Overview
Effective analyzer management in laboratories is crucial and can be achieved through four key practices:
- Selecting and implementing the right analyzers
- Maintaining and calibrating them regularly
- Training staff on their usage
These practices not only enhance operational efficiency but also ensure accurate testing results, thereby helping laboratories comply with regulatory standards. The systematic approach to analyzer management is essential for achieving high-quality outcomes in laboratory settings. By focusing on these critical practices, laboratories can significantly improve their overall performance and reliability.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of pharmaceutical laboratories, analyzers emerge as indispensable instruments, guaranteeing the precision and reliability of testing processes that are foundational to drug development. As these laboratories navigate the multifaceted landscape of regulatory compliance and quality assurance, it becomes essential to master the effective management of these tools. The challenge, however, extends beyond merely selecting the appropriate analyzers; it encompasses the ongoing maintenance of their performance and the training of staff to utilize them proficiently.
What key practices can transform analyzer management from a routine task into a strategic advantage for laboratories?
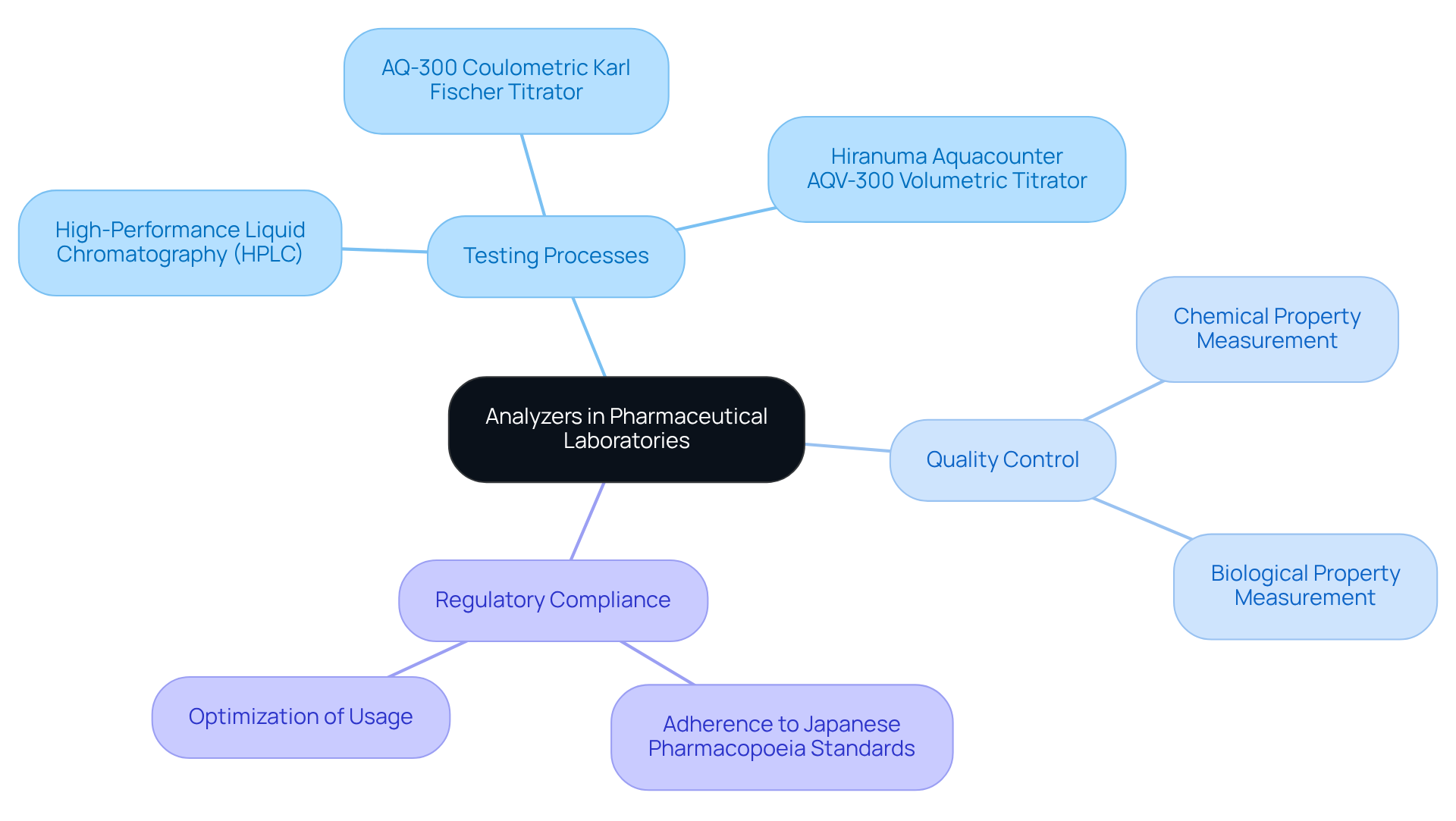
Understand the Role of Analyzers in Pharmaceutical Laboratories
The use of an analyser is pivotal in pharmaceutical laboratories, serving as the backbone for various testing and quality control processes. They facilitate the accurate measurement of chemical and biological properties, which is essential for drug development and regulatory compliance.
High-efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC) instruments, for instance, are commonly employed to separate, identify, and quantify components in a mixture, ensuring that pharmaceutical products conform to rigorous quality requirements.
Furthermore, the AQ-300 Coulometric Karl Fischer Titrator and play crucial roles in moisture content analysis of drugs and medicines, adhering to the stringent standards set by .
Understanding the distinct functions of various evaluators, including these titrators and analyzers, enables managers to optimize their usage, resulting in enhanced efficiency and dependability in operational processes.
Additionally, recognizing the significance of assessment tools in the context of regulatory requirements underscores the necessity for careful management and oversight in their operation.
Select and Implement Analyzers Effectively
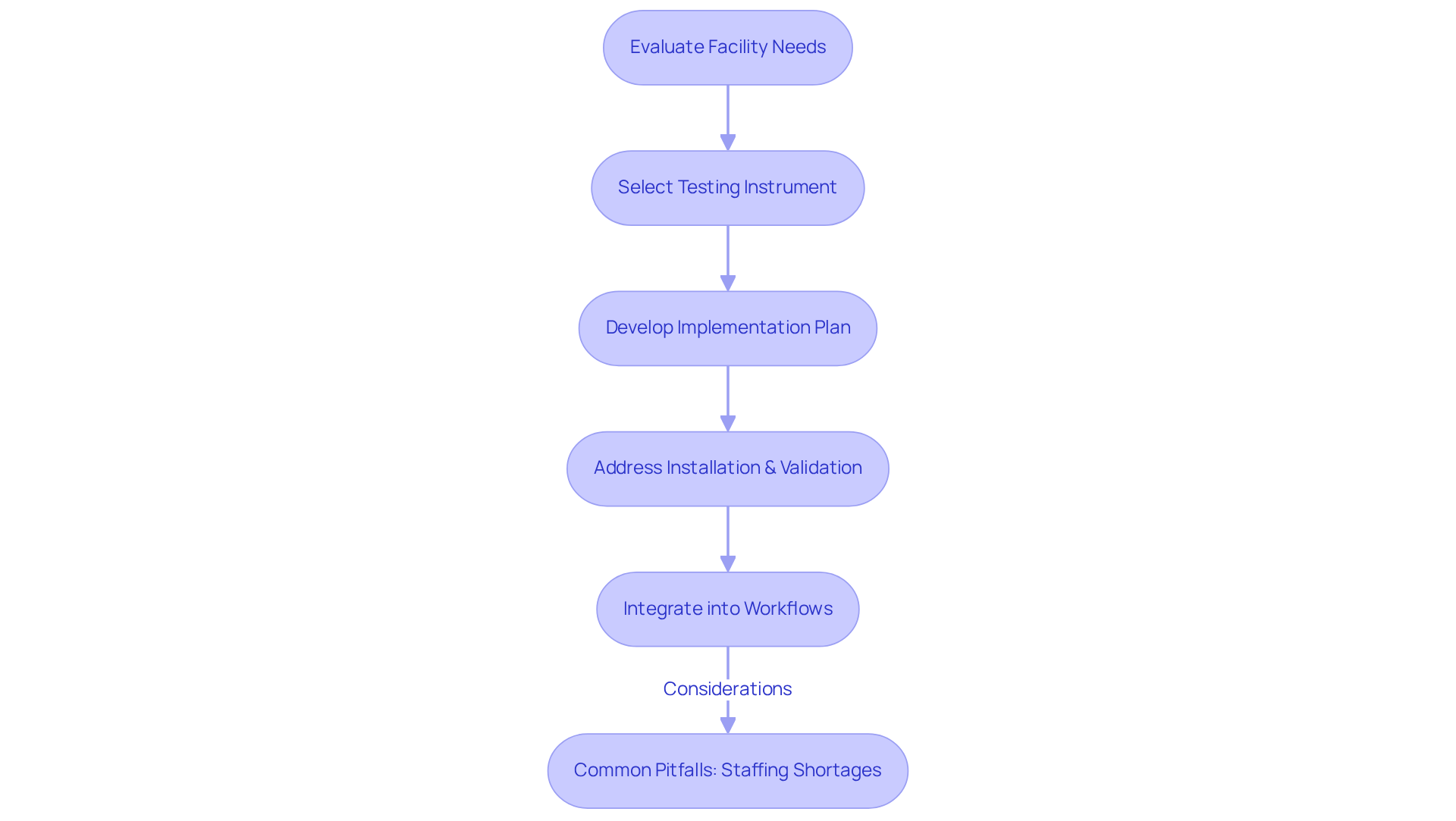
Choosing the appropriate testing instrument requires a comprehensive evaluation of the facility's specific needs, including the types of tests conducted, sample volume, and budget constraints. Engaging in the selection process is essential, as it ensures a variety of perspectives are considered, leading to more informed decisions.
For instance, high-capacity testing devices are vital for facilities that process over 200 tests each hour, significantly impacting operational efficiency. After selecting a testing tool, a thorough implementation plan must be developed, addressing installation, validation, and integration into existing workflows.
When introducing a new high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) system, it is imperative that facilities undertake a rigorous validation process to ensure the analyser meets both performance specifications and regulatory standards. This approach not only enhances the reliability of test results but also facilitates a smooth transition to new technologies, ultimately improving laboratory efficiency and effectiveness.
Furthermore, it is crucial to recognize common pitfalls, such as staffing shortages, which can hinder the implementation process.
Maintain and Calibrate Analyzers for Optimal Performance
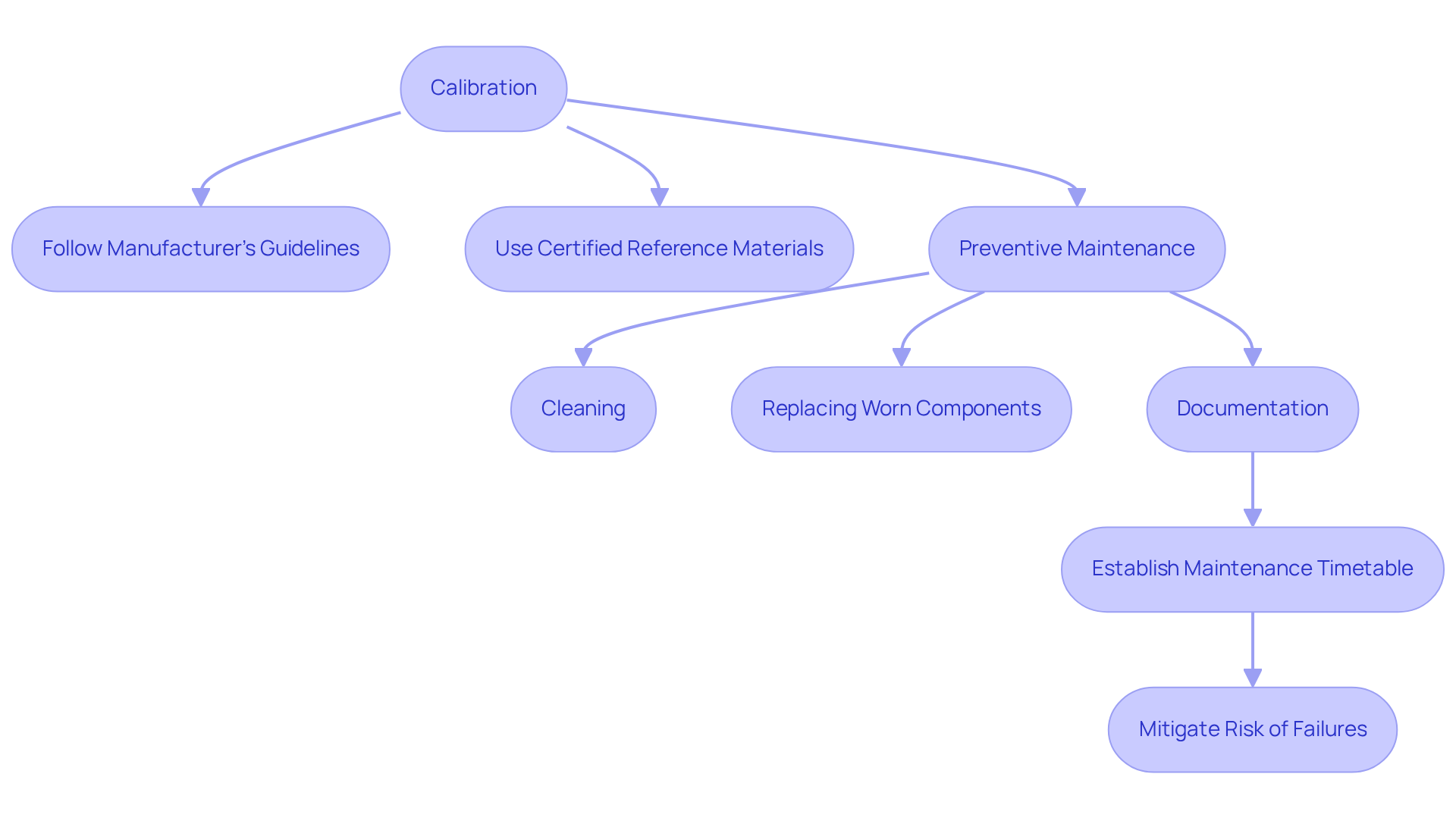
To maintain optimal performance, an analyzer necessitates regular calibration and preventive maintenance. Calibration must adhere to the manufacturer's guidelines and involve the use of certified reference materials, along with an analyser, to ensure accuracy. For instance, a research facility might schedule monthly calibrations for to verify that they produce precise results. Moreover, routine maintenance tasks, such as cleaning and replacing worn components, should be meticulously documented and executed consistently. Establishing a comprehensive maintenance timetable not only extends the lifespan of the equipment but also mitigates the risk of unforeseen failures that could disrupt operations.
Train Staff on Analyzer Usage and Best Practices
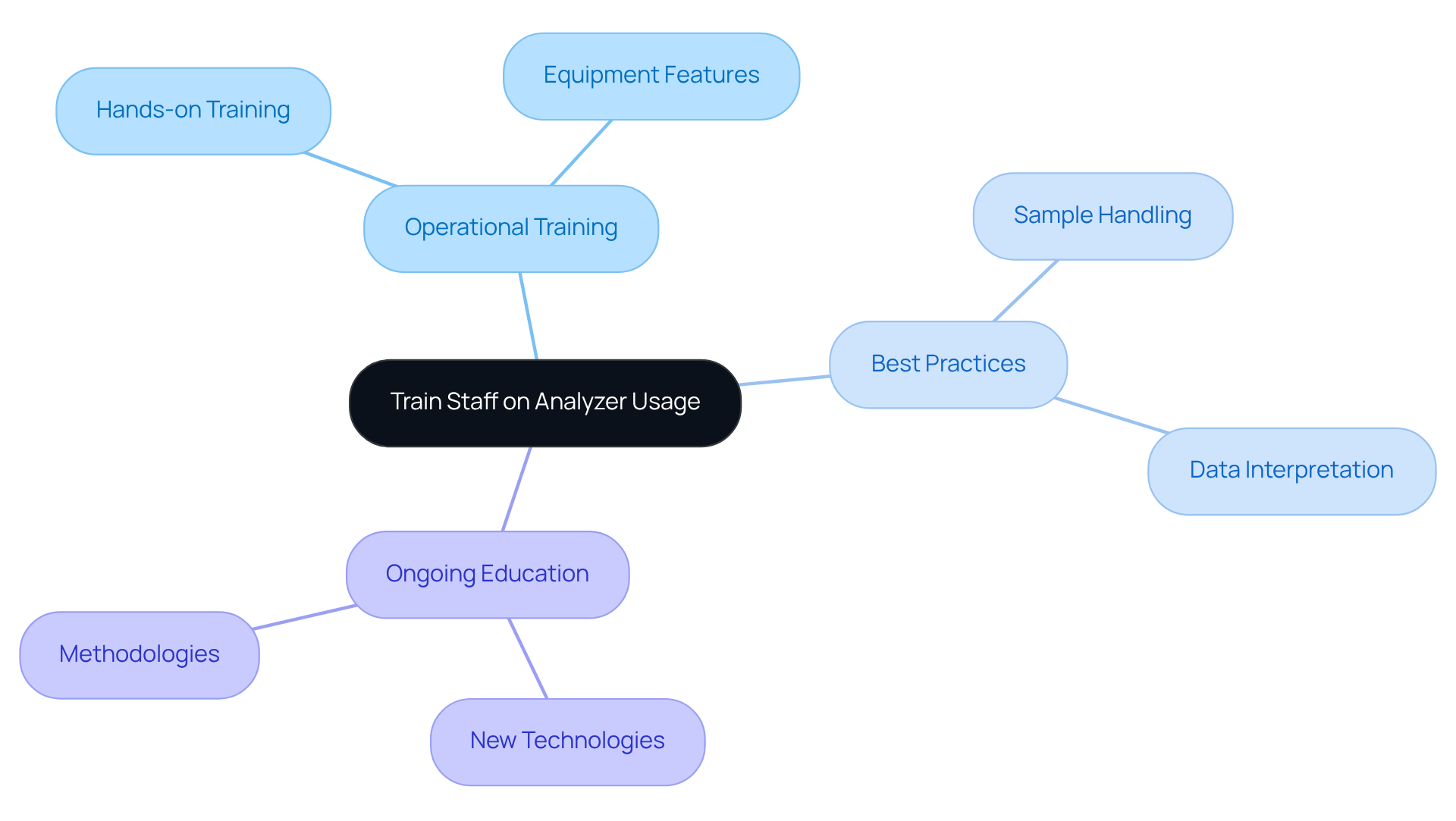
To ensure that all staff are proficient in using testing equipment, effective training programs must be established. These programs should encompass not only the operational aspects of the equipment but also best practices for .
For instance, conducting hands-on training sessions will familiarize staff with the specific features of the analysers they will be utilizing. Furthermore, encouraging ongoing education is essential to keep staff abreast of new technologies and methodologies.
By investing in staff training, laboratories can significantly enhance their operational efficiency and consistently meet high-quality standards.
Conclusion
Effective analyzer management in pharmaceutical laboratories is essential for upholding the integrity of testing and quality control processes. Understanding the pivotal role that analyzers play, selecting the appropriate instruments, ensuring their maintenance and calibration, and investing in staff training are critical steps that laboratories must take to enhance operational efficiency and comply with regulatory standards.
The article delineates four key practices:
- Recognizing the significance of analyzers
- Effectively selecting and implementing them
- Maintaining and calibrating for optimal performance
- Training staff on best practices
Each of these components plays a vital role in the overall functionality of laboratory operations, ensuring that tests are accurate, reliable, and adhere to necessary quality benchmarks.
In conclusion, effective analyzer management transcends mere procedural requirements; it represents a fundamental aspect of laboratory excellence. By prioritizing these best practices, laboratories can enhance their testing capabilities while fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Embracing these strategies will lead to increased productivity and quality assurance, ultimately benefitting the pharmaceutical development process and safeguarding patient safety.




