Overview
This article delves into the mastery of selecting chromatography instruments for laboratory applications. Understanding various chromatography techniques is crucial, as it lays the foundation for effective instrument choice. Evaluating key selection criteria—such as performance specifications and budget—is essential for optimizing laboratory efficiency and effectiveness. By following a structured purchasing process, laboratories can significantly enhance their operational capabilities. Ultimately, the right selection of chromatography instruments not only streamlines processes but also elevates the quality of scientific outcomes.
Introduction
Chromatography serves a crucial function in contemporary laboratories, empowering scientists to separate and analyze intricate mixtures with precision. As the demand for accurate and efficient analytical techniques escalates, it becomes imperative to understand how to choose the appropriate chromatography instruments to optimize laboratory performance. Yet, with a plethora of options available, how can one effectively navigate the complexities of instrument selection to guarantee the best fit for specific analytical requirements?
This guide examines the fundamentals of chromatography, investigates various instrument types, and delineates essential criteria for making informed purchasing decisions, ultimately equipping laboratories to elevate their analytical capabilities.
Understand Chromatography Basics
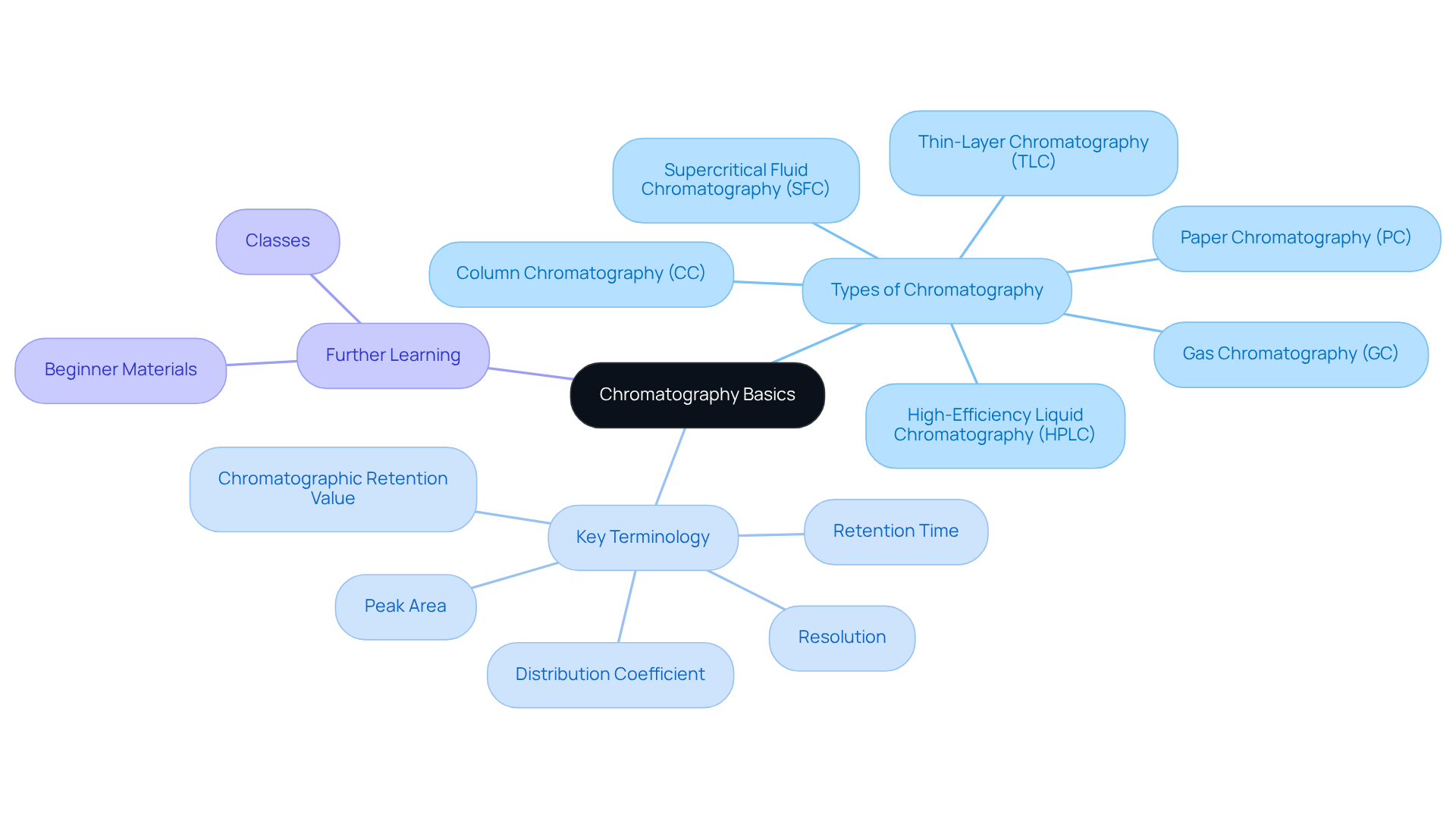
Chromatography stands as a vital technique for separating mixtures into their individual components, fundamentally relying on the principle of differential partitioning between a stationary phase and a mobile phase. Understanding the main forms of chromatography—such as gas chromatography (GC) and high-efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC)—is crucial, as each technique possesses unique applications, advantages, and drawbacks. For instance, HPLC is renowned for its high efficiency and speed, capable of detecting substances at concentrations as low as 1 ng/g, thereby proving invaluable in pharmaceutical analysis.
Key terminology, including:
- Retention time
- Resolution
- Peak area
plays an essential role in evaluating chromatographic devices. Retention time indicates the duration a compound remains in the column, while resolution measures the ability to distinguish between closely eluting peaks. Comprehending these concepts will facilitate the selection of appropriate tools for specific scientific requirements.
To deepen your understanding, consider exploring beginner materials or classes related to chromatography. This foundational knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions when selecting chromatography instruments, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and precision of your analyses.
Explore Types of Chromatography Instruments
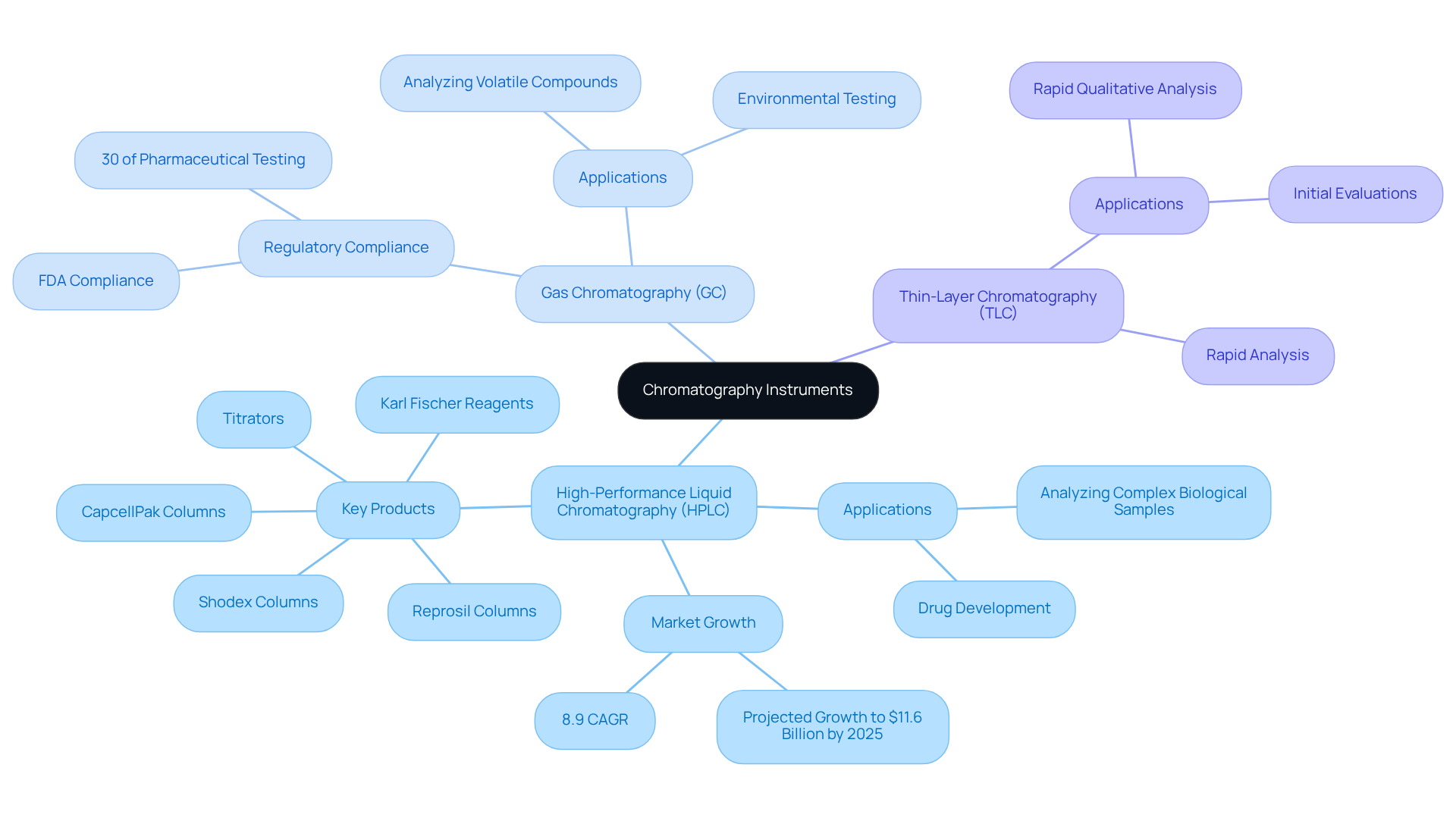
In laboratories, chromatography instruments are indispensable, as each is designed to meet specific analytical requirements. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is particularly favored in pharmaceutical settings due to its exceptional resolution and sensitivity, making it ideal for analyzing complex biological samples and medications. JM Science Inc. offers a comprehensive range of chromatography columns and accessories, including:
- Shodex
- CapcellPak
- Reprosil columns
- Titrators
- Karl Fischer reagents
All vital for achieving peak performance in liquid chromatography applications. The demand for HPLC is projected to rise significantly by 2025, propelled by innovations in drug development and quality control measures. The market for separation devices is anticipated to grow from $10.65 billion in 2024 to $11.6 billion in 2025, reflecting an 8.9% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). Conversely, Gas Chromatography (GC) excels in analyzing volatile compounds and is essential for maintaining compliance with stringent regulatory standards, representing nearly 30% of pharmaceutical testing. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) provides a rapid qualitative analysis method, delivering swift results for initial evaluations.
When selecting a chromatography instrument, it is crucial to consider the characteristics of the sample, the required sensitivity, and the throughput of the facility. Industry leaders emphasize the importance of HPLC in enhancing analytical capabilities, with ongoing innovations aimed at improving efficiency and precision in testing workflows. As the field of separation science evolves, remaining informed about the latest technologies and applications, including those offered by JM Science Inc., is vital for optimizing laboratory performance.
Evaluate Key Selection Criteria
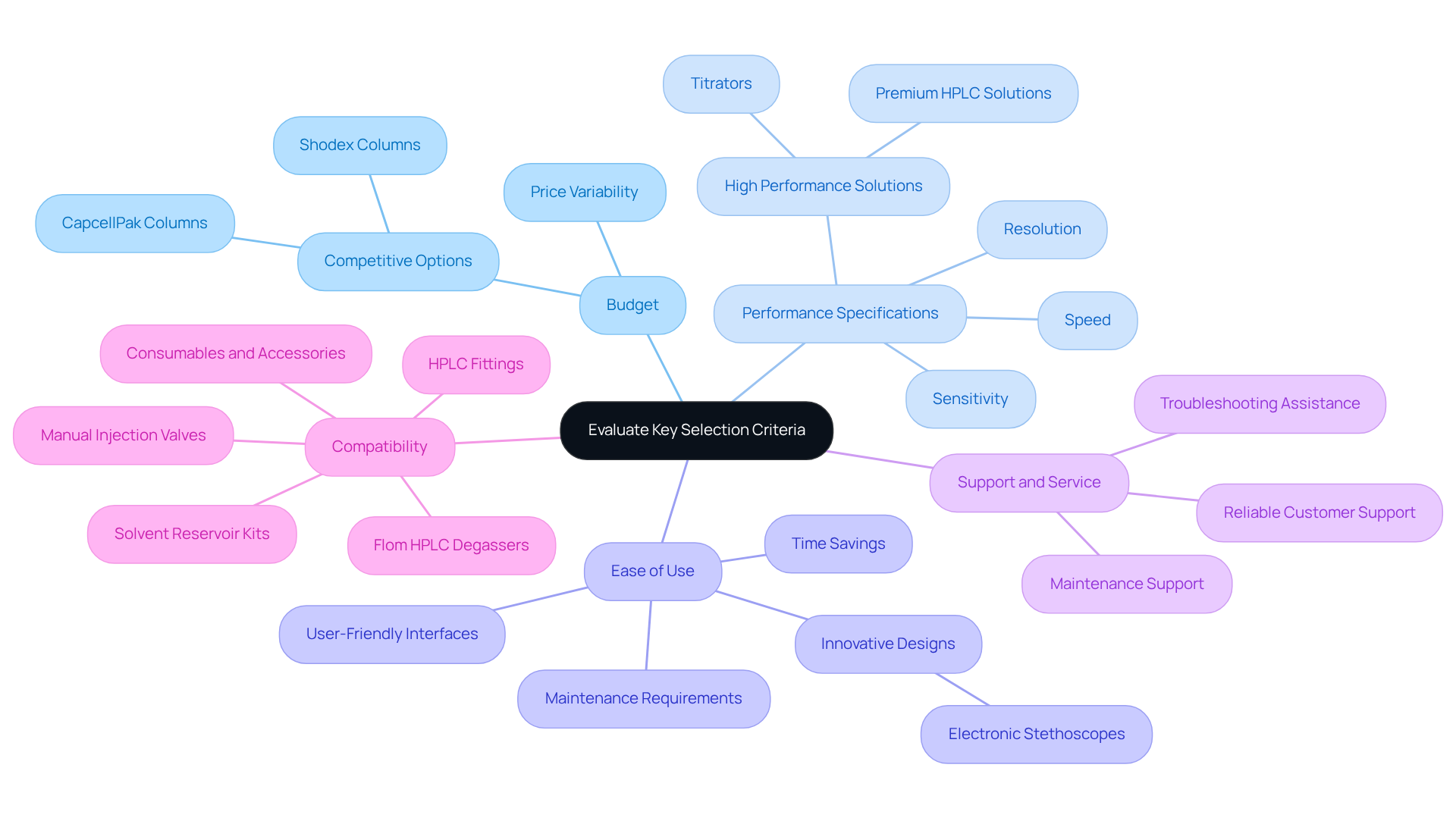
When evaluating a chromatography instrument, it is essential to consider several key criteria that can significantly impact your laboratory's efficiency and outcomes.
-
Budget: Begin by determining your budget constraints, as chromatography equipment can vary widely in price. JM Science Inc. offers a diverse selection of chromatography columns, including Shodex and CapcellPak, alongside accessories at competitive prices. This variety facilitates the discovery of solutions that align with your financial parameters.
-
Performance Specifications: Next, examine critical performance specifications such as sensitivity, resolution, and speed. It is vital to ensure that the chromatography instrument meets the specific requirements of your applications. JM Science's premium HPLC solutions and titrators are engineered to deliver high performance, effectively catering to the needs of pharmaceutical laboratories.
-
Ease of Use: User-friendliness is another crucial aspect to consider. This includes evaluating software interfaces and maintenance requirements. Instruments that are easier to operate can save valuable time and reduce training costs. JM Science's innovative medical devices, such as electronic stethoscopes, exemplify a user-centric design that enhances operational efficiency.
-
Support and Service: Additionally, assess the manufacturer's customer support and service options. Reliable support is essential for the troubleshooting and maintenance of the chromatography instrument. JM Science is committed to providing exceptional customer support, ensuring that you receive the necessary assistance for your chromatography devices.
-
Compatibility: Finally, confirm that the device is compatible with the consumables and accessories you intend to use, such as columns and detectors. JM Science offers a comprehensive range of HPLC fittings, manual injection valves, solvent reservoir kits, and new Flom HPLC degassers, ensuring seamless integration with your existing laboratory setup.
Source and Purchase Your Chromatography Instrument
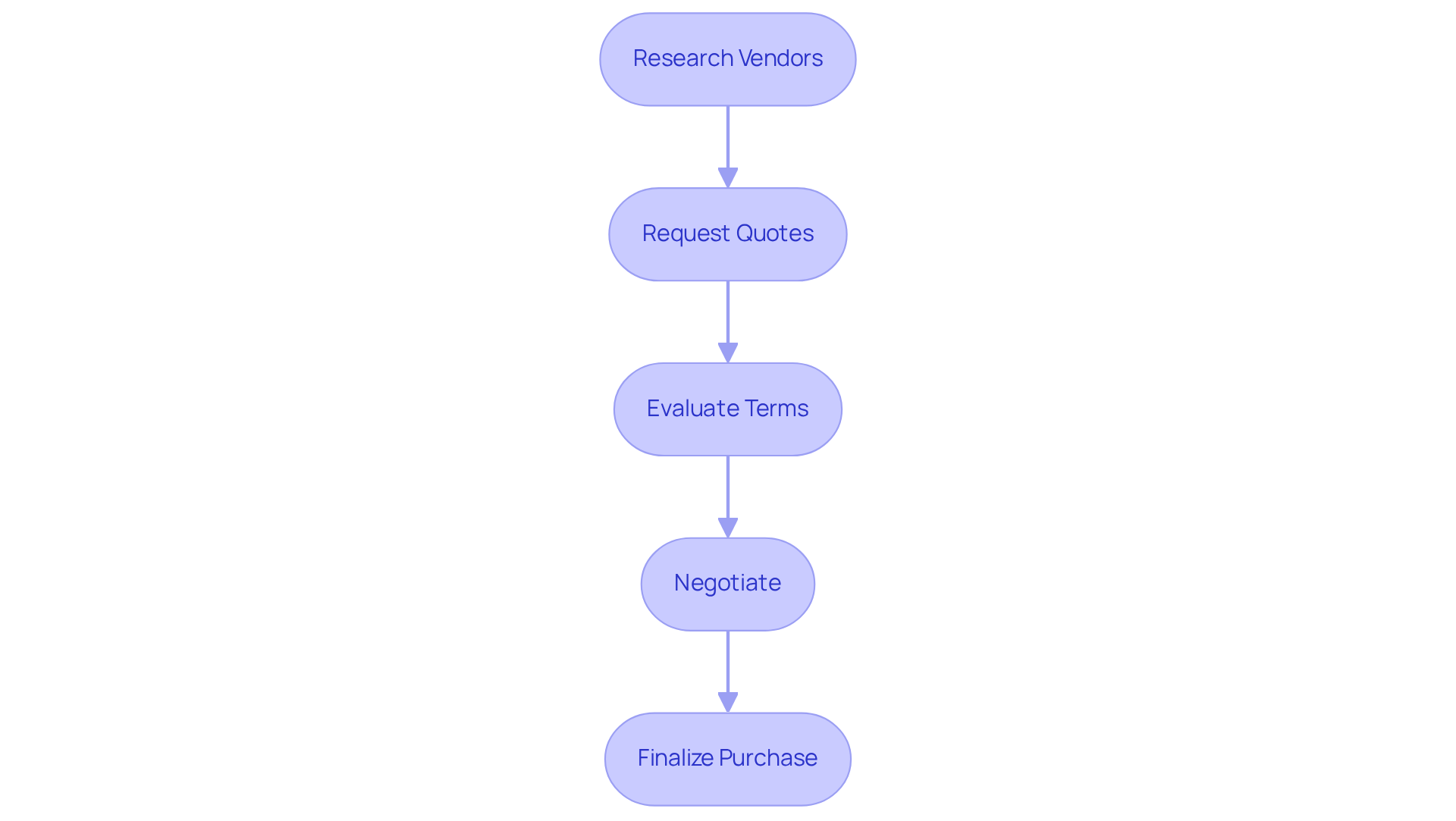
To effectively source and purchase your chromatography instrument, it is essential to follow these steps:
-
Research Vendors: Begin by identifying reliable suppliers that specialize in chromatography devices. JM Science Inc. is notable for its extensive selection of high-quality products tailored to various laboratory needs, establishing a strong foundation for your procurement process.
-
Request Quotes: Reach out to several vendors to obtain quotes. This practice allows for price comparison and provides insight into the average market rates for your preferred items. Notably, the chromatography instrument industry is projected to reach approximately USD 10.8 billion in 2025, reflecting a growing demand in the sector.
-
Evaluate Terms: It is crucial to carefully review the purchase terms, including warranty, return policies, and service agreements. Understanding the support available post-purchase is vital for ensuring long-term satisfaction and reliability with your equipment.
-
Negotiate: Engage in negotiations regarding pricing and terms, especially if you are considering multiple instruments or consumables. Effective negotiation can lead to significant savings; for example, obtaining competitive bids enhances your purchasing power, akin to negotiating for a vehicle.
-
Finalize Purchase: Once you are satisfied with the terms, proceed to finalize your purchase. Arrange for delivery and installation as necessary, ensuring that all required accessories and consumables are ready for immediate use upon arrival. This thorough preparation can significantly streamline the integration of new equipment into your laboratory operations.
Conclusion
Mastering the selection of chromatography instruments is crucial for enhancing laboratory efficiency and ensuring precise analytical outcomes. Understanding the fundamental principles of chromatography alongside the variety of available instruments allows laboratories to make informed choices tailored to their specific needs and applications.
Key considerations outlined in this guide emphasize the importance of evaluating:
- Performance specifications
- Budget constraints
- Ease of use
- Manufacturer support
Each of these factors is instrumental in determining which chromatography instrument will best meet the analytical requirements of a laboratory, especially in fields such as pharmaceuticals where precision is of utmost importance.
Ultimately, remaining informed about the latest advancements in chromatography technology and comprehending the nuances of instrument selection will empower laboratories to optimize their workflows. As the chromatography market continues to expand, taking proactive steps in sourcing, evaluating, and purchasing the right equipment will not only enhance analytical capabilities but also contribute significantly to the overall success of laboratory operations.




