Overview
This article delves into the critical task of troubleshooting HPLC pumps, aiming to ensure optimal performance within chromatographic systems. Understanding pump components and recognizing common issues are paramount for success in this area. A comprehensive step-by-step guide is provided, addressing problems such as:
- Irregular flow rates
- Pressure fluctuations
By resolving these issues, one can significantly enhance the reliability and accuracy of analyses, underscoring the importance of high-quality scientific instruments in laboratory settings.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), the efficiency of analytical processes is fundamentally reliant on the performance of HPLC pumps. These essential components not only facilitate the movement of solvents but also play a pivotal role in ensuring consistent and reliable results across a spectrum of applications, from pharmaceuticals to environmental testing.
A thorough understanding of HPLC pumps, the identification of common issues, and the implementation of effective troubleshooting strategies can significantly enhance laboratory operations. As the industry evolves, it is imperative to stay informed about best practices and leverage available resources to optimize performance and achieve accurate analyses.
Understand HPLC Pump Basics
The HPLC pump is essential for the effective transportation of the mobile phase in chromatographic systems, making its understanding critical for optimal operation. JM Science Inc. offers a diverse range of high-quality liquid chromatography solutions, including high-performance columns and accessories that significantly enhance the efficiency of these devices. Key components of include:
- Piston: The heart of the pump, generating the necessary pressure to propel the fluid through the apparatus.
- Check Valves: These components prevent backflow, ensuring a steady and consistent solvent flow.
- Solvent Reservoir: This holds the mobile phase prior to its introduction into the system.
A thorough familiarity with various types of devices, such as reciprocating and syringe mechanisms, along with their operational principles—like flow rate and pressure generation—is vital. This foundational knowledge not only aids in troubleshooting HPLC pump issues but also enhances the overall efficiency of chromatography applications.
Recent market segmentation analysis indicates that a deep understanding of these components empowers stakeholders to tailor their products effectively to meet diverse industry needs. As Dr. Bob Sandor, a distinguished specialist with over 40 patents and technical publications, states, "This translates to a 15- to 20-minute reduction in time compared to the gravimetric method," underscoring the efficiency advantages of high-performance liquid chromatography systems and their impact on contemporary medical practices, including the innovative medical devices offered by JM Science. Furthermore, with the Korea Lab 2025 event approaching on April 22, 2025, there is a growing emphasis on the significance of chromatography technology in ongoing industry discussions. Staying informed about the latest advancements and operational principles will enable laboratory managers to optimize performance and ensure reliable results in their analyses.
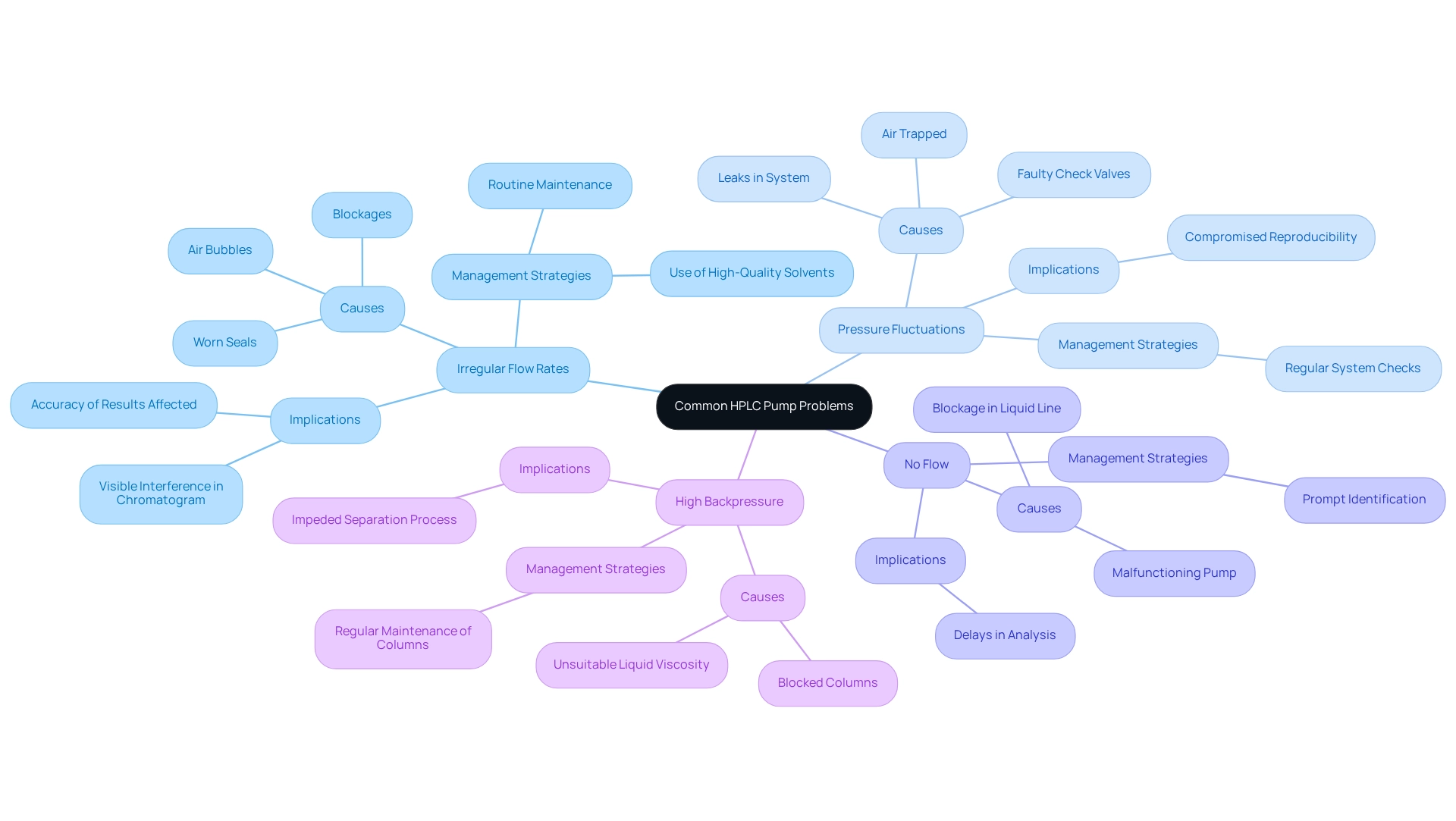
Identify Common HPLC Pump Problems
can significantly impact analytical performance. Among these issues are:
- Irregular Flow Rates: This problem often arises from air bubbles in the apparatus, blockages, or worn seals. The presence of gas bubbles can lead to visible interference in the chromatogram, ultimately affecting the accuracy of results.
- Pressure Fluctuations: These variations are frequently caused by air trapped in the device, faulty check valves, or leaks within the system. Such inconsistencies can compromise the reproducibility of chromatographic separations.
- No Flow: A complete lack of flow may indicate a blockage in the liquid line or a malfunctioning pump. Identifying this issue promptly is crucial to avoid delays in analysis with the HPLC pump.
- High Backpressure: This condition can arise from blocked columns or unsuitable liquid viscosity, impeding the effectiveness of the separation process.
Recognizing these symptoms early is essential for preventing more significant issues and ensuring consistent results from the HPLC pump. According to Sanat Sawant, an analyst in the Analytical Research Department at Sitec Labs Private Limited, three common peak shape problems encountered in high-performance liquid chromatography are peak tailing, split peaks, and peak fronting, which can be exacerbated by inconsistent flow rates.
By applying optimal methods for pressure management in liquid chromatography—such as routine upkeep and the utilization of premium liquids, as detailed in the case study 'Best Practices for Pressure Management'—laboratories can reduce these frequent issues and enhance the overall effectiveness of their systems. Users can also subscribe for free to receive the latest information on new separation science methods and applications.
Resolve HPLC Pump Issues Step-by-Step
To effectively resolve HPLC device issues, follow this comprehensive troubleshooting guide:
- Check for Air Bubbles: Irregular flow rates often indicate the presence of air bubbles. Begin by thoroughly removing gas from the chemicals and ensuring the device is adequately prepared to eliminate any trapped air.
- Inspect Check Valves: If you experience pressure fluctuations, remove the check valves for inspection. Confirm that backpressure remains below 10 bar (145 psi) and clean or replace the valves as necessary to restore consistent pressure and flow.
- Clear Blockages: Blockages can severely impact performance. Flush the setup with a suitable solvent to eliminate any obstructions in the lines, ensuring a clear flow.
- Calibrate the Pump: Regular calibration is crucial. Verify the calibration settings of the HPLC pump, ensuring the flow rate is set to 50 ml/min for the AZURA P 2.1S, and adjust as needed to maintain accuracy in your analyses.
- Inspect Seals and Tubing: Regular maintenance includes checking seals and tubing for wear. Replace any parts that exhibit signs of damage to prevent leaks and ensure dependable operation.
Implementing these steps can significantly improve the performance of your chromatography setup. A case study highlighted the critical role of filtration, emphasizing that utilizing a 0.5-micron filter prior to application can prevent particles from damaging the apparatus. By adopting such practices, laboratories can enhance the longevity and reliability of their HPLC pump systems, leading to consistent and accurate results. Moreover, adequate degassing of solvents optimizes chromatography performance, reducing the likelihood of air bubbles that disrupt flow. Following these troubleshooting steps not only addresses common problems but also contributes to the overall success rates of analyses conducted with .
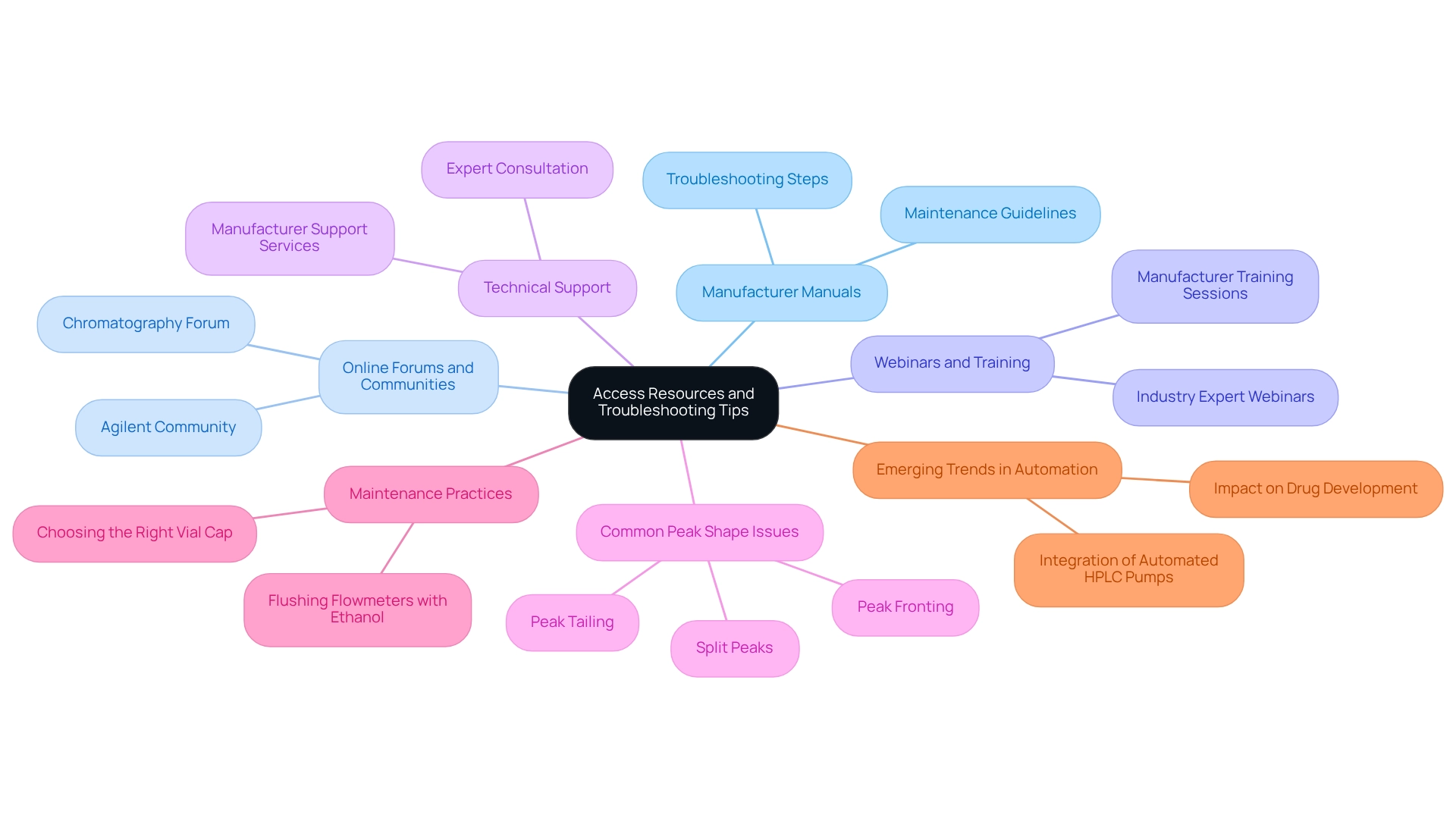
Access Resources and Troubleshooting Tips
To optimize HPLC pump performance and troubleshoot effectively, it is essential to leverage a variety of resources.
- Manufacturer Manuals: Always refer to the specific manual for your high-performance liquid chromatography device. These manuals contain crucial troubleshooting steps and maintenance guidelines customized for your equipment. Understanding the complexities of your device through these manuals can significantly enhance troubleshooting effectiveness.
- Online Forums and Communities: Engage with platforms such as the Chromatography Forum and Agilent Community. These forums provide valuable peer support, allowing users to share experiences and solutions to common issues, fostering a collaborative environment for troubleshooting.
- Webinars and Training: Participate in training sessions offered by manufacturers or industry experts. These sessions are instrumental in enhancing your troubleshooting skills and keeping you updated on best practices, ensuring you remain at the forefront of the field.
- Technical Support: Don’t hesitate to utilize the technical support services provided by your liquid chromatography equipment manufacturer. Their expertise can be invaluable for resolving persistent issues that may arise during operation.
Incorporating these resources into your routine can lead to improved troubleshooting efficiency. For instance, documenting troubleshooting issues can help identify patterns, enabling faster problem resolution. Additionally, understanding —such as peak tailing, split peaks, and peak fronting—can guide your troubleshooting efforts effectively. Regular maintenance practices, like flushing flowmeters with ethanol when not in use, are also crucial for maintaining optimal performance.
Moreover, recent findings emphasize the significance of selecting to avoid contamination or sample loss, which can greatly influence chromatographic results. This is particularly relevant in light of the growing trend towards automation in laboratories, as discussed in the case study titled "Emerging Trends in Automation." The incorporation of automated HPLC pumps into continuous processes for drug development is set to transform the pharmaceutical sector by enhancing throughput and minimizing human errors. By utilizing these resources and best practices, you can ensure the reliability and accuracy of your HPLC operations.
Conclusion
A comprehensive understanding of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) pumps is crucial for achieving optimal analytical performance. This article has meticulously outlined the fundamental components of HPLC pumps—such as pistons, check valves, and solvent reservoirs—highlighting their indispensable roles in ensuring consistent and reliable results across a range of applications. By recognizing common issues, including irregular flow rates, pressure fluctuations, and blockages, and implementing effective troubleshooting strategies, laboratories can significantly enhance their efficiency and accuracy.
Furthermore, leveraging available resources—such as manufacturer manuals, online forums, and technical support—empowers laboratory managers to address challenges proactively. Adopting best practices, including regular maintenance and proper solvent handling, allows laboratories to mitigate prevalent problems associated with HPLC pumps.
In summary, a thorough comprehension of HPLC pump operations, combined with diligent troubleshooting and strategic resource utilization, is essential for optimizing performance and achieving dependable analytical results. As the field evolves, remaining informed about advancements and best practices will ensure laboratories maintain a leading edge in efficiency and accuracy. Embracing these strategies will not only enhance operational capabilities but also contribute to the overarching success of HPLC applications across diverse industries.




