Overview
This article delves into the essential factors for selecting pump tubing, outlining best practices for installation and maintenance, as well as troubleshooting common issues. It highlights the critical importance of:
- Material compatibility
- Temperature resistance
- Proper installation techniques
Furthermore, it underscores the necessity of regular inspections and maintenance to guarantee optimal performance and longevity of the tubing system. By adhering to these guidelines, professionals can ensure the reliability and efficiency of their operations.
Introduction
Selecting the right pump tubing is critical for ensuring the efficiency and reliability of fluid transfer systems in both industrial and laboratory settings. The myriad of materials and specifications available necessitates a deep understanding of key factors such as:
- Material compatibility
- Temperature resistance
- Flexibility
These elements significantly enhance performance and operational effectiveness. However, even the best tubing can encounter issues, from leaks to blockages. This raises an important question: what best practices and troubleshooting strategies can be employed to maintain the optimal functionality and longevity of pump tubing systems?
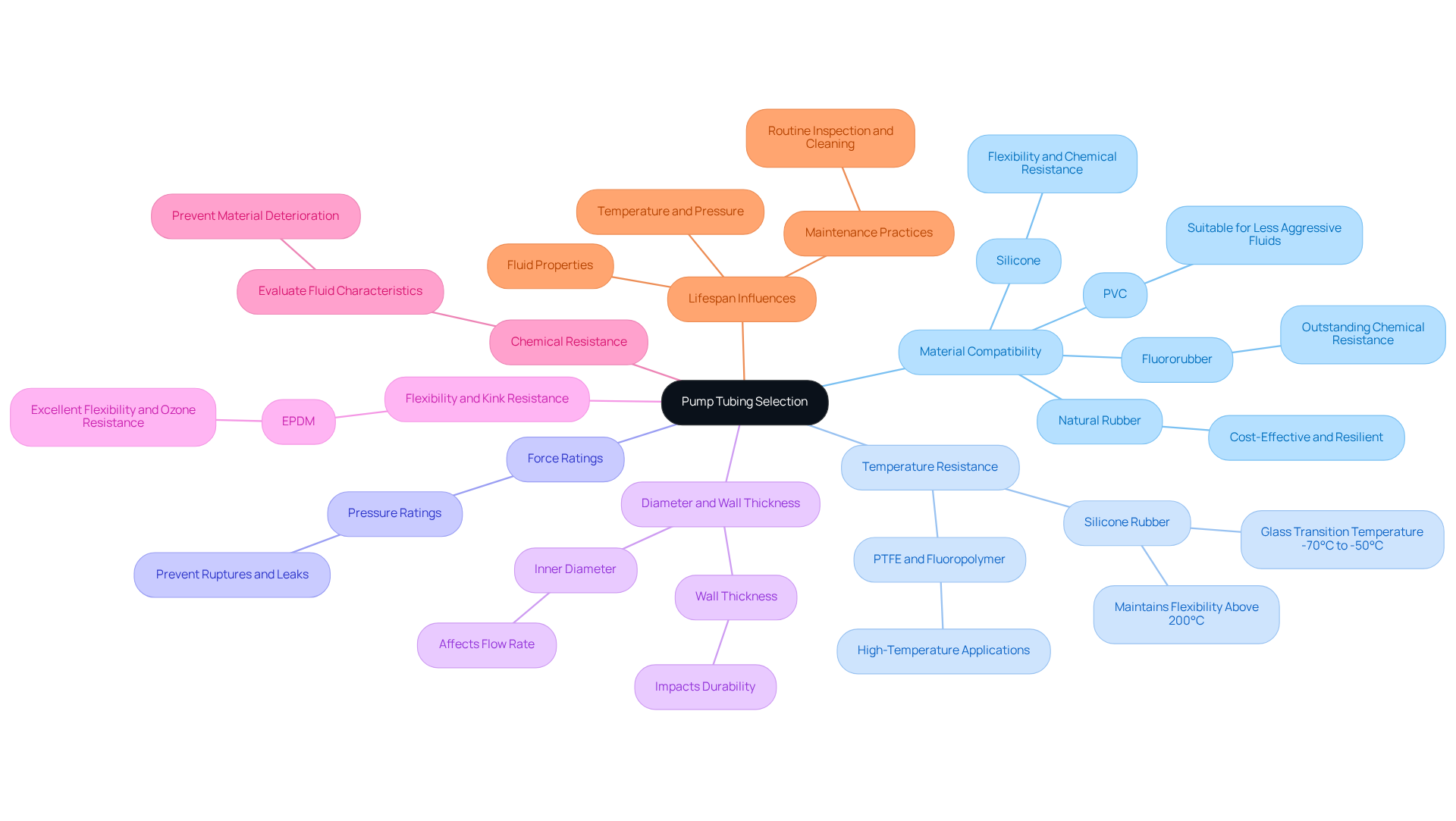
Identify Key Factors for Pump Tubing Selection
When selecting pump tubing, it is essential to consider several critical factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability in .
- Material Compatibility is paramount; the pipe material must align with the fluids being pumped. For example, silicone is frequently chosen for its flexibility and chemical resistance, while materials like PVC may suffice for less aggressive fluids. Additionally, natural rubber serves as a cost-effective option, providing excellent elasticity and resilience.
- Next, Temperature Resistance plays a vital role. Tubing must withstand the temperature range of the application. High-temperature fluids may necessitate specialized materials such as PTFE or fluoropolymer. Silicone rubber, for instance, maintains flexibility at temperatures exceeding 200°C, with a glass transition temperature ranging from -70°C to -50°C, and certain formulations can endure temperatures as low as -100°C.
- Force Ratings are another crucial consideration. Ensure the tubing can manage the maximum force of the system; inadequate pressure ratings can lead to ruptures and leaks, compromising system integrity.
- The Diameter and Wall Thickness of the tubing also significantly influence performance. The inner diameter affects flow rate, while wall thickness impacts durability. A larger diameter may reduce resistance but could require more powerful motors to maintain efficiency.
- Moreover, Flexibility and Kink Resistance are essential for installation. Tubing should be flexible enough to navigate the installation space without kinking, which can restrict flow. Materials like EPDM demonstrate excellent flexibility and ozone resistance, making them suitable for various environments.
- Chemical Resistance must also be assessed. Evaluate the chemical characteristics of the fluid to prevent material deterioration over time. Tubing should exhibit low absorption and high resistance to swelling and corrosion. Notably, fluororubber showcases outstanding resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including strong acids and bases.
- Finally, consider the Lifespan Influences on the peristaltic tube. Factors such as temperature, pressure, fluid properties, and maintenance practices all contribute to longevity. Routine examination, cleaning, and lubrication can significantly prolong the lifespan of the pipes.
By thoughtfully evaluating these factors, users can select piping that enhances the efficiency and dependability of their system operations, ultimately boosting performance in laboratory and industrial environments.
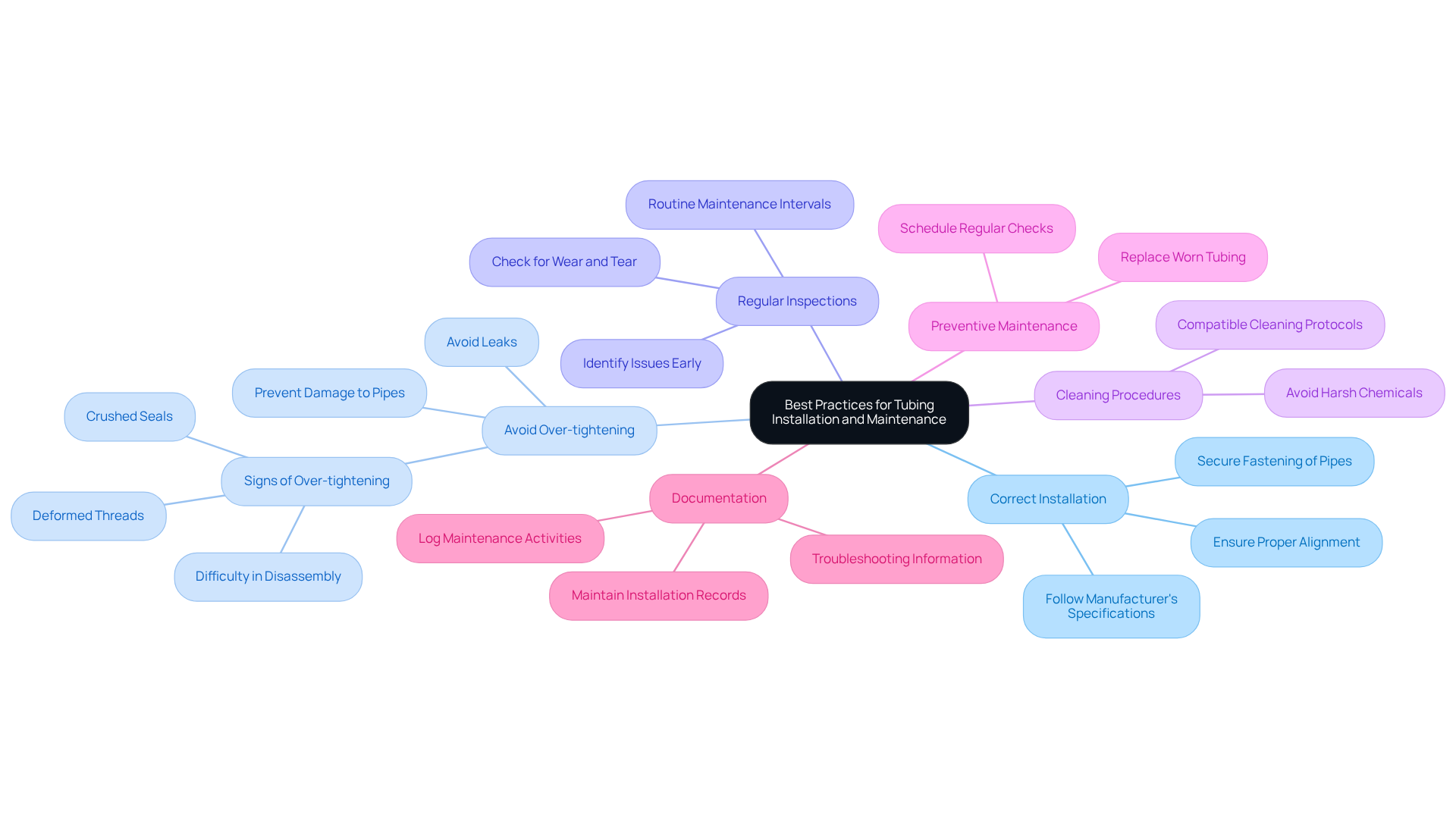
Implement Best Practices for Tubing Installation and Maintenance
To ensure optimal performance, it is essential to follow best practices during the installation and maintenance of pump tubing.
- Correct Installation: Begin by ensuring that the piping is installed according to the manufacturer's specifications. Proper alignment and secure fastening of the pipes are crucial to prevent slippage, which can compromise system integrity.
- Avoid Over-tightening: When securing pipe connections, it is vital to avoid over-tightening clamps. Excessive pressure can damage the pipes and lead to leaks, undermining the system's reliability.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct routine examinations of the piping for signs of wear, such as cracks, discoloration, or swelling. Early detection of these issues can prevent catastrophic failures, safeguarding both equipment and operations.
- Cleaning Procedures: Implement a cleaning protocol compatible with the material of the pipes. It is important to avoid harsh chemicals that may damage the piping, ensuring longevity and performance.
- Preventive Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance checks to replace tubing that shows signs of wear. This proactive approach not only prolongs the lifespan of but also enhances overall efficiency.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed records of installation dates, maintenance activities, and any issues encountered. This information is invaluable for troubleshooting and future maintenance planning.
By adhering to these best practices, users can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of their pump tubing systems.
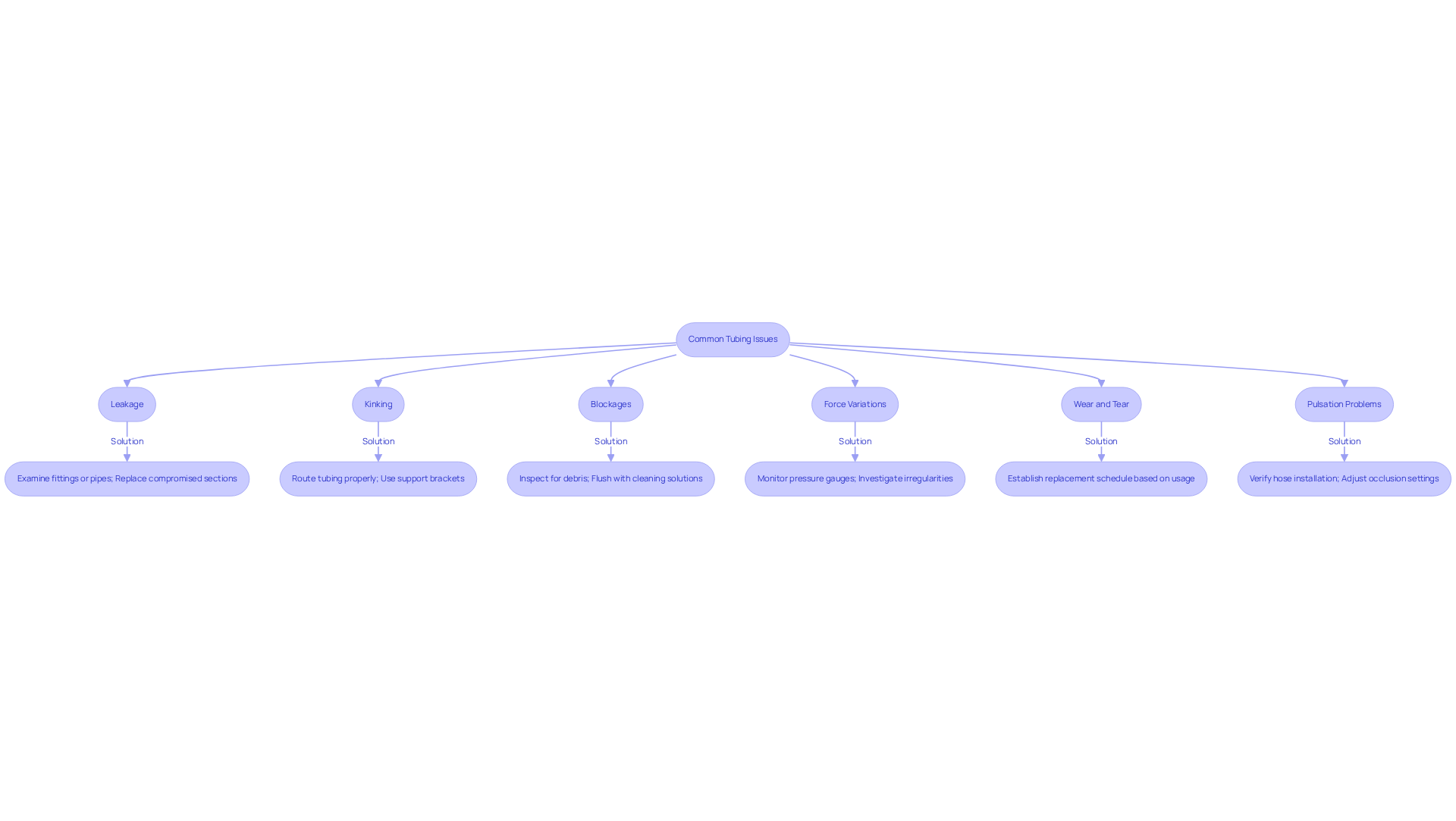
Monitor and Troubleshoot Common Tubing Issues
Monitoring and troubleshooting pipe issues is essential for preventing significant operational disruptions. Consider the following common problems and their solutions:
- Leakage: If leaks are detected, it is crucial to examine for improper fittings or damaged pipes. Replace any compromised sections immediately to ensure system integrity.
- Kinking: Kinks can restrict flow and lead to build-up within the system. Ensure that tubing is routed properly and consider implementing support brackets to maintain the desired shape.
- Blockages: Regular inspections for blockages caused by debris or buildup are vital. Flushing the system with compatible cleaning solutions can effectively clear obstructions, restoring optimal flow.
- Force Variations: Sudden changes in force may indicate a blockage or a failing pump. It is important to monitor pressure gauges closely and investigate any irregularities promptly to prevent further issues.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, materials can deteriorate due to repeated flexing or exposure to harsh chemicals. Establishing a replacement schedule based on usage and environmental conditions is advisable to mitigate risks.
- Pulsation Problems: If pulsation is observed in the device, verify the correct installation of hoses and ensure that the apparatus is accurately calibrated. Adjusting the occlusion settings may also resolve these issues.
By implementing a robust monitoring and troubleshooting strategy, users can maintain and extend the life of their tubing.
Conclusion
Selecting the right pump tubing is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and reliability of fluid transfer systems. Understanding the key factors involved in tubing selection—such as material compatibility, temperature resistance, and flexibility—enables users to make informed decisions that enhance system performance. Furthermore, implementing best practices for installation and maintenance, including avoiding over-tightening and conducting regular inspections, significantly contributes to prolonging the lifespan of the tubing.
Throughout this discussion, we have highlighted various critical considerations, including:
- The importance of force ratings
- Chemical resistance
- The impact of diameter and wall thickness on performance
Additionally, troubleshooting common issues such as leakage, kinking, and blockages is essential to prevent operational disruptions and maintain optimal performance. By adhering to these guidelines, users can effectively manage their pump tubing systems and proactively address potential problems.
In conclusion, prioritizing proper selection, installation, and maintenance of pump tubing is essential for achieving reliable operation in both laboratory and industrial environments. By remaining vigilant and adopting a proactive approach, users can significantly reduce the risk of failures and enhance the overall efficiency of their fluid transfer systems. Embracing these best practices and insights not only safeguards investments but also contributes to smoother operations in the long run.




