Overview
To become a security guard, candidates must meet five essential requirements:
- They need to be at least 18 or 21 years old, depending on the position.
- Be U.S. citizens or legal residents.
- Possess a high school diploma or GED.
- Pass background checks.
- Demonstrate good moral character.
These criteria are crucial as they ensure that security personnel are adequately prepared and trustworthy. Such qualifications are vital for effectively safeguarding locations and upholding safety standards. Understanding these requirements is imperative for anyone considering a career in security, as they lay the foundation for a responsible and reliable workforce.
Introduction
In a world where safety and security are paramount, the role of security guards has never been more critical. Aspiring security personnel must navigate a complex web of:
- Eligibility criteria
- Application processes
- Training requirements
to ensure they are well-prepared for the challenges ahead. Understanding the basic prerequisites for licensure is essential, as is the ongoing education required to maintain their credentials. This journey is both demanding and rewarding, highlighting the importance of commitment in this vital profession. This comprehensive guide delves into the key aspects of becoming a security guard, equipping candidates with the knowledge necessary to thrive.
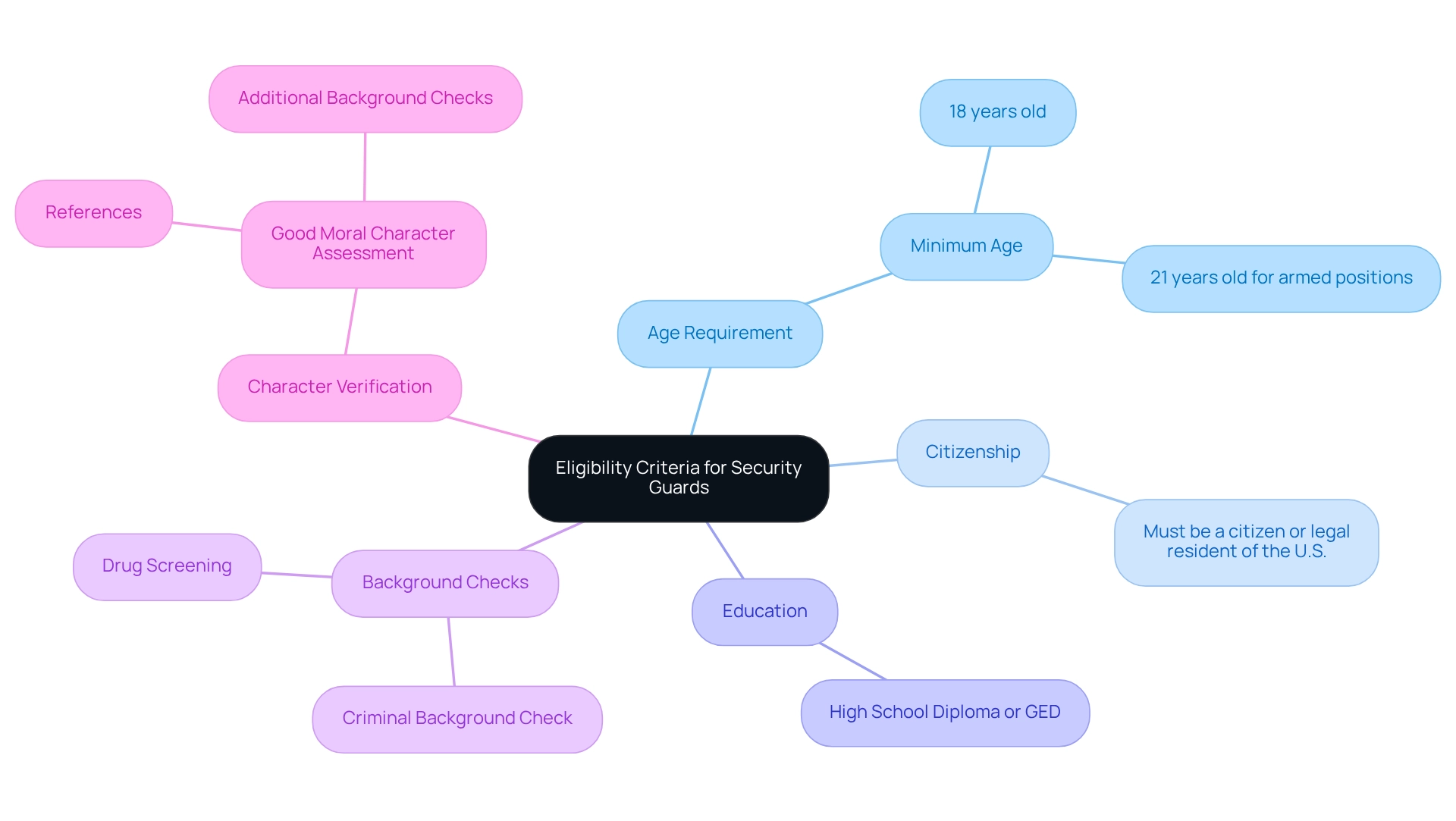
Understanding Basic Eligibility Criteria for Security Guards
To become a safety officer, applicants must typically meet several fundamental eligibility requirements, which can differ considerably by region. The following are the general criteria:
- Age Requirement: Candidates must be at least 18 years old; however, numerous regions necessitate individuals to be 21 years old for armed positions. Statistics indicate that age requirements for protective officer positions can vary, with many states adhering to the 18 or 21-year-old threshold, reflecting a common standard in the industry.
- Citizenship: Candidates must be citizens or legal residents of the United States.
- Education: A high school diploma or GED is usually required.
- Background Checks: All applicants must pass a criminal background check and drug screening to ensure they meet the moral and ethical standards necessary for the role.
- Character Verification: Good moral character is often assessed through references or additional background checks, reinforcing the need for trustworthy personnel in protective roles.
These criteria are essential for ensuring that personnel are capable of handling their responsibilities effectively. For example, in Minnesota, applicants for both unarmed and armed personnel roles must complete 12 hours of pre-assignment training, emphasizing the significance of preparation in this area.
In Wyoming, although there are no state-level licensing prerequisites for unarmed personnel, local regulations might be applicable. This underscores the necessity for potential security personnel to verify particular local regulations before seeking employment, as pointed out in the case study regarding Wyoming Security Personnel Requirements. Furthermore, the function of protective personnel entails safeguarding, patrolling, or overseeing locations to avert theft, violence, or rule violations, and may involve operating x-ray and metal detection devices, which further highlights the significance of comprehending the specific eligibility standards in various areas.
Overall, these eligibility standards are intended to guarantee that protective personnel are adequately prepared to secure locations and uphold safety efficiently.
Navigating the Application Process for Security Guard Licensure
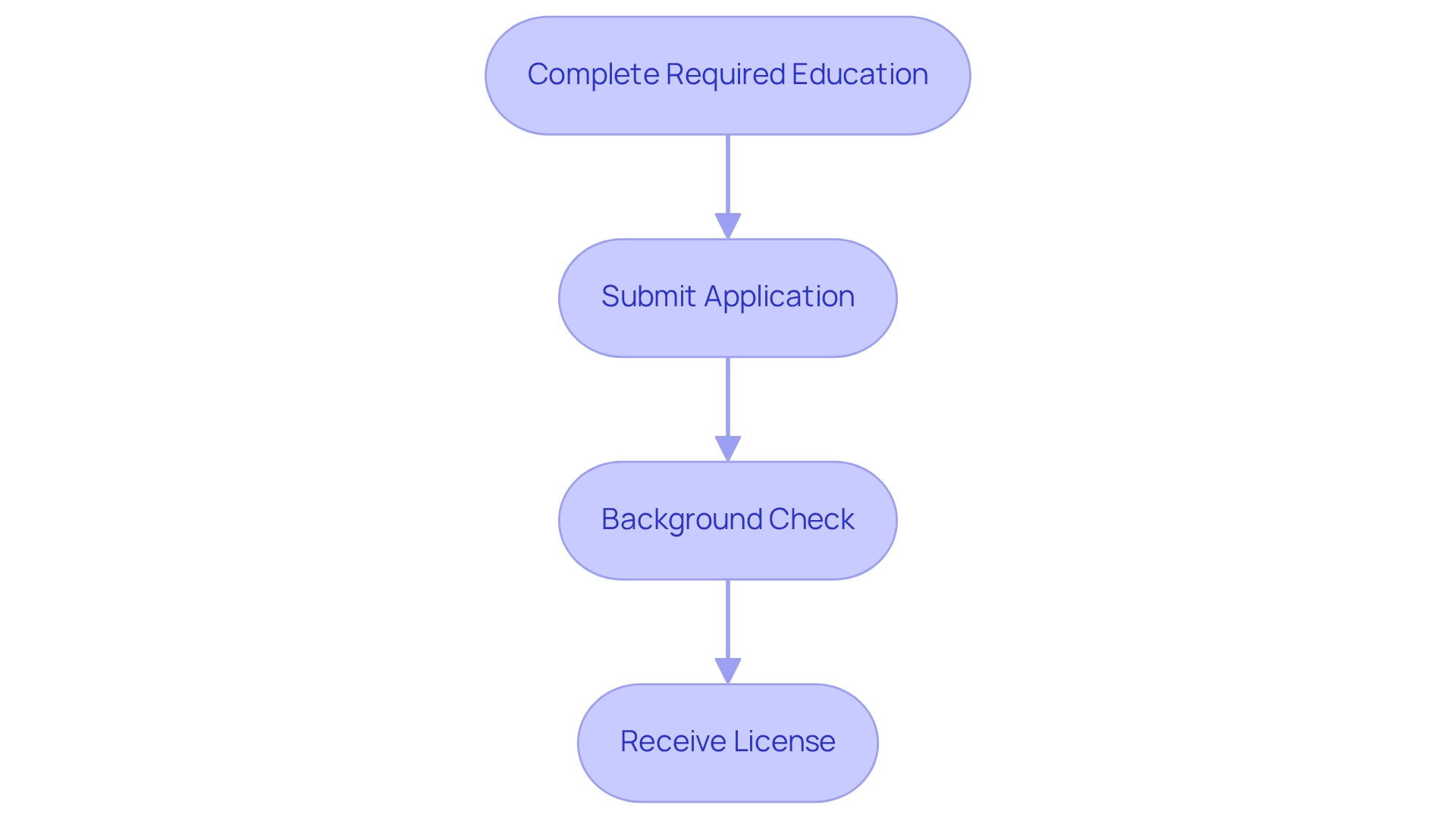
The application procedure for acquiring a security guard license involves several crucial steps that candidates must follow to ensure compliance with local regulations.
- Complete Required Education: Most states mandate the completion of a state-approved program, typically comprising a minimum of 8 hours of pre-assignment instruction. This foundational training is essential for equipping candidates with the necessary skills and knowledge for the role. Notably, completion rates for state-sanctioned educational programs exceed 90%, showcasing a high level of engagement among candidates.
- Submit Application: Following the training, candidates are required to complete and submit an application form to the relevant state authority. This submission often necessitates payment of specific fees, which can differ from state to state.
- Background Check: A thorough background check is a vital part of the application process. This may include fingerprinting and a review of criminal history to ensure the candidate meets the ethical standards required for personnel.
- Receive License: Upon successful approval of the application and background check, candidates will receive their license, enabling them to work legally in the field. It is imperative for applicants to verify particular regional requirements, as these can vary significantly.
In 2025, the average time to obtain a security guard license varies by region, with some areas exhibiting notable differences in processing times. For example, Wyoming lacks overarching state licensing requirements; instead, licensing is managed at the city level. This decentralized approach allows for flexibility but may lead to inconsistencies in preparation and compliance, making it essential for candidates to thoroughly understand local regulations.
Moreover, Belfry consolidates skill development and certification oversight, monitoring credentials and tracking expiration dates to ensure personnel remain compliant.
Successful case studies indicate that applicants who meticulously follow these steps are more likely to navigate the application process efficiently and secure their licenses without unnecessary delays. Grasping the implications of the decentralized licensing approach in Wyoming can better prepare candidates for the challenges they may encounter during the application process.
Essential Training and Certification for Aspiring Security Guards
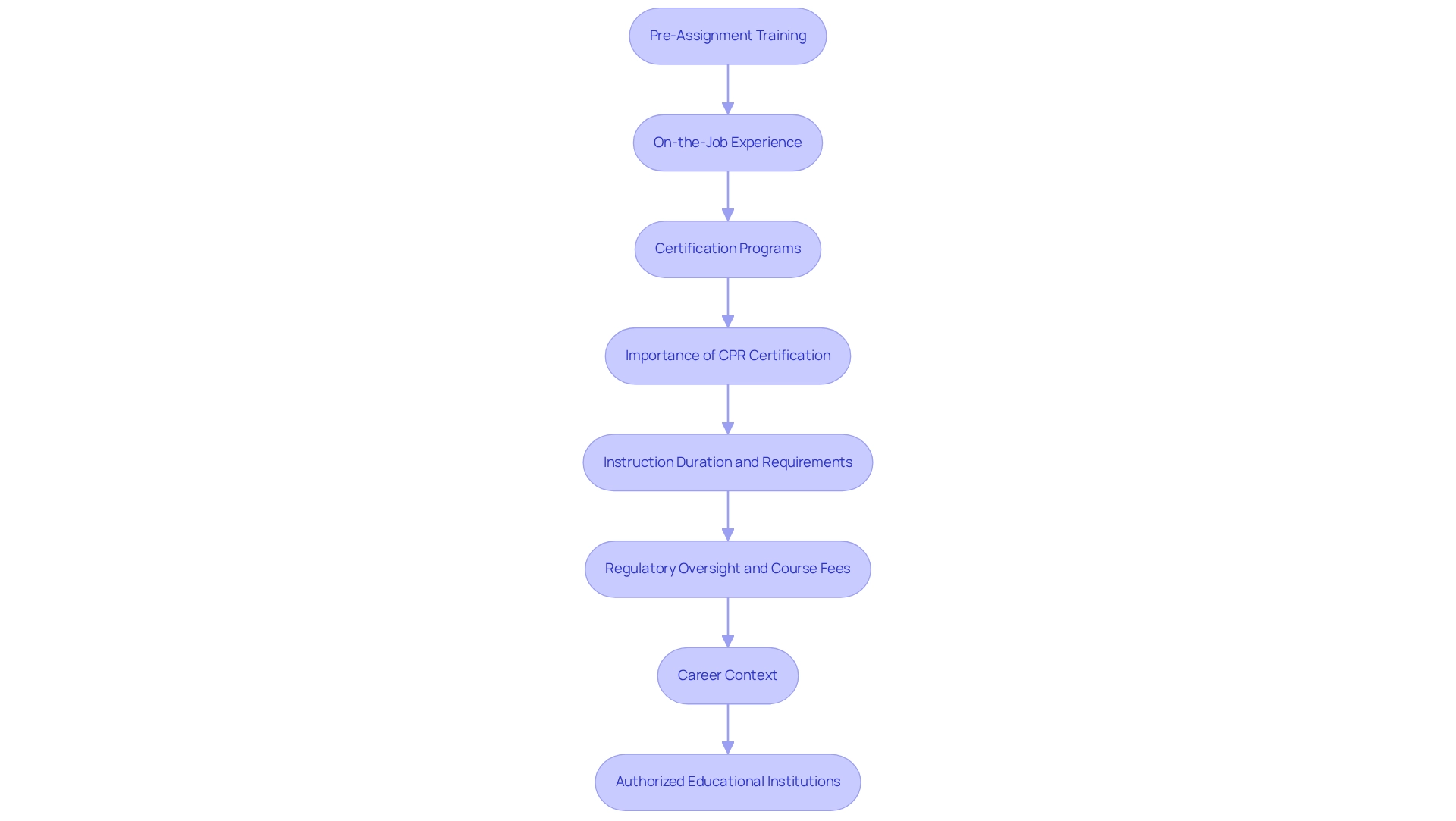
Aspiring protectors must navigate a structured pathway of instruction and certification to qualify for their roles effectively. This process encompasses several important elements:
-
Pre-Assignment Training: This foundational course familiarizes candidates with essential safety concepts, legal responsibilities, and emergency procedures. It serves as a crucial first step in equipping individuals for the challenges they will encounter in the field.
-
On-the-Job Experience: Following initial instruction, many states require further on-the-job experience. This phase highlights location-specific protocols and procedures, ensuring that personnel are knowledgeable about the distinct safety requirements of their designated areas. Statistics indicate that a substantial percentage of personnel complete this pre-assignment preparation, underscoring its significance in the overall development framework.
-
Certification Programs: Depending on their specific roles, personnel may be required to obtain certifications in areas such as CPR, first aid, and the appropriate use of force. These certifications not only enhance a guard's qualifications but also improve their career prospects in a competitive job market. Ongoing education and specialized development programs are increasingly acknowledged as essential for career progression in the protection domain.
-
Importance of CPR Certification: CPR certification is particularly crucial, as it provides personnel with life-saving skills that can be vital in emergency situations. This instruction is frequently a prerequisite for numerous safety roles, reflecting the sector's commitment to safety and readiness.
-
Instruction Duration and Requirements: The length and intensity of instruction can vary significantly. For instance, while patrol personnel may finish their preparation in a matter of weeks, positions like gambling surveillance officers often necessitate several months of extensive instruction centered on emergency protocols and crime prevention tactics. This variance emphasizes the diverse nature of protective roles and the customized instruction needed to fulfill specific job requirements.
-
Regulatory Oversight and Course Fees: It's important to note that protection personnel education institutions set their own charges for the programs they provide, with no regulatory supervision for these costs. This absence of oversight can influence the availability and cost-effectiveness of educational programs for individuals aiming to become protectors.
-
Career Context: According to CareerOneStop, profiles and salary details for jobs related to protectors can offer important context for those contemplating a profession in this area. Understanding the broader scope of jobs related to safety can assist candidates in making informed choices about their education and career trajectories.
-
Authorized Educational Institutions: The New York State Division of Criminal Justice Services maintains a list of recognized safety personnel educational institutions that can be accessed online. This resource is crucial for applicants pursuing respected training programs that comply with regional standards.
By comprehending these training criteria and the significance of certification, aspiring protectors can better equip themselves for successful careers in the protection field.
Maintaining Your Security Guard License: Renewal and Continuing Education
Maintaining a security personnel license involves several ongoing responsibilities that are vital for compliance and professional development.
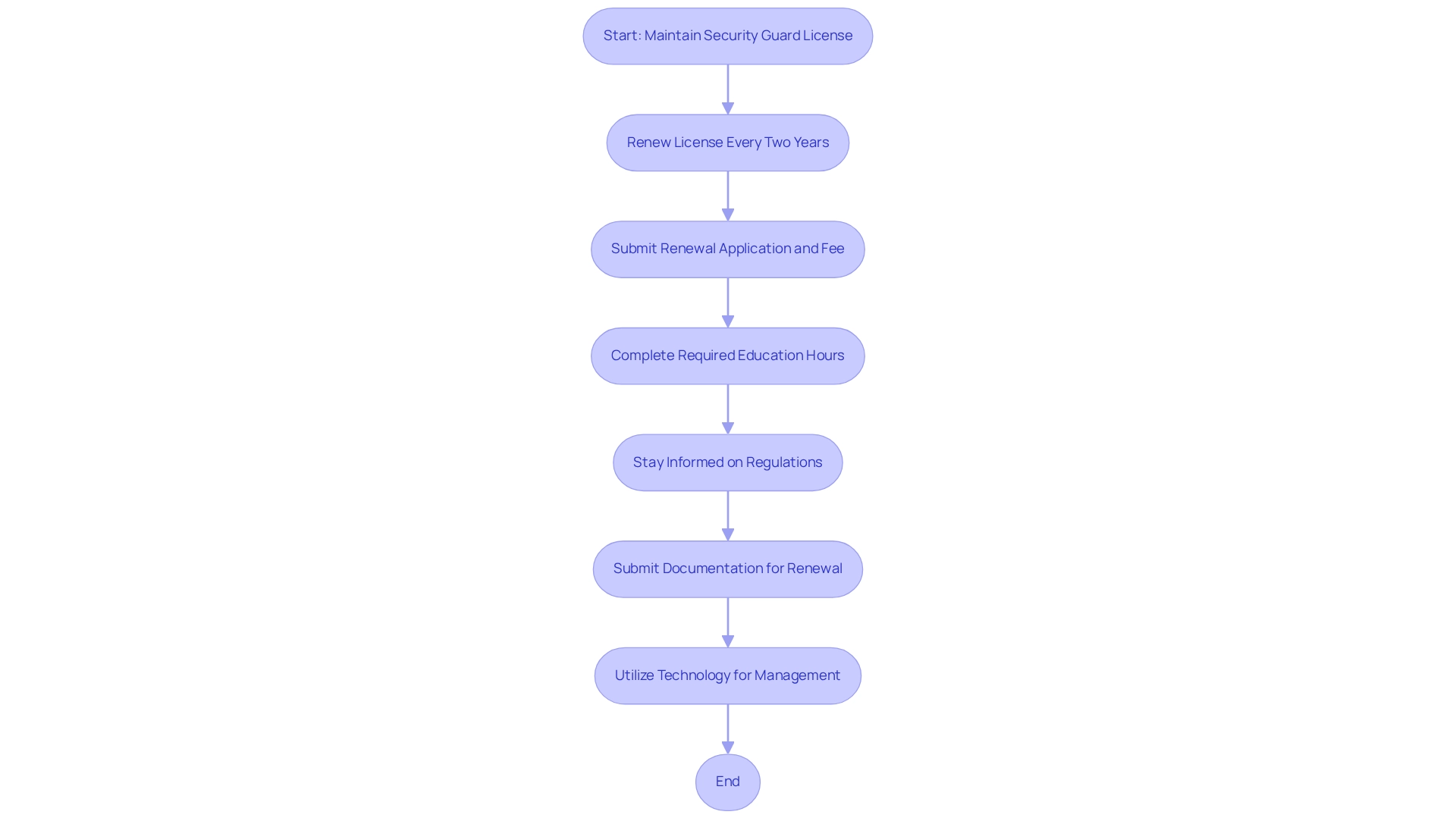
License Renewal: In most regions, security personnel must renew their licenses every two years. This renewal process typically requires submitting a renewal application along with a fee, which may vary by region. For instance, some areas may require up to 30 additional hours of firearm instruction for Class G personnel. This requirement underscores the importance of continuous education, ensuring security personnel are well-equipped to handle their roles and respond effectively in various situations.
Ongoing Education: Many regions mandate that security personnel complete a specific number of instructional hours or courses to remain informed about best practices and legal changes. For example, Minnesota offers both unarmed and armed permits, necessitating 12 hours of pre-assignment instruction. This requirement ensures that guards possess the most up-to-date knowledge and skills essential for their positions, highlighting the diverse educational prerequisites across states that can impact a guard's career trajectory.
Staying Informed: It is imperative for guards to regularly review updates in state regulations and educational standards to maintain compliance. Participating in additional training not only improves job performance but also prepares individuals for advancement opportunities. Programs focusing on risk assessment and threat response, as illustrated in case studies of professionals in the field, emphasize the importance of tactical knowledge and physical skills. These experts are trained to conduct risk evaluations and respond to threats, showcasing the practical application of their training.
Average Renewal Rates: Gaining an understanding of the average renewal rates for license holders by region can provide valuable insights into industry standards and expectations. This information assists security personnel in organizing their preparation and renewal schedules effectively, ensuring compliance with local regulations.
How to Renew a Security Personnel License: The renewal process generally involves submitting the necessary documentation and proof of completed continuing education courses. Guards should familiarize themselves with their state's specific procedures to facilitate a smooth renewal experience.
Utilizing Technology: Platforms such as Belfry's management system can streamline operations and ensure compliance with state-specific licensing requirements through automated scheduling, time tracking, client communication, and development management. This technology enables guards to manage their training and renewal processes more efficiently.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, security guards can effectively maintain their licenses while contributing to a safer environment through enhanced skills and knowledge.
Conclusion
Aspiring security guards embark on a multifaceted journey characterized by essential eligibility criteria, a structured application process, rigorous training, and ongoing education. Understanding the age, citizenship, and educational requirements is vital for candidates to ensure they meet the necessary standards for this critical role. The significance of background checks and character verification cannot be overstated, as they play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of the security profession.
Equally important is the application process, which requires candidates to:
- Complete state-approved training
- Submit applications
- Pass comprehensive background checks
This process can vary by state, underscoring the necessity for candidates to familiarize themselves with local regulations to navigate it successfully. Furthermore, the role of training—including pre-assignment and on-the-job training—as well as the requirement for certifications in areas such as CPR, significantly enhances a guard's readiness for emergencies.
Maintaining a security guard license demands a commitment to continuous education and renewal, ensuring that guards remain compliant and well-prepared for the evolving demands of their roles. By adhering to state requirements for license renewal and engaging in ongoing training, security personnel not only enhance their skills but also contribute to a safer environment.
In conclusion, the path to becoming a security guard is fraught with challenges; however, with the right knowledge and dedication, candidates can excel in this vital profession. Emphasizing preparation, compliance, and continuous improvement will benefit individuals in their careers and strengthen the overall security landscape.

