Overview
The article presents a comprehensive overview of the various types of titration, including:
- Acid-base titrations
- Redox titrations
- Precipitation titrations
- Complexometric titrations
These methods are not merely techniques; they are essential for achieving precise measurements in critical fields such as:
- Pharmaceuticals
- Food safety
- Environmental testing
Their critical role in ensuring product quality and regulatory compliance cannot be overstated. Understanding these titration methods is vital for professionals seeking to uphold standards in their respective industries.
Introduction
Titration serves as a cornerstone of quantitative analysis, playing a pivotal role in determining the concentration of various substances within solutions. This meticulous process not only enhances the accuracy of scientific research but also proves crucial across diverse industries, from pharmaceuticals to environmental monitoring. As the demand for precision and efficiency escalates, laboratories must adapt their titration techniques to address modern challenges. By exploring the various types of titration and their applications, we uncover not only the complexity of this analytical method but also its vital significance in ensuring safety and compliance across multiple fields.
Define Titration: Understanding the Basics
Titration represents a quantitative analytical method essential for determining the amount of a specific substance, known as the analyte, within a solution. This meticulous process involves the gradual addition of a titrant, a solution with a known strength, to the analyte until the reaction reaches completion, signaled by a measurable change such as a color shift or a specific pH level.
As a foundational technique across various scientific disciplines—including chemistry, biology, and environmental science—types of titration facilitate precise measurements of chemical concentrations, which are critical for both research and quality control.
In 2025, the significance of this technique in laboratory practices is underscored by its role in ensuring compliance with safety standards and enhancing the precision of analytical results. Current trends reveal a rising demand for automated measurement systems that minimize human error and boost efficiency, reflecting the dynamic evolution of laboratory techniques.
The real-world applications of various types of titration techniques are extensive, encompassing areas from pharmaceutical quality control to environmental monitoring, thereby demonstrating their integral role in upholding the integrity of scientific research and industrial processes.
Explore Types of Titration: Acid-Base, Redox, and More
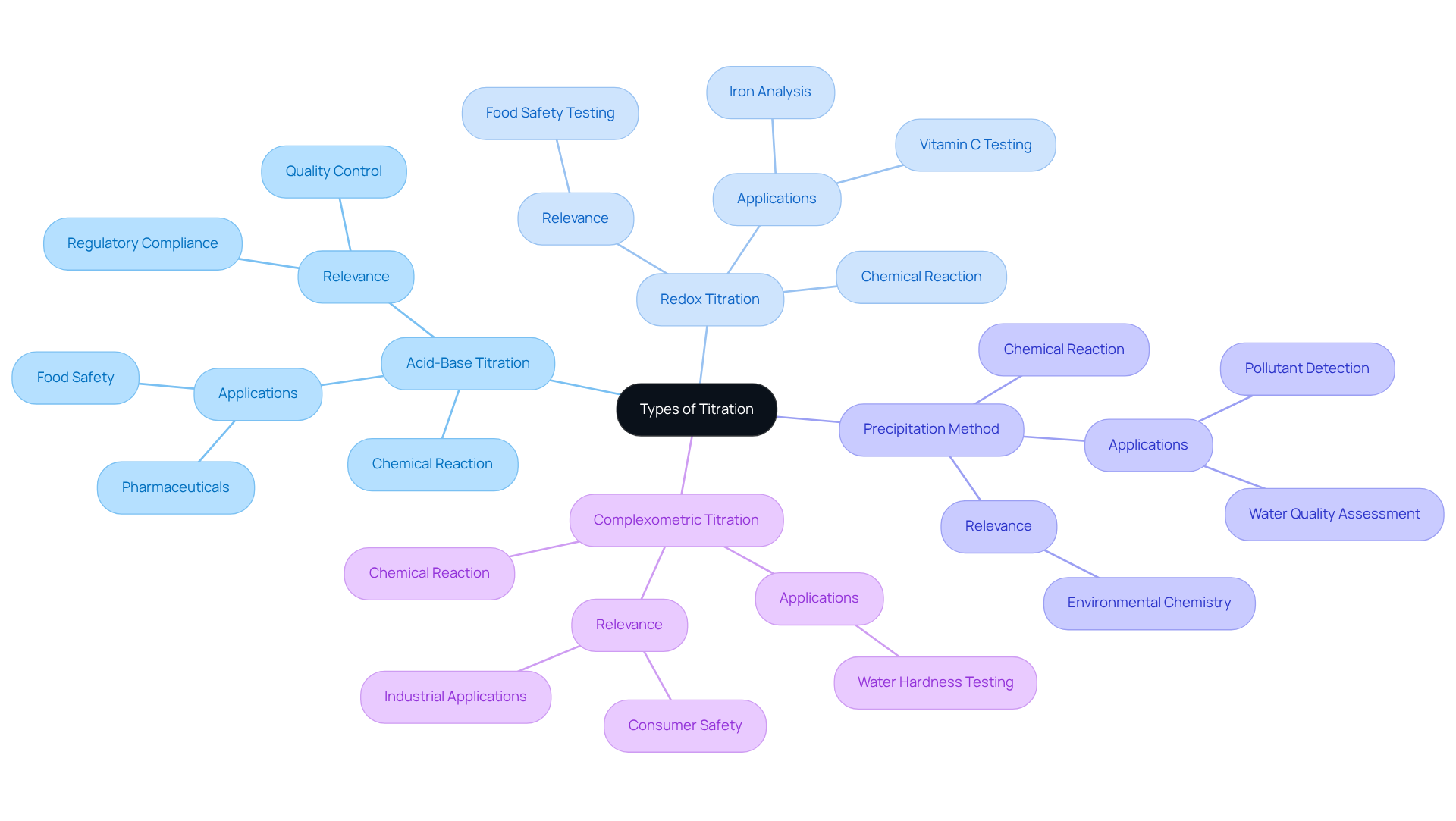
This analytical technique includes various types of titration, each characterized by the specific chemical reactions involved. The most prevalent types include:
- Acid-Base Titration: This method entails the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base, monitored through pH indicators or meters to accurately determine the endpoint. Acid-base titrations are critical in pharmaceuticals for ensuring the precise amount of active ingredients, as even slight variations can significantly impact patient safety and regulatory compliance. JM Science's premium titrators enhance quality control processes, ensuring accuracy in active ingredient concentrations.
- Redox Titration: This technique centers on oxidation-reduction reactions, where electron transfer is essential. Commonly employed to analyze substances such as iron and vitamin C, redox titrations are pivotal in food safety testing, ensuring that products meet quality standards and are free from harmful contaminants. JM's innovative solutions support these analyses, providing reliable results.
- Precipitation Method: This approach relies on the formation of a precipitate during the reaction, frequently utilized to ascertain levels of halides or sulfates. It is particularly important in environmental chemistry for evaluating water quality and identifying pollutants, further emphasizing the necessity for accurate instruments akin to those provided by JM.
- Complexometric Titration: Utilizing the formation of complex ions, this method determines the concentration of metal ions in a solution. It is commonly applied in water hardness testing, which is essential for both industrial applications and consumer safety. JM's advanced measurement technologies ensure precise readings in these crucial evaluations.
Each type of analysis, such as types of titration, possesses distinct procedures and applications, rendering them indispensable tools in both research and industry. As the pharmaceutical industry progresses, the integration of cutting-edge technologies and automation in measurement techniques, including JM's Karl Fischer reagents and HPLC solutions, is expected to enhance accuracy and effectiveness, further reinforcing their significance in quality assurance and analysis. Understanding the curves is vital for grasping the dynamics of these processes, thereby improving the overall comprehension of this essential analytical technique.
Detail Titration Procedures: Techniques and Best Practices
Conducting various types of titration involves several key steps to ensure accuracy, particularly when utilizing premium instruments from JM Science Inc. First, prepare by gathering all necessary equipment, including a burette, pipette, Erlenmeyer flask, and appropriate indicators. Consider using JM's high-quality titrators for precise measurements, as they play a crucial role in achieving reliable results.
Next, standardization is essential. Before starting, standardize the titrant to ensure its concentration is known accurately. This is frequently accomplished with a primary standard, which can be backed by JM's dependable reagents, ensuring the integrity of your results.
The setup phase follows. Fill the burette with the titrant and record the initial volume. Measure a specific volume of the analyte into the Erlenmeyer flask, ensuring that all equipment is calibrated for optimal performance. This attention to detail is vital for the successful execution of various types of titration.
During the different types of titration process, slowly add the titrant to the analyte while continuously swirling the flask. As the endpoint approaches, add the titrant dropwise to avoid overshooting. Utilizing JM's advanced titrators can enhance this process with automated features, making it more efficient and accurate.
Identifying the endpoint is the next step in the types of titration, which can be done using a color change or a pH meter. Document the final volume of the titrant utilized, ensuring accuracy with JM's precision instruments. This meticulous documentation is crucial for subsequent calculations.
Finally, calculate the concentration of the analyte based on the volume of titrant used and its known concentration. Optimal methods involve utilizing high-quality reagents from JM, maintaining stable temperature conditions, and conducting multiple trials to guarantee reproducibility. Incorporating HPLC columns and accessories from JM can further enhance analytical capabilities.
By leveraging JM's innovative solutions, including their electronic stethoscope for remote patient monitoring, pharmaceutical lab managers can significantly enhance their titration processes and overall laboratory efficiency. This commitment to quality and precision underscores the importance of using the right tools in scientific research.
Highlight the Importance of Titration in Scientific Research and Industry
The various types of titration play a pivotal role across numerous fields, demonstrating their essential nature in various applications. In the Pharmaceutical Industry, it is crucial for determining the concentration of active ingredients in drugs, ensuring dosage accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. Titrations are employed to monitor purity levels, which is vital for maintaining the safety and efficacy of pharmaceuticals. JM Science Inc. provides premium titrators that enhance this process, ensuring precision and reliability in pharmaceutical analyses.
In the Food and Beverage Industry, titration is utilized to measure acidity levels, which are critical for flavor, preservation, and product safety. For instance, wine and vinegar manufacturers rely on titration to ensure consistent acidity, directly impacting flavor profiles and adherence to safety regulations.
Environmental Testing also benefits from titration, as it aids in assessing water quality by identifying pollutant levels and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Acid-base measurement methods are employed to track pH levels in water bodies, assisting in detecting potential contamination and directing remediation efforts, thus safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and public health.
In Chemical Manufacturing, titration is vital for quality control, enabling manufacturers to verify the concentration of raw materials and final products. This ensures that production processes meet safety and quality standards, minimizing the risk of defects and enhancing product reliability. JM Science's innovative measurement solutions effectively support these quality control measures.
Overall, the various types of titration are indispensable analytical tools that enhance the reliability and accuracy of chemical analyses across different sectors, contributing significantly to advancements in science and technology. Furthermore, it is essential for characterizing chemical species and understanding reaction mechanisms in research laboratories, underscoring its fundamental role in scientific research. It is also important to acknowledge the challenges and potential sources of error in titration experiments to improve the reliability of results. As Dr. Lydia M. Cutter noted, monitoring pH is not merely a procedural step; it represents a commitment to public safety.
Conclusion
Titration stands as a pivotal quantitative analytical method, integral to various scientific fields, enabling the precise determination of substance concentrations within solutions. This meticulous process, defined by the gradual addition of a titrant to an analyte until a measurable change occurs, is foundational for ensuring safety and accuracy in both research and industrial applications.
The discussion encompasses various types of titration, including:
- Acid-base
- Redox
- Precipitation
- Complexometric
Each possessing unique applications across pharmaceuticals, food safety, environmental monitoring, and chemical manufacturing. Emphasis is placed on key procedures and best practices to ensure accuracy, highlighting the necessity of utilizing high-quality instruments and reagents to achieve reliable results. Moreover, the integration of advanced technologies significantly enhances the effectiveness of these analytical techniques, showcasing their evolving nature within laboratory practices.
Ultimately, the significance of titration transcends mere measurement; it underpins the integrity of scientific research and industrial processes. As the demand for precision across various sectors continues to escalate, adopting innovative titration methods and adhering to established best practices becomes essential. By prioritizing accuracy and reliability, industries can ensure compliance with safety standards while propelling the frontiers of science and technology. Understanding and implementing effective titration techniques is not merely a procedural necessity but a commitment to excellence in analytical chemistry.




