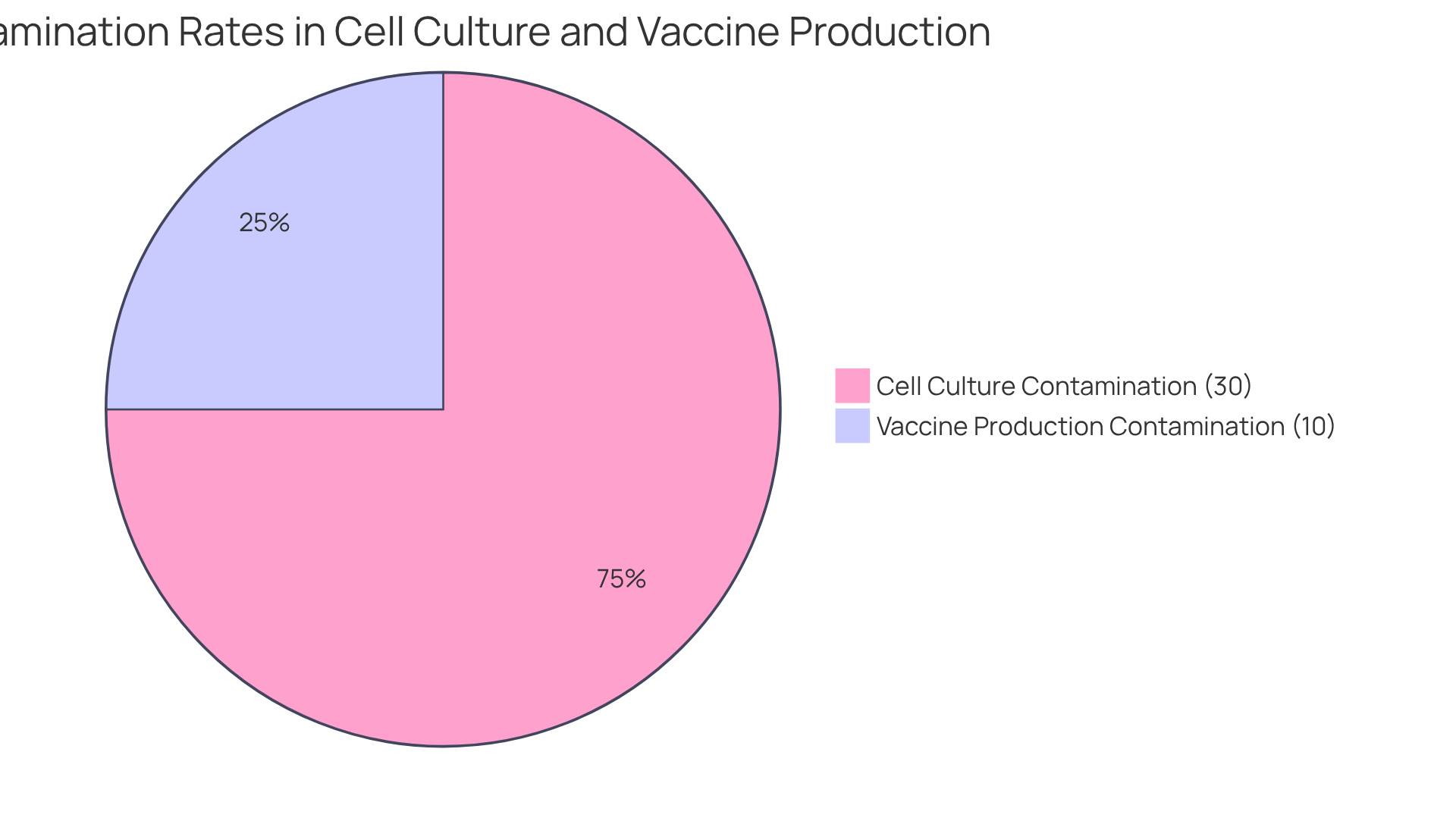
A 0.22um filter syringe membrane is indispensable for sterile filtration, effectively eliminating bacteria and other microorganisms from solutions. This capability is particularly critical in applications such as cell culture and vaccine production, where contamination can severely compromise outcomes.
Research indicates that contamination incidents in cell culture can reach alarming levels of up to 30%, while vaccine production can experience contamination rates of approximately 10%. These statistics underscore the necessity of utilizing a membrane with a pore size of 0.22 micrometers. By ensuring that samples are devoid of microbial contamination, researchers can uphold the integrity of their experiments and achieve precise results.
Microbiologists emphasize that the use of a 0.22um filter syringe is vital for safeguarding the quality of laboratory procedures, especially in vaccine production, where even minimal contamination can lead to significant delays. As Dr. Jane Smith, a microbiologist, asserts, "The accuracy of the 0.22um filter syringe is non-negotiable in our field; it is the final barrier against contamination."
Understanding the purpose and applications of these devices enables users to select appropriate separation solutions, thereby enhancing the reliability and success of their laboratory efforts.
Gather Necessary Tools and Materials for Filtration
To ensure a smooth and effective filtration process, it is essential to gather the following tools and materials:
- Select a device such as a
0.22um filter syringethat is compatible with both your injector and the specific specimen type you are handling. A recommended option is the Merck Millex™-GS Sterile Syringe Filter Unit, which utilizes a0.22um filter syringewith a pore size of 0.22 µm, making it ideal for sterilization and capturing most bacteria and microorganisms. It is important to note that injection device membranes are single-use and should not be recycled to prevent material contamination. Syringe: Utilize a sterile syringe, which typically ranges from 1 mL to 60 mL, depending on the volume of your solution.Sample Solution: Prepare the liquid intended for filtration, ensuring it is free from large particulates to prevent clogging the filter.Collection Container: Have a clean, sterile container ready to collect the filtered solution, preserving the integrity of your samples.Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Equip yourself with gloves, a lab coat, and safety goggles to maintain a sterile environment and ensure personal safety during the separation process.
By keeping these items readily accessible, you can streamline the purification process and enhance the reliability of your results. It is noteworthy that the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors utilize syringe screens in over 65% of preparations to ensure the removal of particulates and bacteria. Furthermore, consider that 33 mm screens offer nearly 20% additional surface area compared to 25 mm screens, which can significantly improve efficiency. Proper preparation is paramount for effective filtration of specimens.
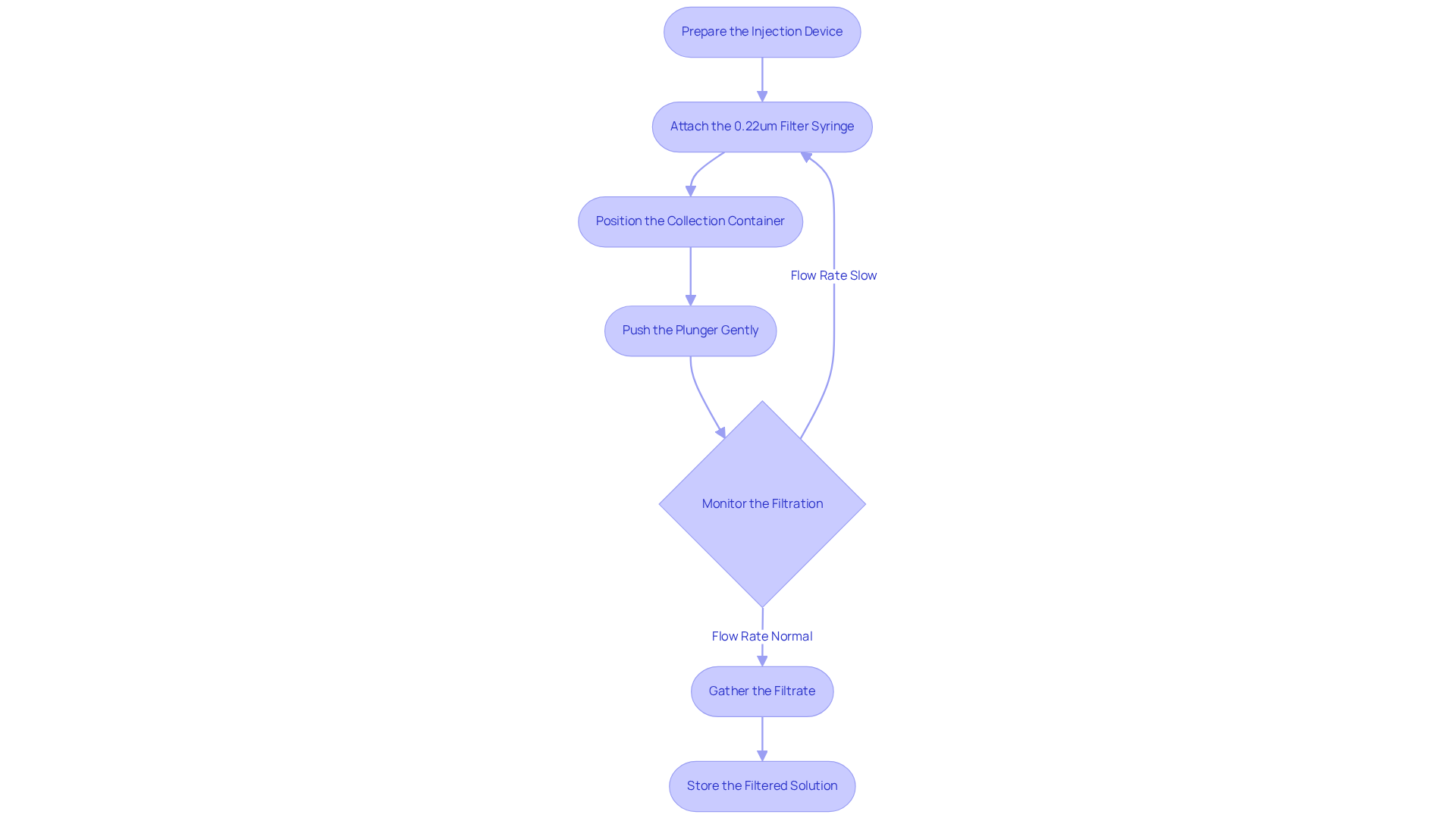
Follow Step-by-Step Instructions for Using the Syringe Filter
To effectively utilize a 0.22 micron syringe filter, follow these essential steps:
- Prepare the Injection Device: Begin by opening the sterile injection device and drawing the sample solution into it, ensuring that no contaminants are introduced.
- Attach the 0.22um filter syringe: Securely connect the 0.22um filter syringe to the device's luer lock, ensuring a tight fit to prevent any leaks.
- Position the Collection Container: Place your collection container directly beneath the sieve to catch the filtered solution.
- Hold the syringe upright and gently push the plunger to separate the solution using the syringe filter. Apply steady pressure to avoid damaging the strainer.
- Monitor the Filtration: Observe the flow rate closely; if it slows significantly, this may indicate an obstruction, necessitating a replacement. Industry standards affirm that the use of a 0.22um filter syringe provides superior filtration efficiency, effectively eliminating bacteria and certain viruses, making it ideal for sterile applications.
- Gather the Filtrate: Once the solution has been filtered, carefully remove the syringe strainer and dispose of it according to your laboratory's waste disposal protocols.
- Store the Filtered Solution: If the solution is not used immediately, store it in a sterile container to preserve its integrity.
A laboratory technician noted, 'Utilizing a 0.22um filter syringe has significantly enhanced our sample quality, especially when working with sensitive biological specimens.' This approach has led to a marked reduction in contamination rates, which is crucial for our research.
Cost Consideration: It is important to recognize that while individual 0.22um filter syringe units may cost approximately $4.00 each, purchasing in bulk can yield substantial savings. For instance, acquiring 10,000 units at this rate would total $40,000, highlighting the economic implications of selection in laboratory operations.
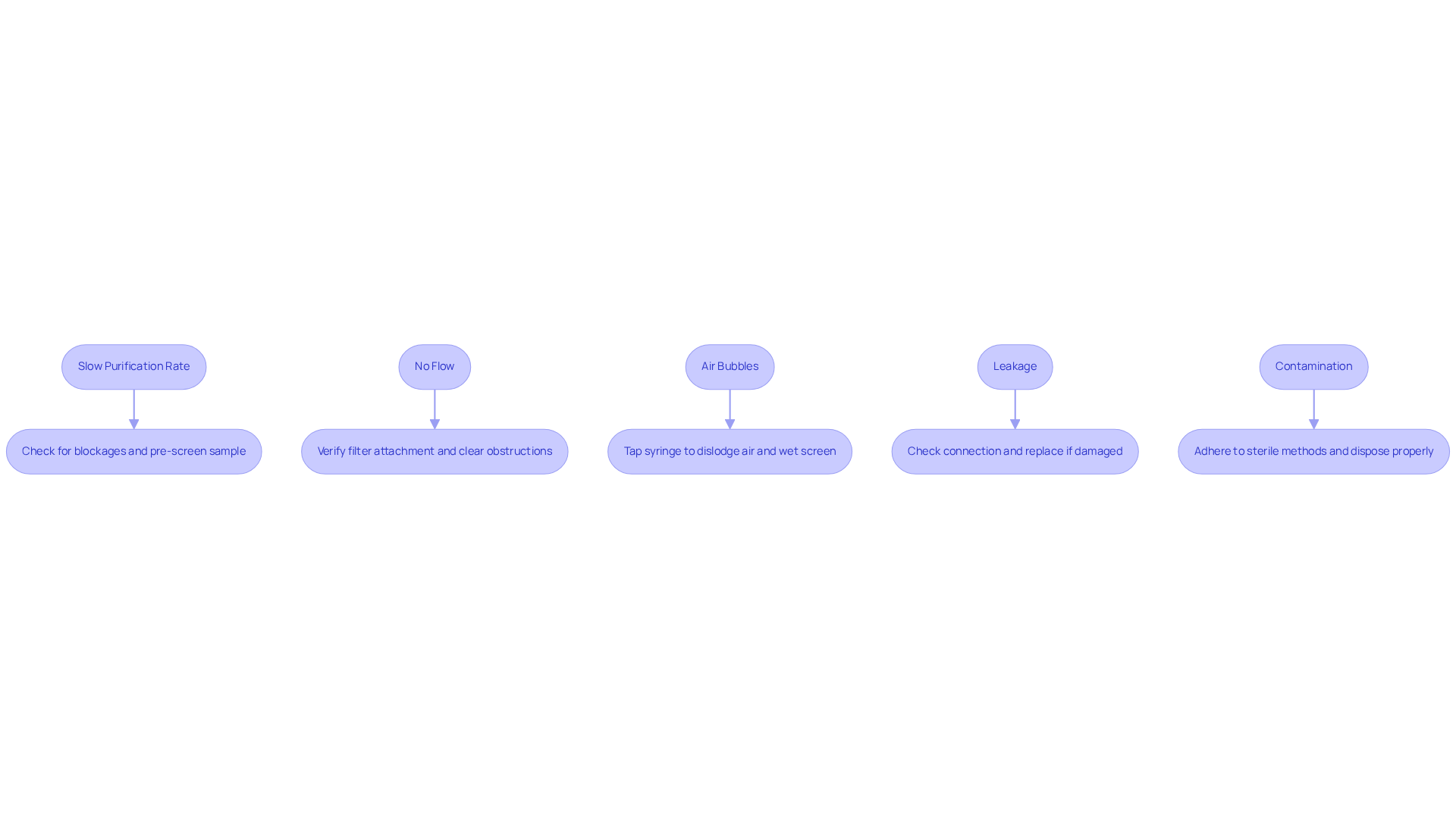
Troubleshoot Common Issues During Filtration
When utilizing a 0.22um filter syringe, several common issues may arise that could hinder your filtration process. Below are effective troubleshooting tips designed to enhance your purification efforts:
-
Slow Purification Rate: Should you experience a reduced purification rate, it is essential to examine the screen for potential blockages. Pre-screening your sample with a larger pore size mesh can effectively remove larger particles that may be causing the obstruction. Additionally, be aware that increased flow rates can lead to inadequate contact time with the membrane, potentially compromising efficiency.
-
No Flow: In situations where no liquid is passing through, verify that the filter is securely attached and that there are no obstructions in the syringe. For thicker substances, consider diluting the material or exploring alternative separation techniques to facilitate flow. It is crucial to recognize that viscous samples are more prone to bubble formation due to their flow properties.
-
Air Bubbles: The presence of air bubbles can significantly disrupt the filtration process. Gently tapping the syringe may help dislodge trapped air. Furthermore, ensuring the screen is adequately wetted prior to use can markedly reduce air entrapment. Remember that pre-screening with a medium of larger pore size can also decrease viscosity and enhance flow dynamics.
-
Leakage: If leakage occurs around the strainer, it is vital to check the connection between the syringe and strainer for a secure fit. Should the connection be loose or if the element appears damaged, replacing it is necessary to maintain integrity during purification.
-
Contamination: To prevent contamination of your samples, always adhere to sterile methods and ensure the proper disposal of used materials. This practice is critical for maintaining the quality of your results.
Incorporating these troubleshooting strategies can optimize your filtration process using a 0.22um filter syringe, leading to reliable outcomes in your laboratory work. As a noteworthy reminder, more than 40% of healthcare professionals and laboratory technicians remain unaware of syringe filter compatibility, underscoring the importance of understanding these processes.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of a 0.22um filter syringe is crucial for ensuring sterile filtration in laboratory settings. This guide emphasizes the critical role these filters play in preventing contamination, especially in sensitive applications such as cell culture and vaccine production. By utilizing a 0.22um filter syringe, researchers can greatly enhance the reliability of their results and uphold the integrity of their experiments.
The article provides a comprehensive overview of the essential tools and materials needed for effective filtration, along with detailed step-by-step instructions for proper usage and practical troubleshooting tips for common issues encountered during the filtration process. Understanding these elements equips users with the knowledge to navigate potential challenges and optimize their laboratory practices.
Ultimately, the significance of employing a 0.22um filter syringe cannot be overstated. Given that contamination rates in critical applications can be alarmingly high, implementing these best practices is essential for achieving accurate and reliable outcomes in scientific research. By adopting a meticulous approach to filtration, researchers not only safeguard the quality of their results but also contribute to advancements in laboratory efficiency and effectiveness.




