Overview
SEC HPLC columns stand as essential chromatography tools, expertly designed for the separation of molecules based on size. They operate on the principle of steric exclusion, facilitating precise separations of biomolecules such as proteins and polymers. In the realm of analytical laboratories, particularly within the biopharmaceutical industry, these columns are indispensable. They play a critical role in:
- Characterizing biomolecules
- Monitoring protein aggregation
- Ensuring product quality
This effectiveness is achieved through the analysis of large biomolecules, all while preserving their structural integrity.
Introduction
In the realm of analytical chemistry, the significance of Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) HPLC columns is paramount. These specialized tools are essential for separating molecules based on size, utilizing a distinct methodology that sets them apart from traditional chromatographic techniques. As the demand for precise characterization of biomolecules escalates—especially within the biopharmaceutical industry—the role of SEC columns becomes increasingly pivotal. Their capability to analyze complex biological samples without altering their structure not only ensures product quality but also enhances compliance with stringent regulatory standards. This article explores the functionality, historical development, and key characteristics of SEC HPLC columns, underscoring their indispensable contribution to modern analytical laboratories.
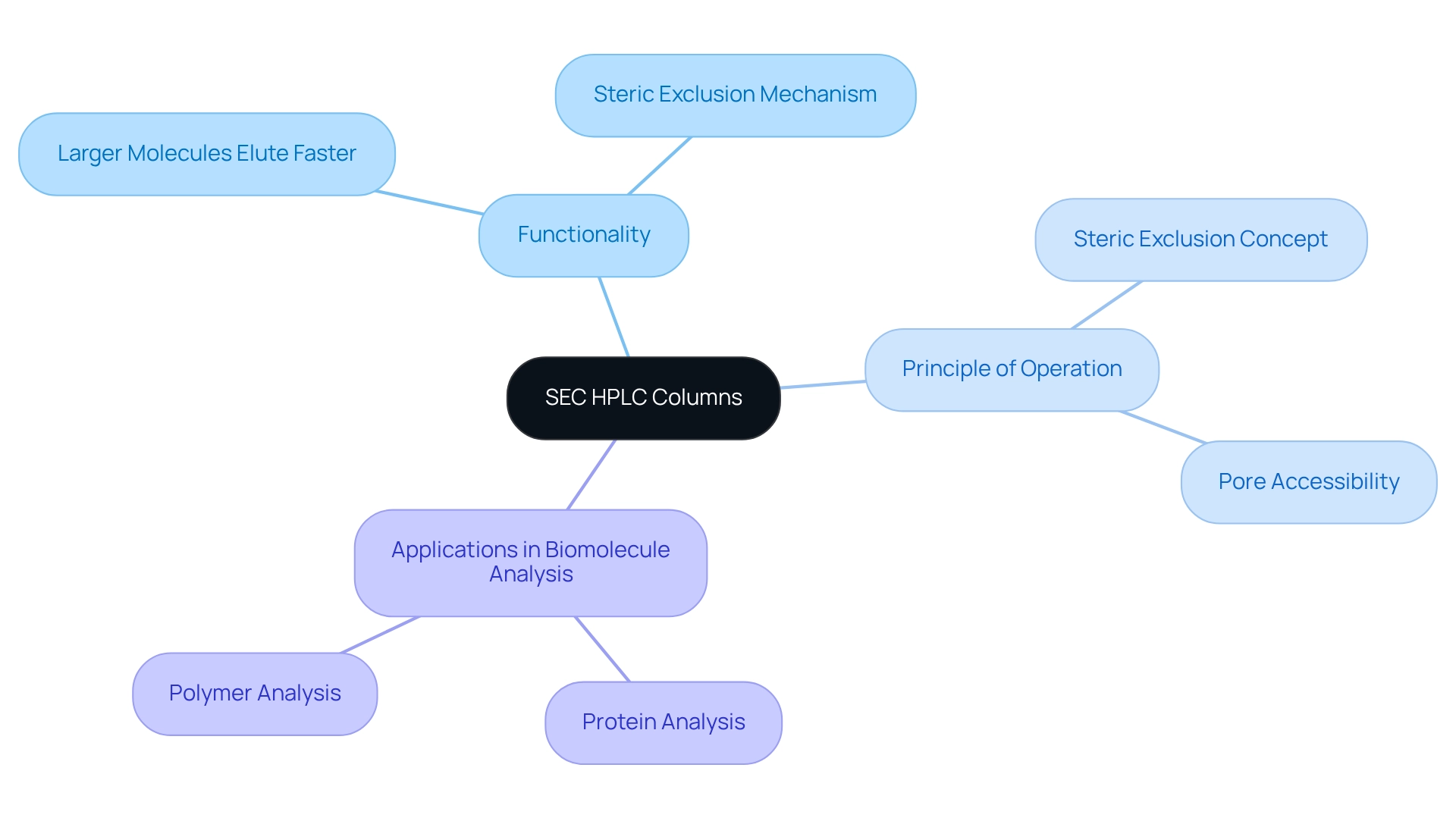
Define SEC HPLC Columns and Their Functionality
SEC HPLC columns represent a pivotal advancement in testing laboratories, specifically designed for the separation of molecules based on their dimensions. Unlike traditional chromatographic techniques that depend on chemical interactions, SEC operates on the principle of steric exclusion. In this innovative method, larger molecules are unable to penetrate the pores of the stationary phase, allowing them to elute more rapidly than their smaller counterparts, which can partially access these pores. This unique functionality underscores the value of SEC HPLC columns in the analysis of biomolecules such as proteins and polymers, where size critically influences behavior and interactions. By employing these specialized instruments, laboratories can achieve precise separations, enhancing their analytical capabilities and ensuring reliable results.
Explore the Importance of SEC HPLC Columns in Analytical Laboratories
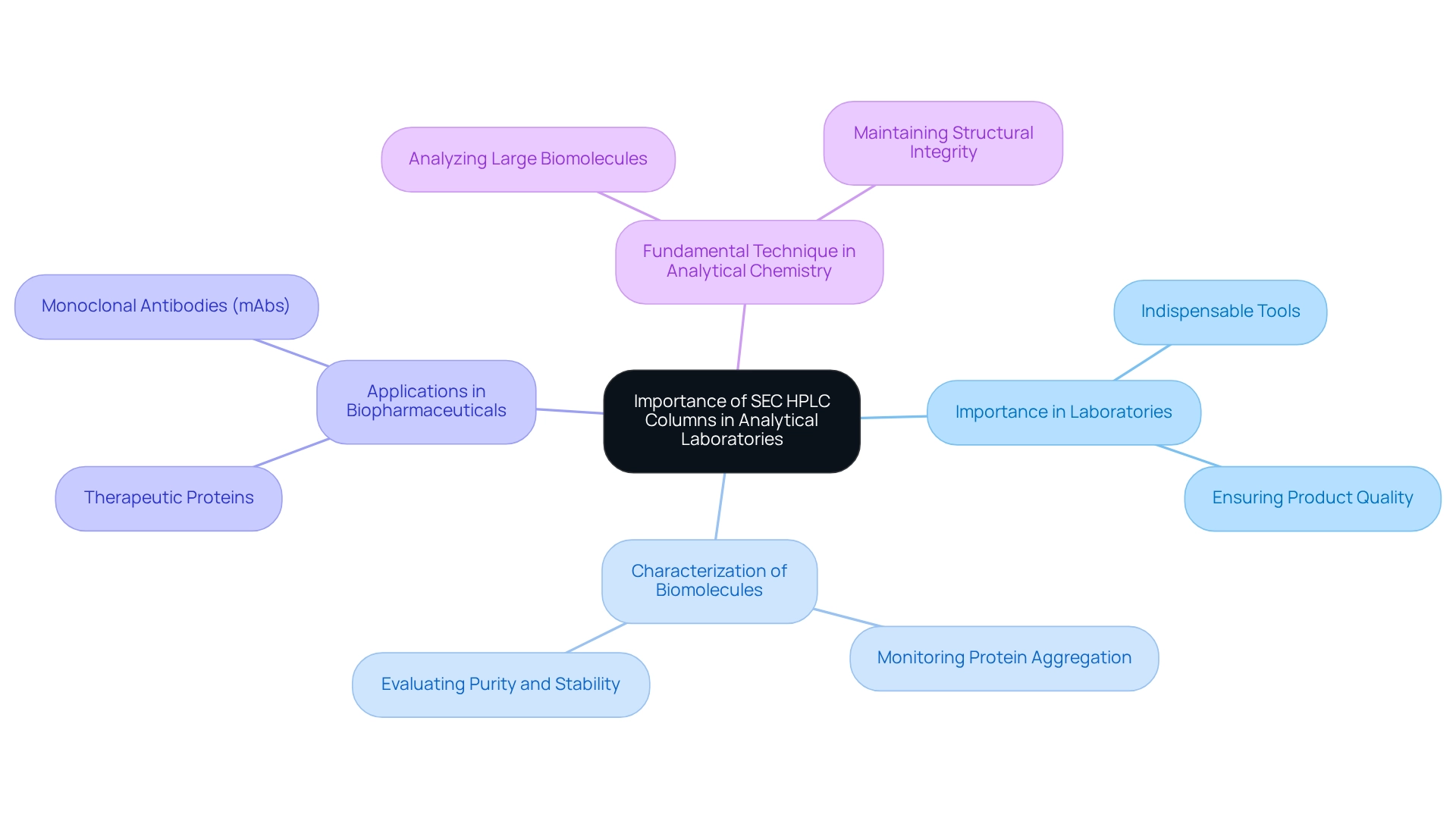
SEC HPLC columns are indispensable tools in testing laboratories, particularly within the biopharmaceutical industry. They play a crucial role in the characterization of biomolecules, especially in monitoring protein aggregation, which is essential for ensuring product quality.
For example, SEC is employed to evaluate the purity and stability of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and other therapeutic proteins. By providing a method to separate and quantify aggregates, SEC HPLC columns empower researchers and manufacturers to uphold regulatory standards while enhancing the safety and efficacy of their products.
Moreover, the capability to analyze large biomolecules without compromising their structure solidifies SEC as a fundamental technique in modern analytical chemistry.
Trace the Historical Development of SEC HPLC Columns
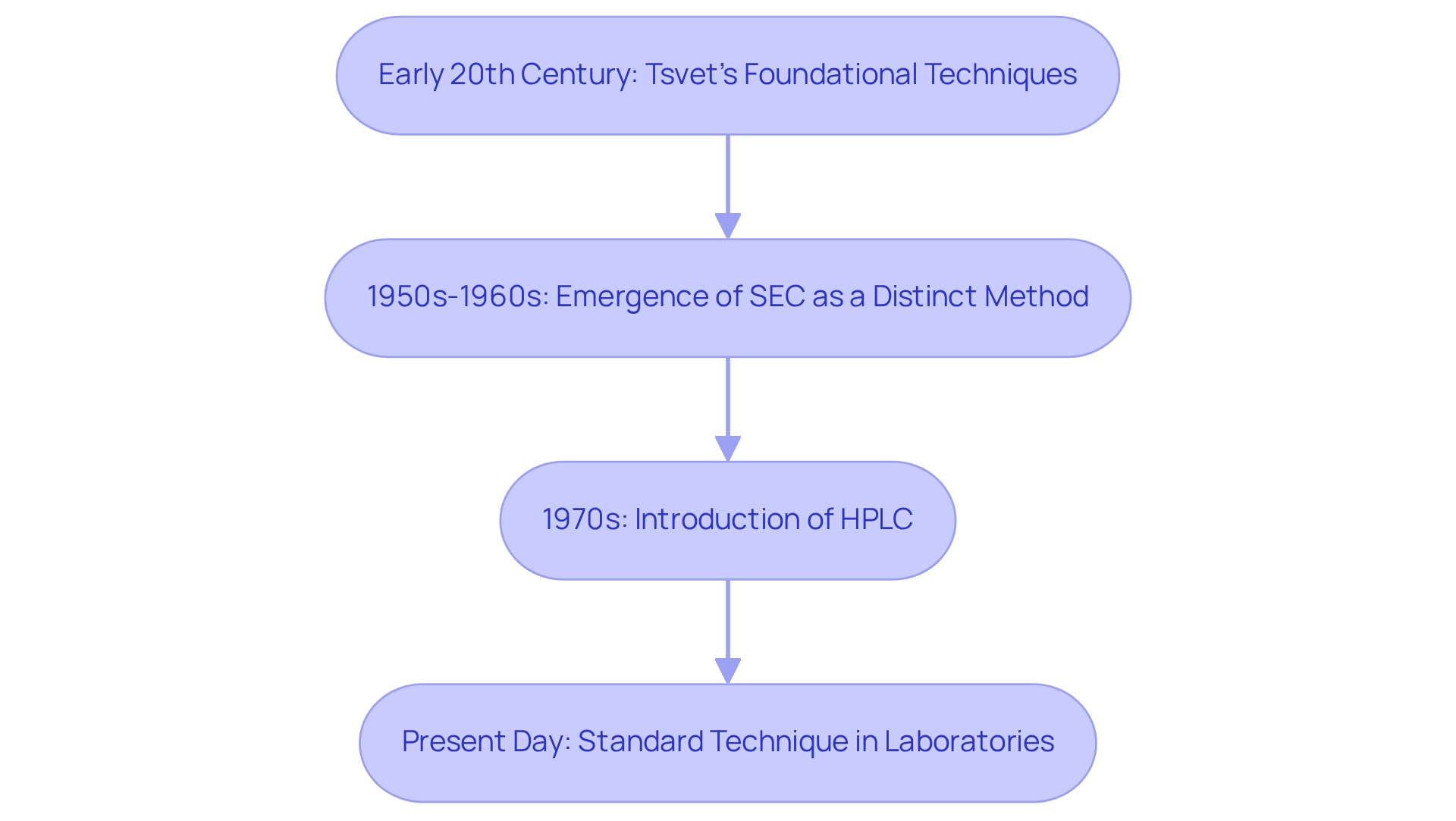
The advancement of SEC HPLC devices can be traced back to the early 20th century, rooted in the pioneering work of Mikhail Tsvet, who established foundational chromatography techniques. However, it was in the 1950s and 1960s that SEC emerged as a distinct method, gaining recognition particularly for its applications in biochemistry. Over the decades, innovations in packing materials and detector technologies have significantly improved the resolution and efficiency of SEC. The introduction of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) in the 1970s marked a pivotal advancement, allowing for more precise and rapid analyses. Today, the utilization of is essential for the characterization of complex biological samples, reflecting their evolution into a standard technique within analytical laboratories.
Identify Key Characteristics and Variations of SEC HPLC Columns
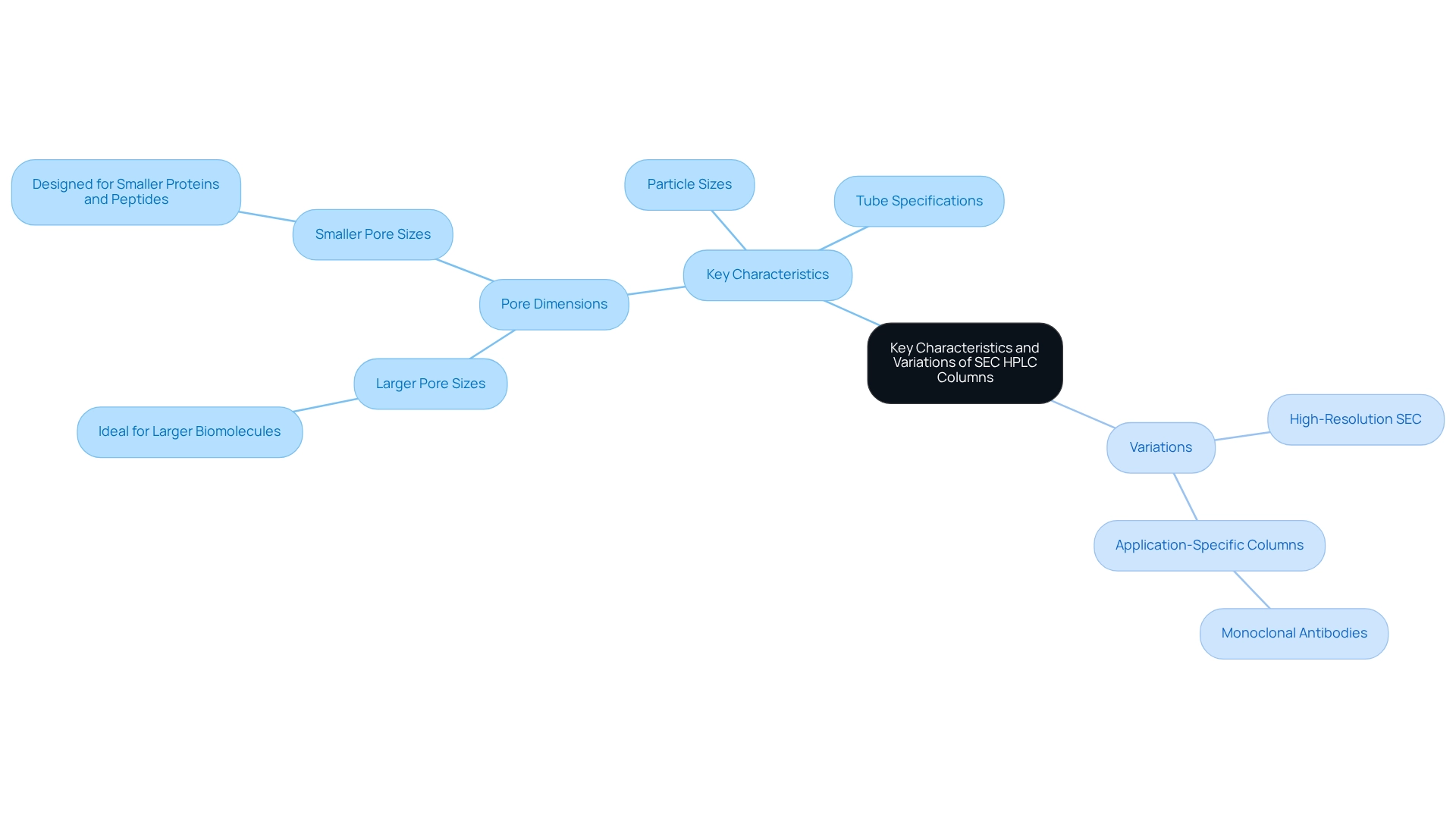
SEC HPLC columns are offered in a variety of designs and specifications, meticulously tailored for specific applications. Key characteristics include pore dimensions, particle sizes, and tube specifications, all of which significantly influence separation effectiveness and clarity.
For example, columns with larger pore sizes are ideal for isolating larger biomolecules, while smaller pore sizes are specifically designed for smaller proteins and peptides. Furthermore, SEC columns can be constructed from diverse materials, such as agarose or polyacrylamide, each providing unique advantages depending on the sample type.
Notably, variations like high-resolution SEC setups and those aimed at particular applications, such as the analysis of monoclonal antibodies, further enhance the versatility of SEC in testing laboratories. By comprehensively understanding these characteristics, researchers are empowered to select the most suitable SEC HPLC columns for their distinct analytical challenges.
Conclusion
The exploration of Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) HPLC columns underscores their pivotal role in modern analytical chemistry, particularly within the biopharmaceutical sector. By effectively separating molecules based on size, SEC columns deliver a reliable means of characterizing biomolecules, which is essential for ensuring product quality and compliance with regulatory standards. Their unique methodology enables the analysis of complex biological samples without compromising structural integrity, establishing them as invaluable tools in laboratories.
Historically, SEC has undergone significant evolution since its inception, with technological advancements enhancing its efficiency and resolution. The advent of high-performance liquid chromatography has further entrenched SEC's status as a standard technique. As researchers persist in innovating and refining SEC methodologies, the versatility of these columns becomes evident through their tailored designs and specifications, accommodating a wide range of applications.
In conclusion, SEC HPLC columns are not merely fundamental components of analytical laboratories; they are crucial in advancing our understanding of biomolecular behavior and interactions. Their application ensures the safety and efficacy of therapeutic products, reinforcing their indispensable contribution to the field. As the demand for precise biomolecular analysis escalates, the significance of SEC columns will undoubtedly continue to grow, shaping the future landscape of analytical chemistry.




