Overview
Free fatty acids (FFAs) are liberated lipid molecules that play crucial roles in energy metabolism, cell signaling, and maintaining cellular structure, originating from the hydrolysis of triglycerides. Their significance in health cannot be overstated, particularly regarding their influence on metabolic conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Additionally, FFAs have noteworthy applications in pharmaceuticals and nutrition, establishing their importance not only in biological processes but also in industrial advancements. Understanding the multifaceted roles of FFAs is essential for appreciating their impact on health and industry.
Introduction
Free fatty acids (FFAs) are not merely components of dietary fats; they are pivotal players in the complex network of biological processes. These liberated lipids, originating from the breakdown of triglycerides, are vital for energy metabolism, cell signaling, and overall metabolic health. As research reveals their substantial impact on conditions such as obesity and diabetes, one must consider: how do these seemingly simple molecules unlock insights into intricate health challenges and foster advancements in therapeutic innovations? Delving into the definition, significance, and applications of free fatty acids uncovers a compelling intersection of nutrition, health, and science that merits thorough exploration.
Define Free Fatty Acid: A Comprehensive Overview
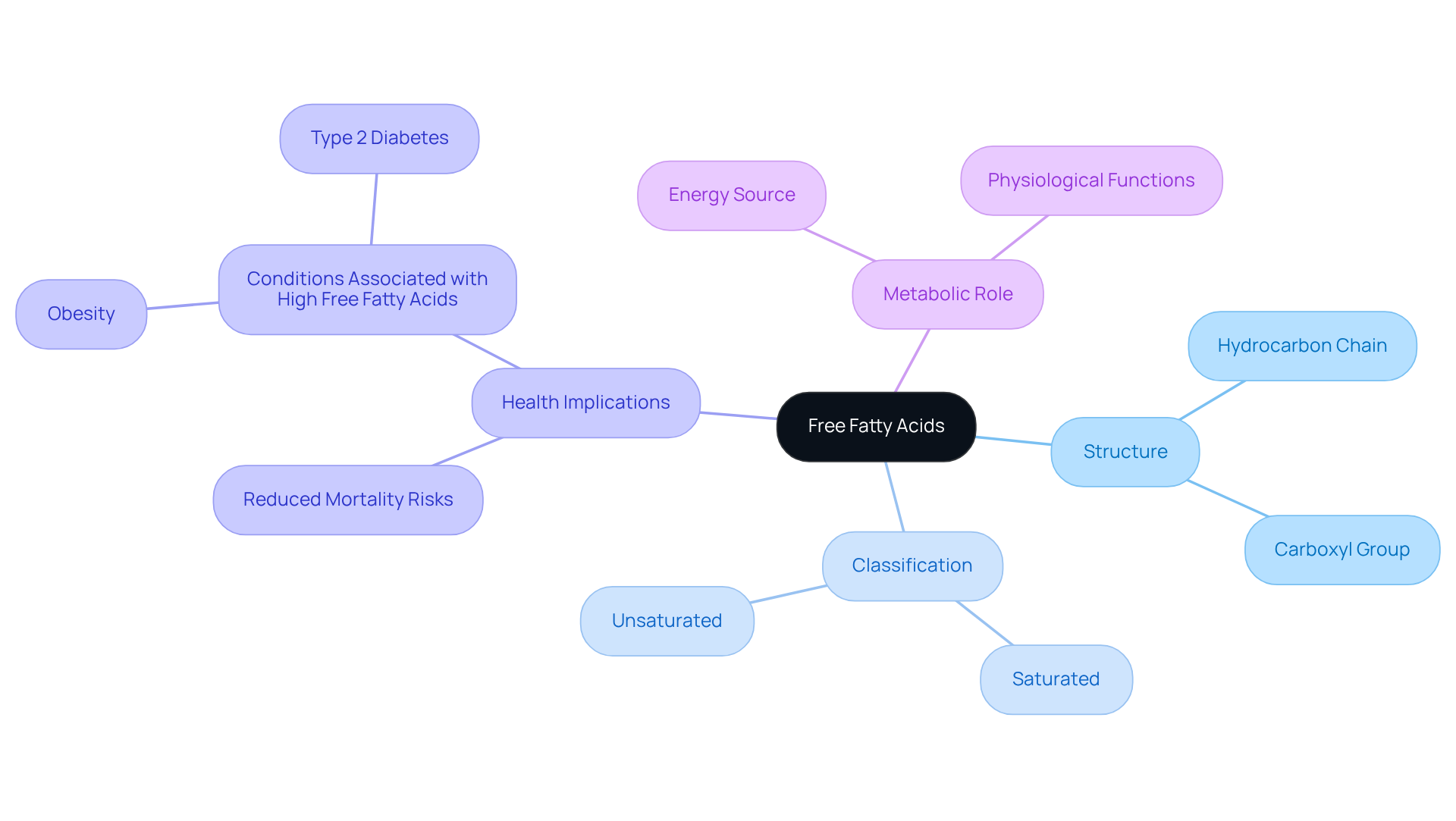
Free lipids represent distinct lipid molecules that exist in a liberated form, unbound to glycerol. They originate from the hydrolysis of triglycerides, the primary components of fats and oils. Structurally, fatty acids consist of a hydrocarbon chain capped with a carboxyl group (-COOH) at one end. The variation in the length of this hydrocarbon chain gives rise to different categories of lipids, which are classified as saturated or unsaturated.
Recent studies identified a total of 30 distinct free lipids, comprising 19 unsaturated and 11 saturated varieties. Fatty acids play a crucial role in metabolism, acting as a major energy source for cells and fulfilling vital functions in various physiological processes. Notably, recent research underscores the significance of specific fatty acids in influencing health outcomes, with certain unsaturated fatty acids linked to reduced mortality risks.
For example, achieving optimal concentrations of what is free fatty acid may decrease the risk of all-cause mortality; however, this benefit was not observed concerning cardiovascular mortality, as noted by Meng Li. Furthermore, substantial increases in free fatty acids, or what is free fatty acid, are frequently observed in conditions such as obesity and type 2 diabetes, underscoring their importance in metabolic health. Understanding the structure and function of fatty acids is essential for advancing research in nutrition and health.
Explore the Importance of Free Fatty Acids in Science
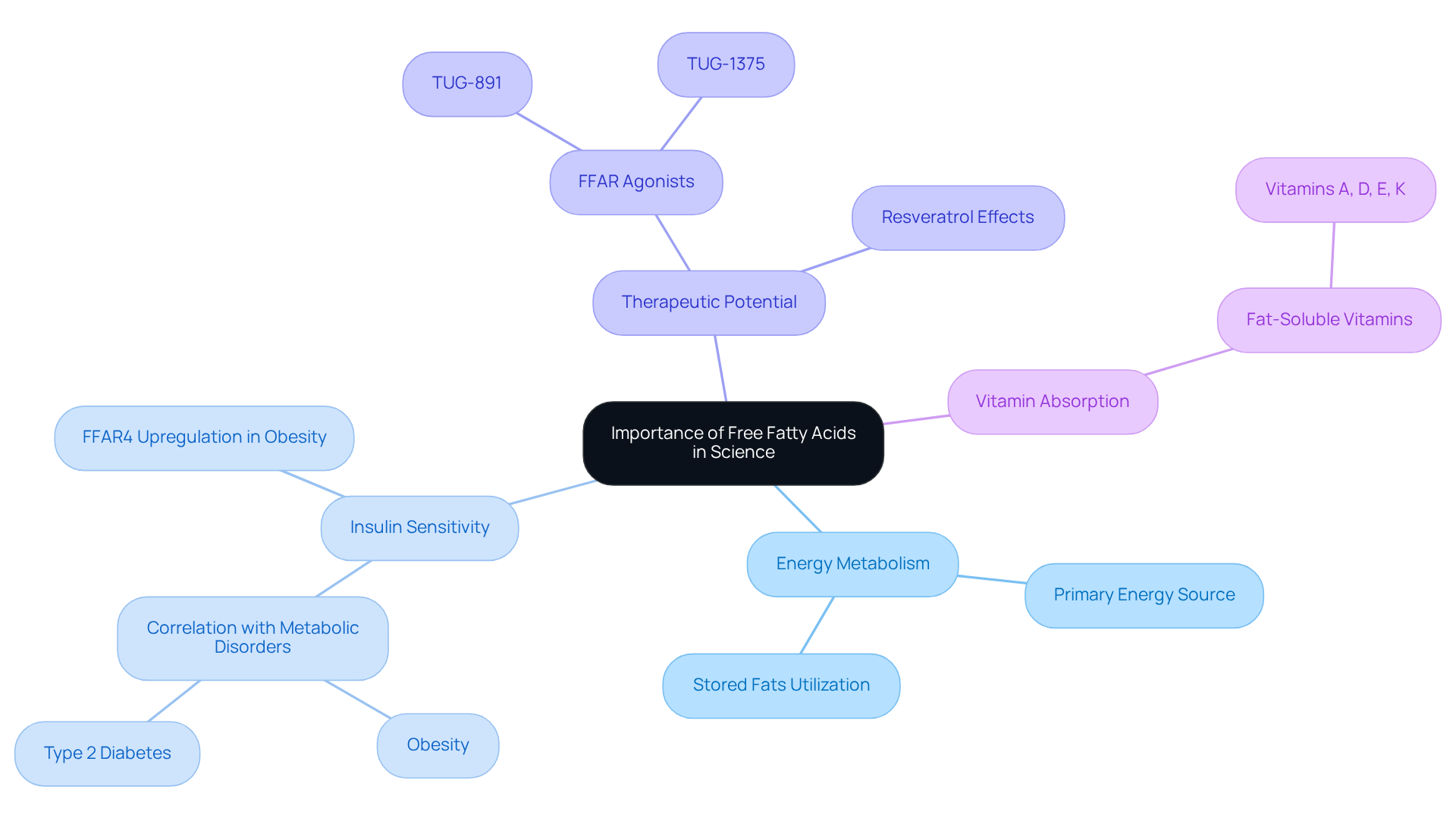
What is free fatty acid is its pivotal role in various biological processes, including energy metabolism, cell signaling, and the structural integrity of cellular components. What is free fatty acid serves as a primary energy source that is especially crucial during fasting or vigorous exercise, when the body utilizes stored fats for energy. Recent studies have highlighted what is free fatty acid and its significant influence on insulin sensitivity, with elevated levels in the bloodstream often correlating with metabolic disorders such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. For instance, research indicates that FFAR4, a receptor activated by fatty acids, is markedly upregulated in the adipose tissue of obese individuals compared to lean subjects, establishing a direct connection between fatty acids and insulin resistance.
Moreover, case studies demonstrate that specific FFAR agonists, such as TUG-891—the first extensively studied synthetic agonist for FFAR4—can enhance glucose uptake and improve insulin signaling, showcasing their therapeutic potential in managing metabolic conditions. Furthermore, free fatty acids are involved in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, and they can activate specific cell surface receptors like G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), influencing various physiological processes. Fatty acids are transported in the bloodstream attached to carrier proteins, primarily albumin, aiding their metabolism and function in the body.
Understanding what is free fatty acid and its complex connection to energy metabolism underscores their significance in health sciences, establishing them as a vital area of focus for ongoing research and therapeutic advancement.
Examine Applications of Free Fatty Acids in Research and Industry
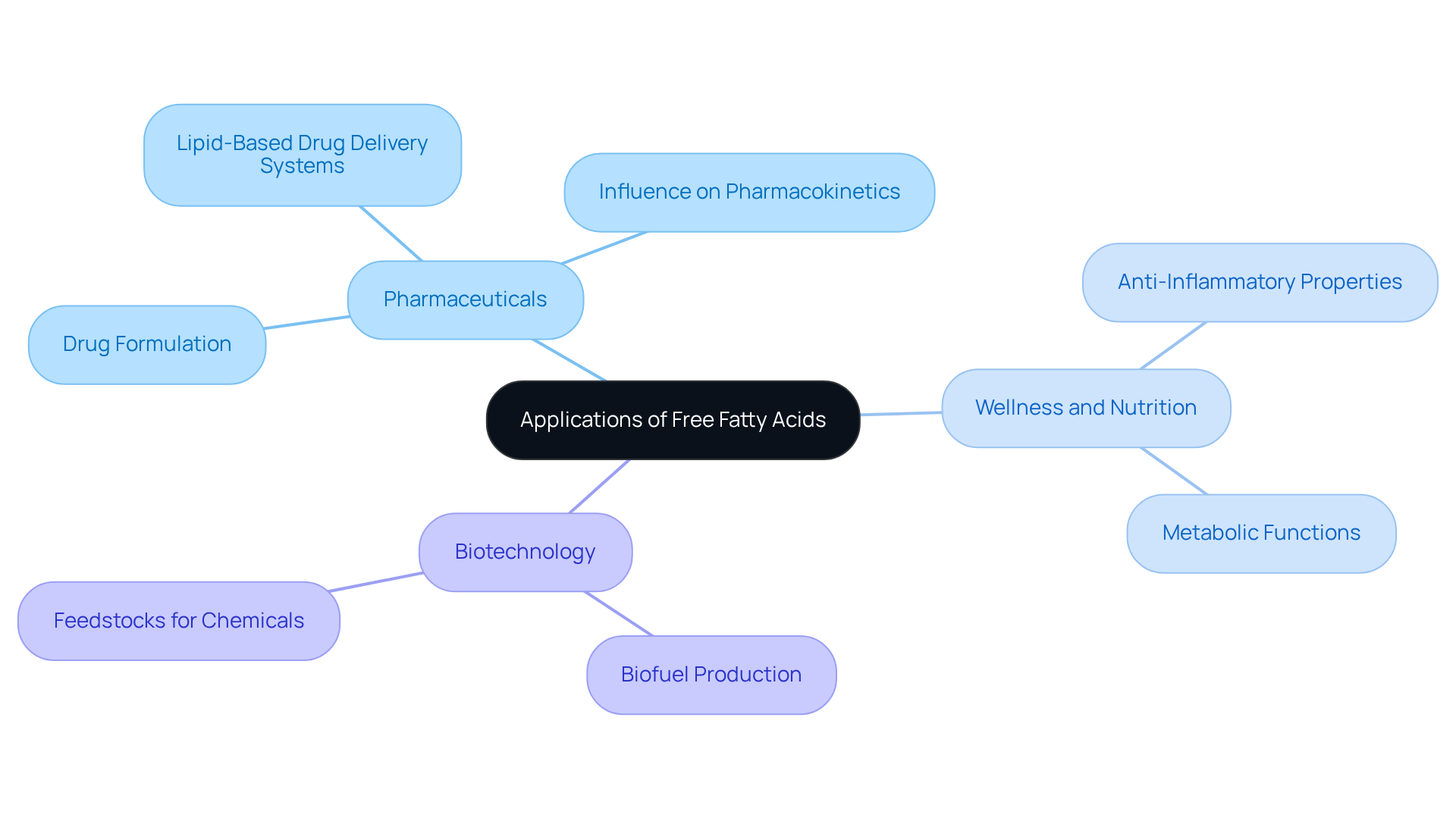
What is free fatty acid, and how do free fatty acids (FFAs) play a pivotal role across various sectors, particularly within pharmaceuticals, where they are essential to drug formulation and metabolism? Their importance is especially evident in lipid-based drug delivery systems, which significantly enhance the bioavailability of therapeutic agents. Recent studies underscore what is free fatty acid's ability to influence the pharmacokinetics of drugs, solidifying their status as critical components in the development of effective pharmaceutical formulations. For example, the maximum FFA level for crude palm oil (CPO) is established at 5%, a benchmark crucial for maintaining quality parameters such as peroxide value and bleachability index. Additionally, expert opinions underscore the potential of fatty acid esters in modulating drug release profiles, thereby improving therapeutic outcomes.
Ongoing research continues to unveil the diverse applications of fatty acids in wellness and nutrition. For instance, what is free fatty acid is currently under investigation for its anti-inflammatory properties and its roles in metabolic functions, potentially leading to groundbreaking therapies for various health issues. Moreover, free fatty acids are increasingly recognized in the biotechnology sector, where they serve as feedstocks for the production of biofuels and other chemicals, showcasing their versatility beyond traditional applications. The research highlights that the accumulation of free fatty acids in fresh fruit bunches is influenced by pre- and post-harvesting factors, emphasizing the need for prompt processing to preserve oil quality.
As our understanding of FFAs evolves, their implications for pharmaceutical development and industrial applications are becoming more pronounced. This progression paves the way for advancements that could significantly impact health and wellness.
Conclusion
Free fatty acids (FFAs) are fundamental components of biological systems, playing a critical role in various physiological processes and impacting overall health. Their significance extends beyond mere energy sources; they are integral to metabolism, cell signaling, and the structural integrity of cellular components. Understanding the nuances of FFAs is essential for grasping their implications in health, nutrition, and disease management.
This article has delved into the definition and importance of free fatty acids, highlighting their classification into saturated and unsaturated types, and their pivotal roles in energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Research has shown that elevated levels of FFAs can be indicative of metabolic disorders, while specific fatty acids have been linked to positive health outcomes, including reduced mortality risks. Additionally, the article explored the applications of FFAs in pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, emphasizing their role in drug formulation and biofuel production.
The exploration of free fatty acids reveals their multifaceted impact on health and industry. As research continues to uncover their properties and functions, it is crucial to recognize the potential of FFAs not only in therapeutic advancements but also in enhancing nutrition and wellness. Engaging with this knowledge can inspire further inquiry and innovation, paving the way for improved health outcomes and sustainable practices in various sectors.




