Overview
The article emphasizes the mastery of the phosphoric acid titration curve, a critical skill for achieving precise results across various applications. It highlights the triprotic nature of phosphoric acid and underscores the importance of understanding equivalence points. To support this, the article details the significance of:
- Employing proper titration techniques
- Selecting appropriate indicators
- Addressing potential challenges
These elements are essential for ensuring reliable outcomes in fields such as pharmaceuticals and environmental testing, where accuracy is paramount. In summary, mastering these aspects not only enhances expertise but also contributes to the integrity of scientific results.
Introduction
Mastering the intricacies of phosphoric acid titration transcends mere laboratory exercise; it is an essential skill vital across various industries, including pharmaceuticals and environmental testing. This tutorial explores the significance of comprehending the titration curve of phosphoric acid, emphasizing its triprotic nature and the critical importance of accurately identifying equivalence points.
As practitioners navigate the complexities of pH changes and the selection of suitable indicators, what challenges might they encounter that could jeopardize their results? Addressing these elements will unveil the essential practices required to ensure precision and reliability in titration outcomes.
Explore the Basics of Phosphoric Acid Titration
Phosphoric acid (H₃PO₄) is a triprotic substance, meaning it has the capacity to donate three protons (H⁺) in a stepwise manner. This characteristic is significant, as it results in multiple equivalence points that can be observed on the phosphoric acid titration curve during the neutralization process.
To effectively conduct this procedure, a known concentration of a base, referred to as the titrant, is gradually introduced to the solution until the reaction reaches completion, which is indicated by a change in pH.
Understanding the dissociation of phosphate and its behavior in solution is crucial for accurately interpreting the phosphoric acid titration curve in analytical results. Furthermore, familiarity with essential laboratory equipment, such as burettes and pH meters, is necessary for executing titrations effectively.
Understand the Purpose and Applications of Titrating Phosphoric Acid
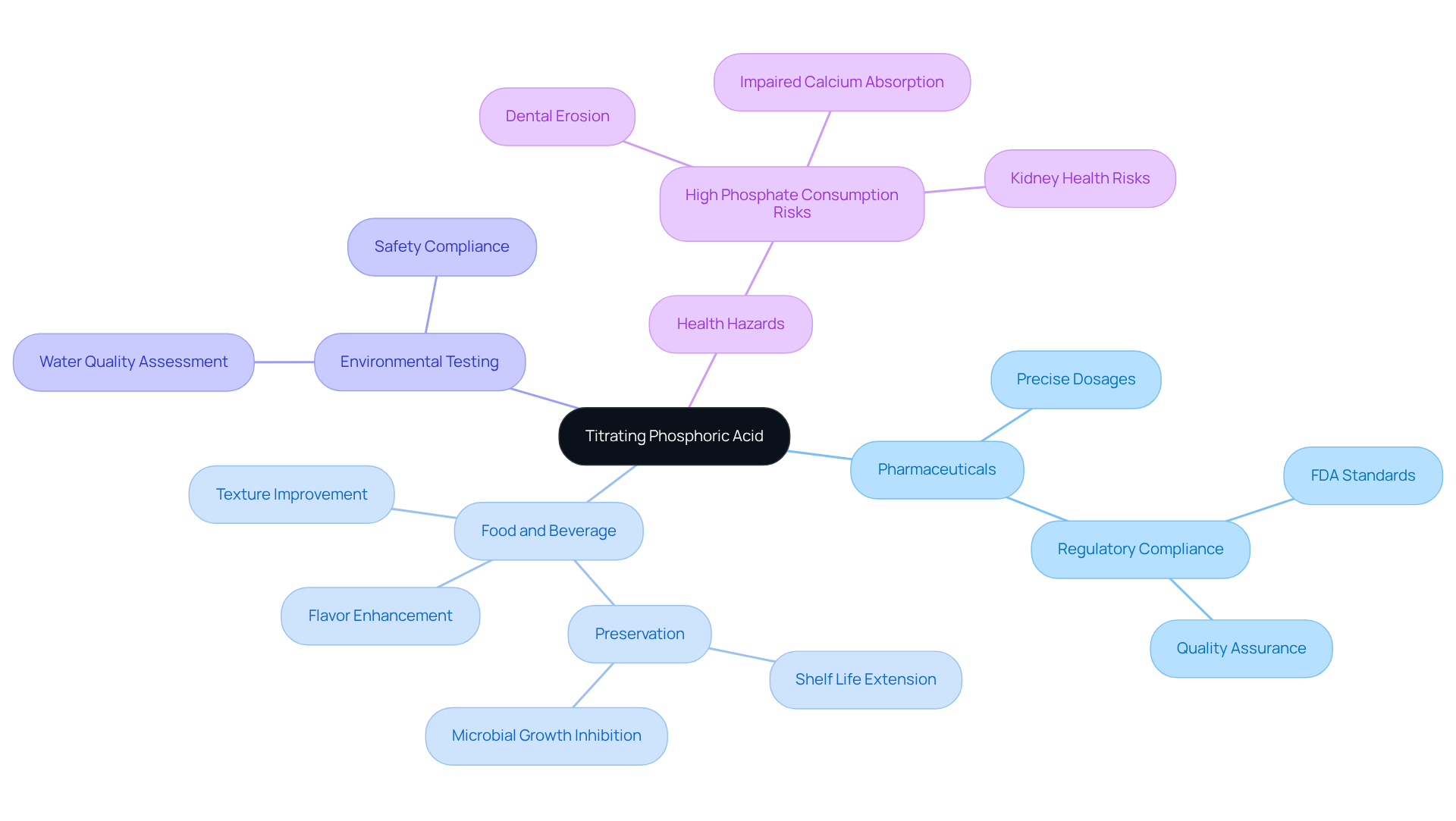
Titrating this solution is essential across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverage analysis, and environmental testing. As a moderately strong substance compared to citric and acetic solutions, this compound is crucial for determining acidity levels, which significantly influence flavor profiles and preservation methods.
For instance, a specific substance is frequently utilized in fizzy drinks to enhance flavor and ensure product consistency, as illustrated in a case study on flavor enhancement in carbonated beverages. In the pharmaceutical sector, accurate measurement is vital for ensuring precise dosages of active ingredients, thereby safeguarding patient health and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Environmental laboratories also employ specific solution titration to assess water quality, guaranteeing safety and adherence to environmental regulations. It is imperative to note that providing a certain acid requires compliance with certifications such as FSSAI, FDA, and HACCP, which are critical for regulatory adherence in both the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Furthermore, understanding the health hazards associated with high phosphate consumption is essential for pharmaceutical lab managers and food safety experts. Mastering this technique is imperative, as it directly impacts product quality, safety, and regulatory compliance, establishing it as a cornerstone of industry best practices.
Analyze the Titration Curve: pH Changes and Equivalence Points
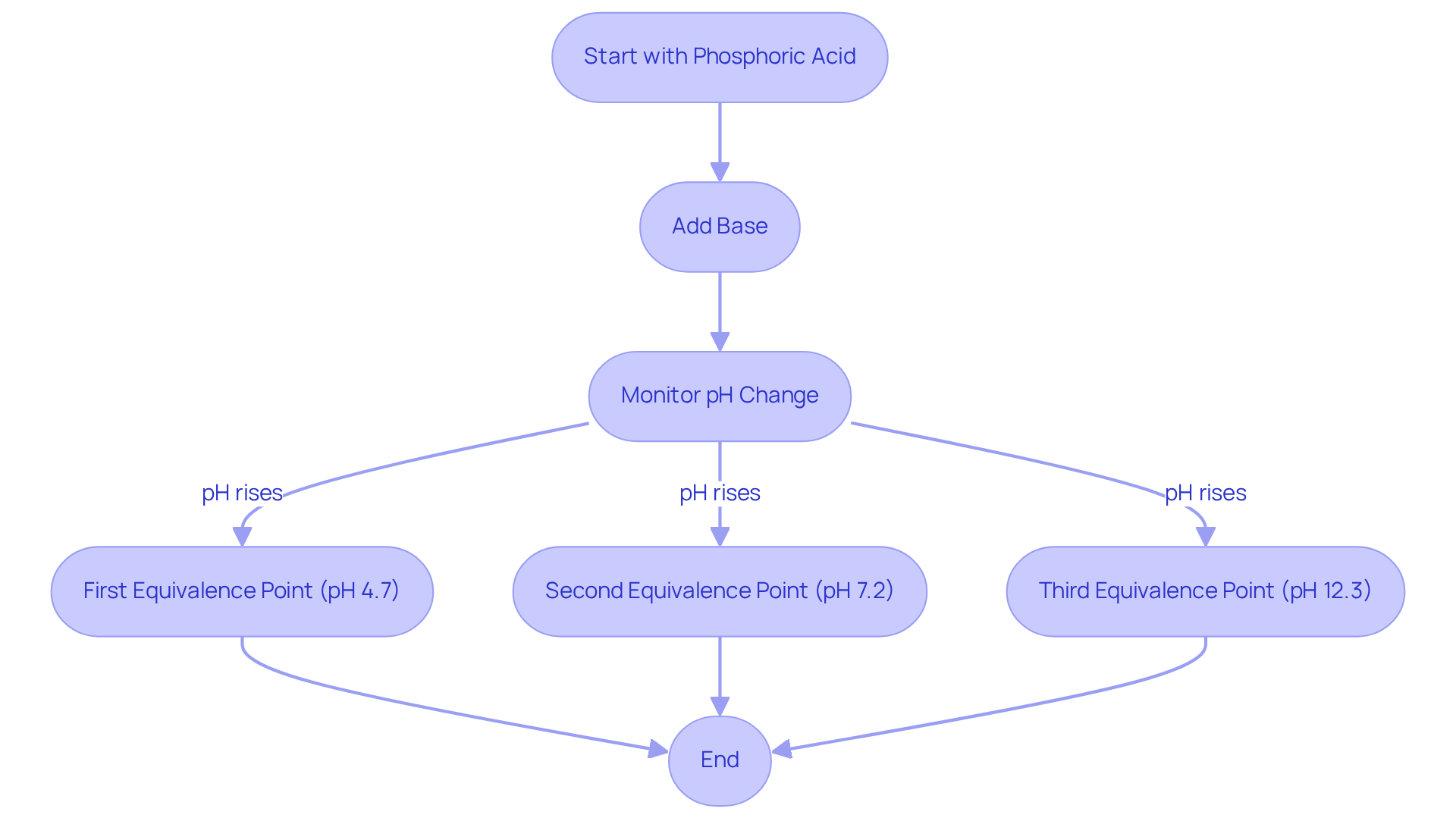
The phosphoric acid titration curve is characterized by three distinct regions, each representing its triprotic nature and the sequential dissociation of protons. As a base is progressively added, the pH of the solution exhibits a steady rise, punctuated by sudden increases at each equivalence stage.
The first equivalence stage is reached when the initial proton is neutralized, followed by the second and third stages as additional base is introduced. By plotting the pH against the volume of titrant added, one can effectively visualize the transitions in the phosphoric acid titration curve and accurately pinpoint the equivalence points.
This understanding is crucial for determining the concentration of phosphoric acid in a solution, which plays a vital role in various applications, including fertilizer production and quality control within the pharmaceutical industry. Titration is essential for characterizing pharmaceutical raw materials and finished products, underscoring its importance in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Furthermore, effective dosage practices, bolstered by user education and adherence to standard operating procedures, can significantly reduce errors, ensuring reliable results in critical analytical processes. Collaboration among healthcare practitioners, such as pharmacists and laboratory supervisors, is also pivotal for enhancing dosing workflows and achieving precise outcomes.
Select Indicators and Address Challenges in Phosphoric Acid Titration
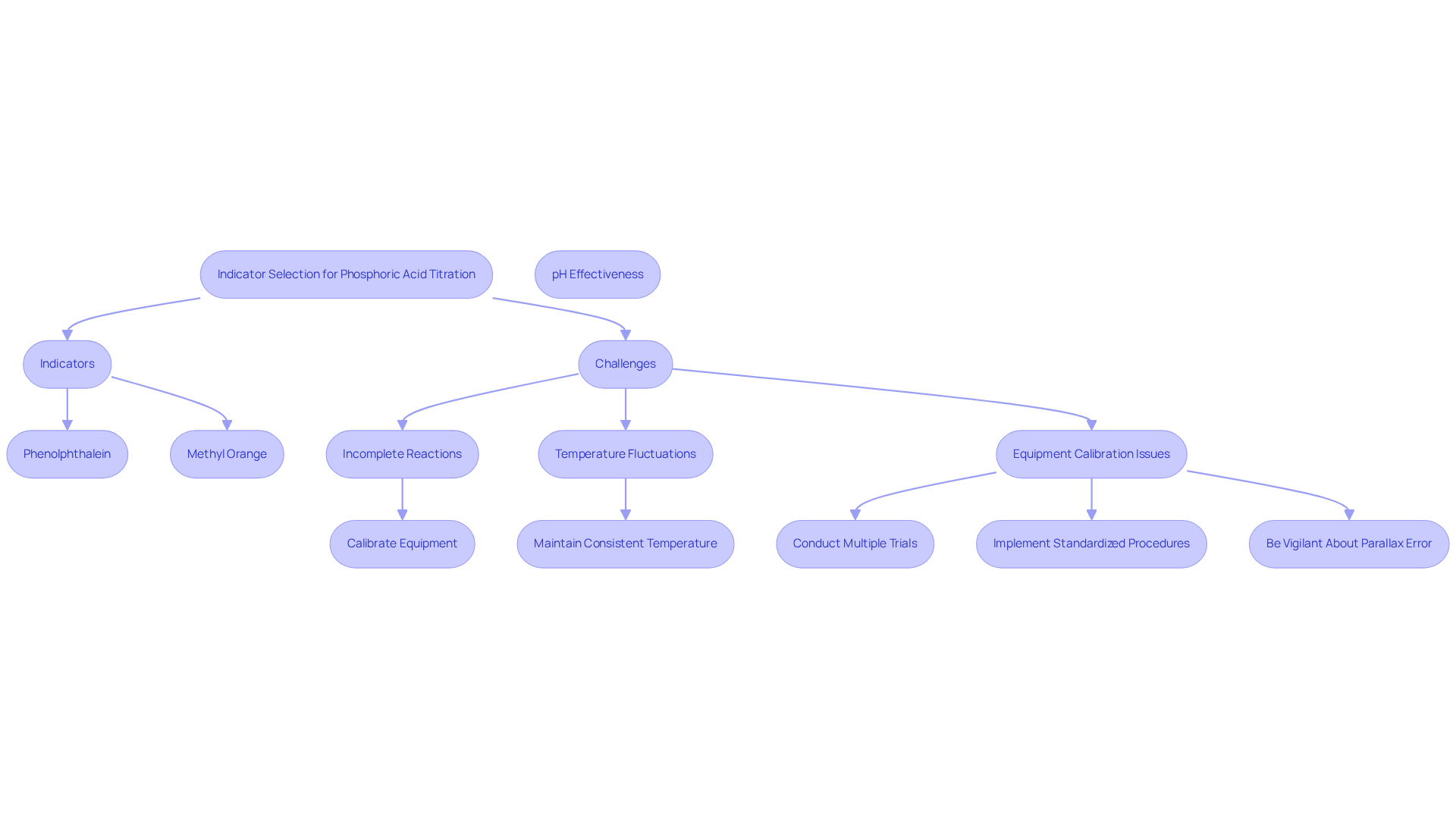
Selecting the appropriate indicator for the phosphoric acid titration curve is essential for accurately determining the endpoint. Common indicators, such as phenolphthalein and methyl orange, exhibit color changes at different pH levels. Phenolphthalein is well-suited for the initial equivalence, while methyl orange is preferable for the second. The effectiveness of these indicators hinges on their transition ranges aligning with the pH at the equivalence points observed on the phosphoric acid titration curve.
However, challenges can arise, including:
- Incomplete reactions
- Temperature fluctuations
- Equipment calibration issues
All of these can affect results. To address these challenges, ensure that all equipment is calibrated properly, carry out measurements at a consistent temperature, and conduct multiple trials to verify results. Implementing standardized procedures and conducting self-assessments can further minimize human error during measurements. Additionally, be vigilant about parallax error, which can lead to inaccurate volume readings.
By proactively addressing these challenges, you can significantly enhance the reliability of your titration outcomes. This careful approach not only strengthens your results but also establishes a foundation of credibility in your laboratory practices.
Conclusion
Mastering the phosphoric acid titration curve is essential for achieving accurate and reliable analytical results across various industries. The triprotic nature of phosphoric acid, with its ability to donate three protons, creates multiple equivalence points that must be understood and accurately measured. This process is fundamental not only in laboratory settings but also critical for ensuring product quality and safety in sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and environmental testing.
Key insights throughout this article highlight the importance of comprehending the titration curve, selecting appropriate indicators, and addressing the challenges that may arise during the titration process. By recognizing the significance of pH changes and equivalence points, practitioners can effectively determine the concentration of phosphoric acid, which is vital for applications ranging from flavor enhancement in beverages to ensuring compliance with regulatory standards in pharmaceuticals.
In conclusion, mastering phosphoric acid titration transcends mere technical skill; it is a vital practice underpinning quality control and safety across multiple fields. Embracing best practices, addressing potential challenges, and continuously enhancing knowledge in this area will contribute to more precise outcomes and uphold the integrity of laboratory results. Engaging with this subject matter is crucial for professionals aiming to excel in their respective industries and ensure that their analytical processes meet the highest standards of accuracy and reliability.




