Overview
Titration serves as a quantitative analytical technique that is indispensable in the pharmacy sector for accurately determining the concentration of substances in solutions. This precision is vital for ensuring correct medication dosages and formulations. The article underscores the critical role of titration in quality control and regulatory compliance, detailing how various methods—including acid-base and redox analysis—are systematically employed to uphold the integrity and safety of pharmaceutical products.
Introduction
Titration serves as a cornerstone in the realm of pharmacy, representing a precise method for determining the concentration of substances within solutions. This analytical technique not only guarantees the accuracy of medications but also plays a vital role in quality control, thereby safeguarding patient safety and therapeutic efficacy. The complexities inherent in titration prompt a critical inquiry: how do pharmacists adeptly navigate this intricate process to uphold the integrity of drug formulations in an ever-evolving industry?
Define Titration in Pharmacy
The titrate definition in pharmacy describes a quantitative analytical technique that is essential for determining the concentration of specific substances in solutions. This process entails the meticulous addition of a titrant—a solution with a known concentration—to a sample containing the analyte until the reaction reaches its endpoint, marked by a measurable change. Such a method is critical for ensuring the accuracy and efficacy of medications, as understood in the titrate definition pharmacy, empowering pharmacists to adjust dosages and formulations based on precise measurements.
The titrate definition pharmacy highlights the paramount importance of titration in drug analysis. It plays a pivotal role in quality control, ensuring that active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) comply with stringent regulatory standards. As experts assert, 'Titration, according to the titrate definition pharmacy, plays an important role in pharmaceutical analysis,' underscoring its necessity in preserving the integrity of drug formulations.
Real-world applications of this analytical technique are extensive. For instance, potentiometric analysis is frequently utilized to evaluate APIs and excipients, providing rapid feedback for content uniformity testing. This technique proves particularly effective for substances like benzbromaron, where content can be determined in as little as eight minutes, closely aligning with the manufacturer's specifications. Such efficiency is vital in drug manufacturing, where timely results are crucial for quality assurance.
Moreover, the process aligns with the FDA's Quality by Design (QbD) initiative, emphasizing the comprehensive characterization of medicinal products and processes. By delivering both swift in-process feedback and precise quality control, the titrate definition pharmacy is a cornerstone of drug analysis, ensuring that every tablet, vial, or tube contains the correct active substance content as indicated on the packaging. This unwavering commitment to precision not only enhances patient safety but also fosters trust in medical products, bolstered by innovative solutions from JM Science Inc., which include premium titrators, HPLC columns, and Karl Fischer reagents.
Contextualize Titration's Role in Pharmaceutical Applications
The titrate definition pharmacy highlights the importance of titration in pharmaceutical applications, particularly for drug formulation and quality control. This analytical technique is vital for determining the concentration of active ingredients in medications, as described in the titrate definition pharmacy, ensuring that each dose delivers the correct amount of the active substance.
For instance, a method is routinely employed in the analysis of antibiotics to confirm their strength and purity, which is crucial for patient safety and therapeutic effectiveness. Furthermore, volumetric analysis techniques are indispensable in the development of new medications, where precise measurements are critical for achieving the intended therapeutic outcomes while minimizing potential side effects.
Experts in the field emphasize that accurate measurement, as outlined in the titrate definition pharmacy, not only enhances drug formulation precision but also plays a significant role in ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, ultimately contributing to the overall quality of pharmaceutical products. The impact of this process on drug formulation precision cannot be overstated, as it directly influences the efficacy and safety of medications.
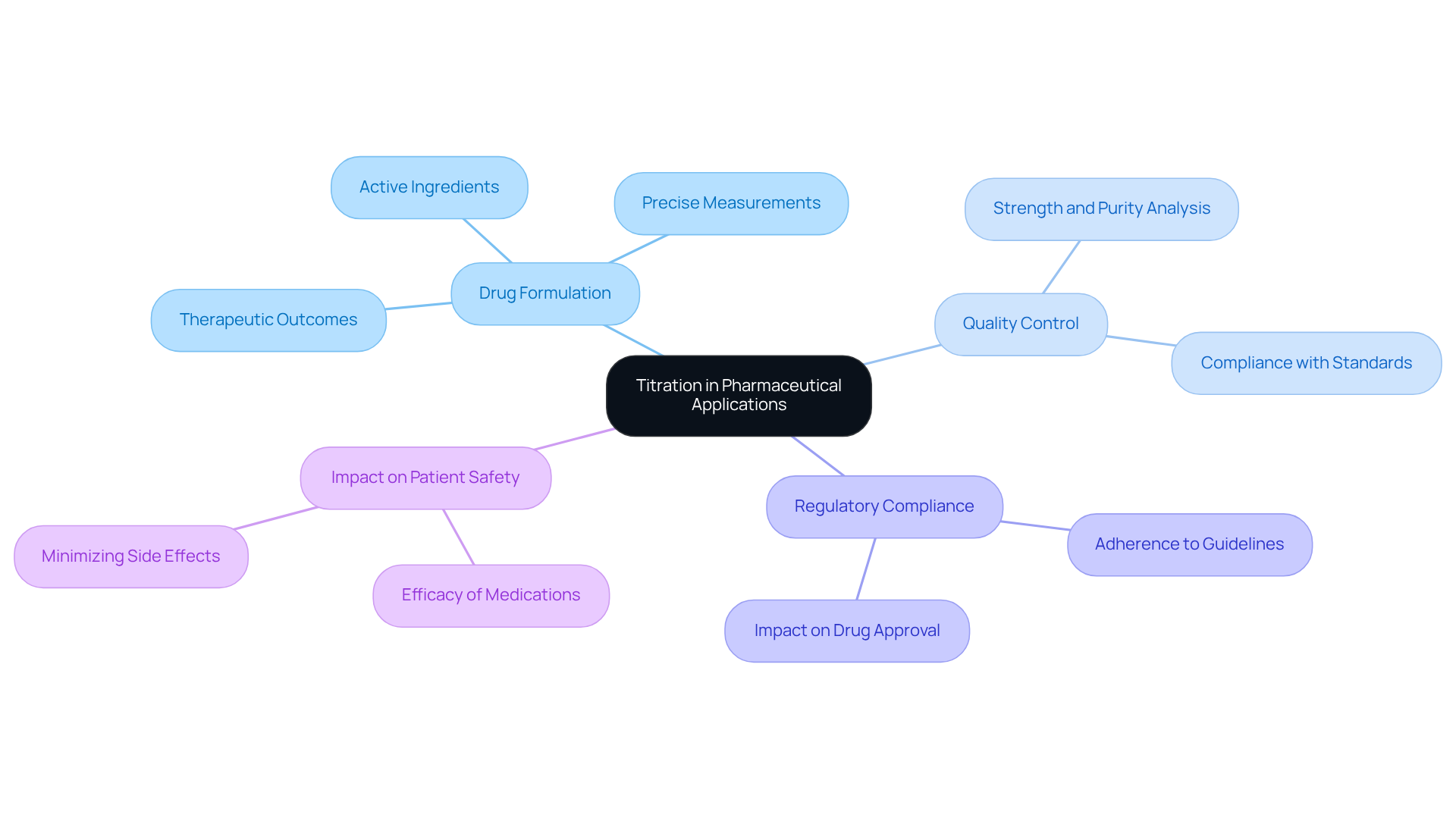
Trace the Historical Development of Titration Techniques
The origins of this analytical technique can be traced back to the late 18th century, significantly marked by the contributions of chemists such as François Antoine Henri Descroizilles, who invented the first burette in 1791. Initially, measurement techniques were straightforward, primarily relying on visual indicators to ascertain endpoints. However, as analytical chemistry progressed, more sophisticated methods emerged. Notably, potentiometric analysis, which employs electronic sensors, enhances accuracy in measurements. JM Science Inc. plays a pivotal role in this evolution by offering premium titrators and HPLC solutions that support contemporary measurement techniques.
Titration encompasses four main types:
- Acid-base
- Redox
- Precipitation
- Complexometric
Each serving distinct purposes within analytical processes. These advancements have solidified the titrate definition pharmacy as a fundamental technique in pharmaceutical analysis, enabling precise measurements that are crucial for ensuring drug safety and efficacy. The development of quantitative analysis techniques reflects a broader narrative of innovation in analytical chemistry, underscoring the discipline's unwavering commitment to enhancing measurement accuracy and reliability.
Identify Key Characteristics and Types of Titration Methods
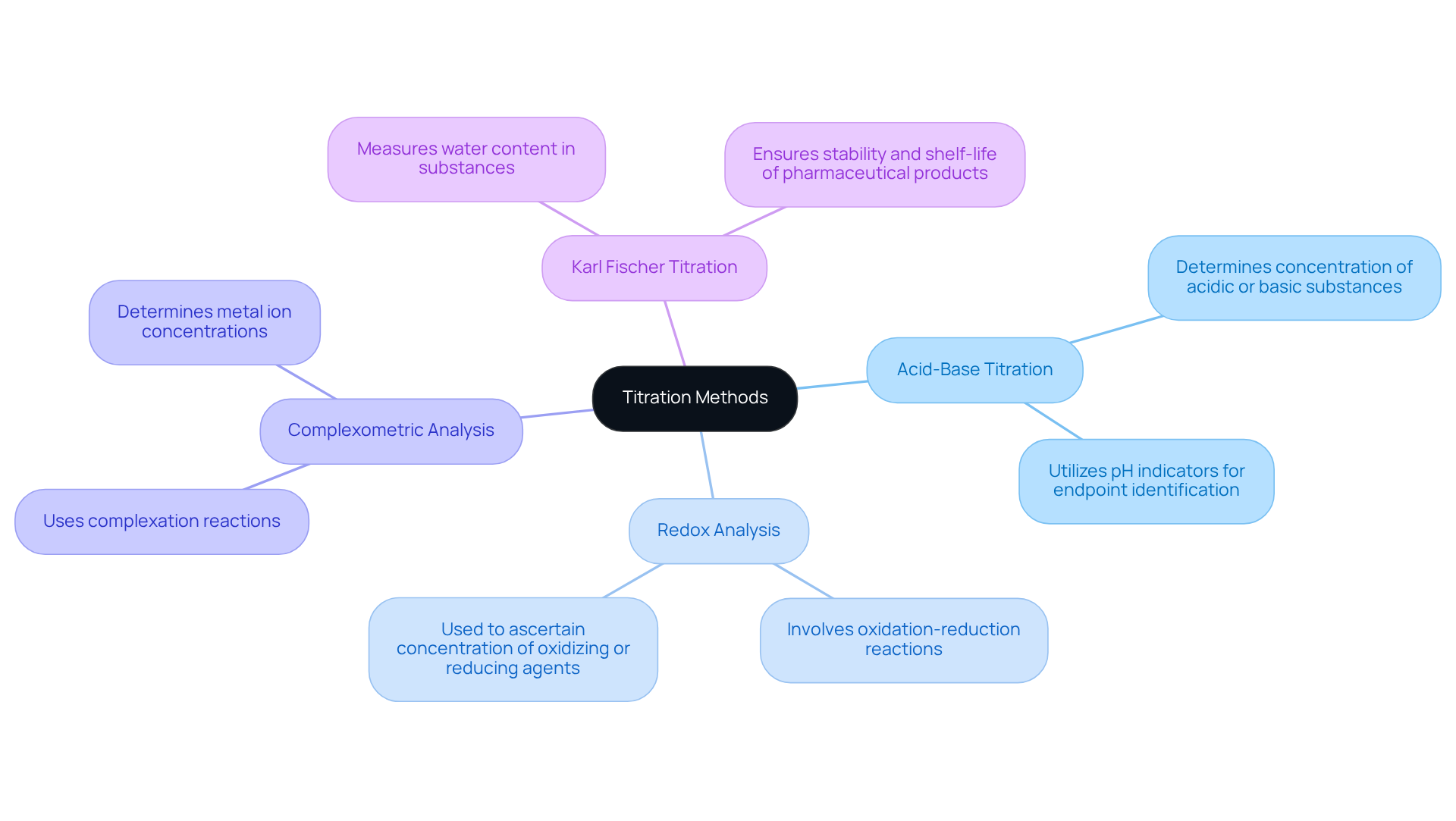
The essential features of volumetric analysis hinge on the use of a titrant with a known concentration, a clearly defined endpoint, and the ability to measure the volume of titrant used. In pharmacy, various titration methods are employed, each serving distinct purposes:
- Acid-Base Titration: This method is pivotal for determining the concentration of acidic or basic substances in a solution, frequently utilizing pH indicators to identify the endpoint effectively.
- Redox Analysis: This technique involves oxidation-reduction reactions, where the titrant and analyte engage in electron transfer. It is commonly employed to ascertain the concentration of oxidizing or reducing agents.
- Complexometric Analysis: This method uses complexation reactions to determine metal ion concentrations, which is essential for analyzing drugs containing metal components.
- Karl Fischer Titration: A specialized technique designed for measuring water content in substances, this method is crucial for ensuring the stability and shelf-life of pharmaceutical products.
Each of these methods has unique applications and is selected based on the specific requirements of the analysis, which includes the titrate definition pharmacy.
Conclusion
Titration stands as a cornerstone analytical technique in pharmacy, essential for the precise determination of substance concentrations in various solutions. By carefully adding a titrant to a sample until a definitive endpoint is achieved, pharmacists can guarantee that medications are formulated with accurate dosages, thereby bolstering patient safety and therapeutic effectiveness. This meticulous process not only underscores the critical nature of precision in drug formulation but also highlights broader implications for regulatory compliance and quality control within the pharmaceutical industry.
This article has explored the multifaceted role of titration, tracing its historical development and examining its application in contemporary pharmaceutical practices. Key insights reveal its indispensable contribution to quality assurance, the diverse titration methods employed, and the technological advancements that have improved measurement accuracy. The incorporation of titration into initiatives such as the FDA's Quality by Design further underscores its importance in ensuring that all medications adhere to stringent safety and efficacy standards.
Ultimately, grasping the significance of titration in pharmacy is vital for anyone engaged in drug formulation and analysis. As the industry progresses, adopting innovative titration techniques and technologies will be imperative for upholding high standards of quality and safety in pharmaceuticals. The unwavering commitment to precision in titration not only cultivates trust in medical products but also plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health.




