Overview
This article serves as an authoritative guide on calibrating a pH probe, underscoring the critical role of accurate calibration in ensuring reliable measurements within laboratory environments, especially in pharmaceuticals. It outlines the essential tools required, presents a detailed step-by-step procedure, and offers troubleshooting tips to guarantee the optimal functioning of pH meters. Regular calibration, coupled with the use of fresh buffers, is emphasized as vital for maintaining measurement precision and ensuring the integrity of laboratory results.
Introduction
Ensuring accurate pH measurements is a critical component in various laboratory settings, particularly within the pharmaceutical industry, where precision can directly impact product safety and efficacy. Calibration of pH probes transcends mere procedural task; it is an essential practice that safeguards the integrity of scientific findings. However, many lab managers may overlook the nuances of this process, leading to potential inaccuracies that could compromise research outcomes.
How can laboratories effectively implement a robust calibration strategy that addresses common pitfalls and enhances measurement reliability?
Understand the Importance of pH Meter Calibration
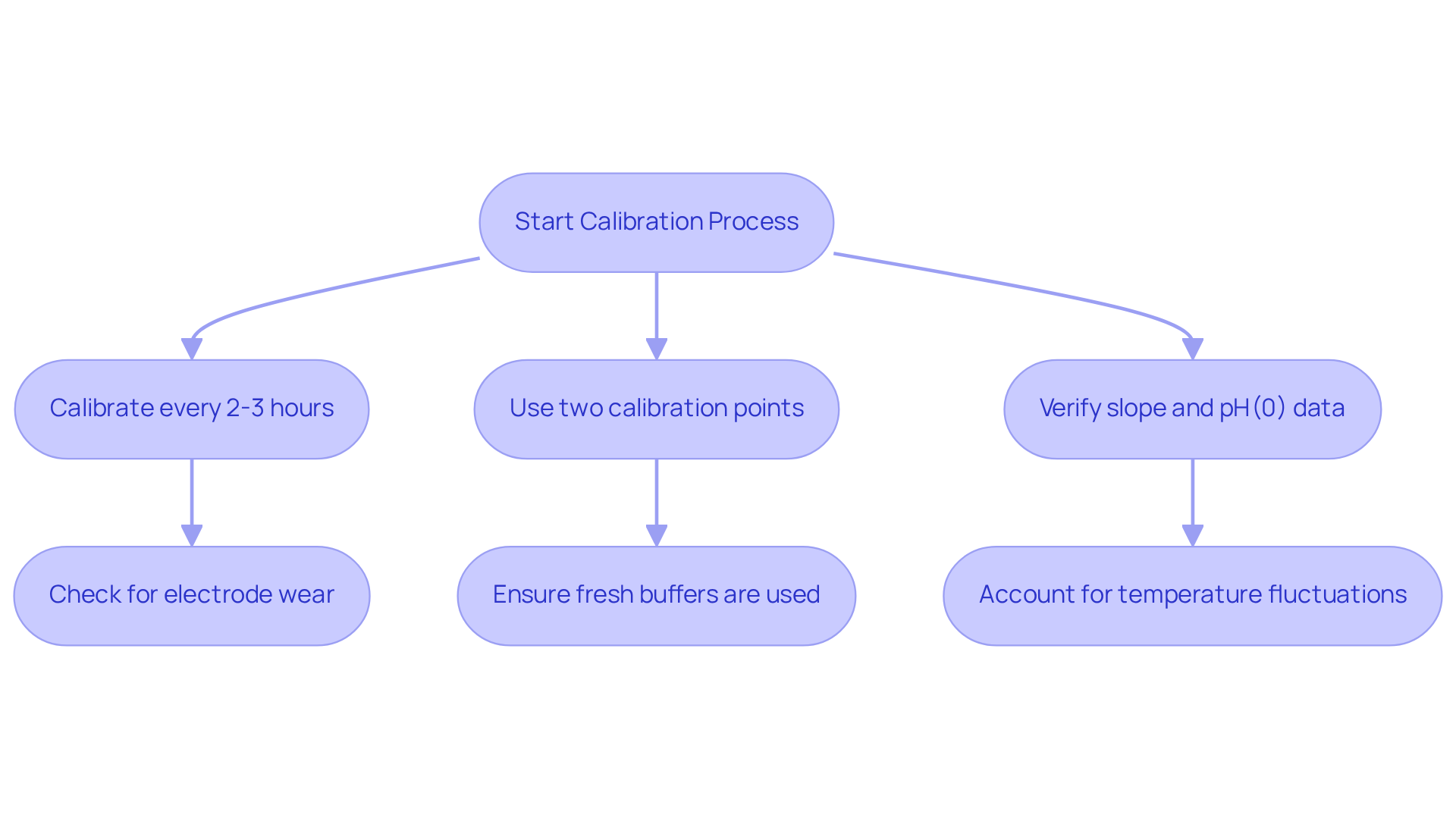
Knowing how to calibrate pH probe is essential for achieving accurate and reliable measurements, especially in pharmaceutical applications where precision is critical. Over time, pH meters may experience drift due to factors such as electrode wear, contamination, and temperature fluctuations. Therefore, frequent adjustments are necessary to ensure that the measurements accurately reflect the actual pH of the substances being examined.
To understand how to calibrate pH probe, calibration should be conducted at least every 2-3 hours using two points that are close to the expected pH of the sample solution. Neglecting proper calibration can lead to misleading results, which may result in incorrect conclusions in research and development.
For instance, inaccurate pH readings can significantly affect drug formulation and stability, potentially jeopardizing patient safety. Industry experts emphasize that even minor deviations from the desired pH can negatively impact the quality, efficacy, and safety of pharmaceutical products. Consequently, verifying the slope and pH(0) data after adjustment is crucial to ensure the precision of the pH meter. Furthermore, utilizing fresh buffers for adjustment is vital, as expired or contaminated buffers can produce flawed outcomes.
Understanding how to calibrate pH probe is crucial, as it involves recognizing the while considering the effects of temperature fluctuations and contamination, which is the first step toward ensuring the reliability of laboratory results and compliance with regulatory standards. By prioritizing these practices, laboratories can maintain high-quality scientific instruments that uphold the integrity of their findings.
Gather Necessary Tools and Set Up Your pH Meter
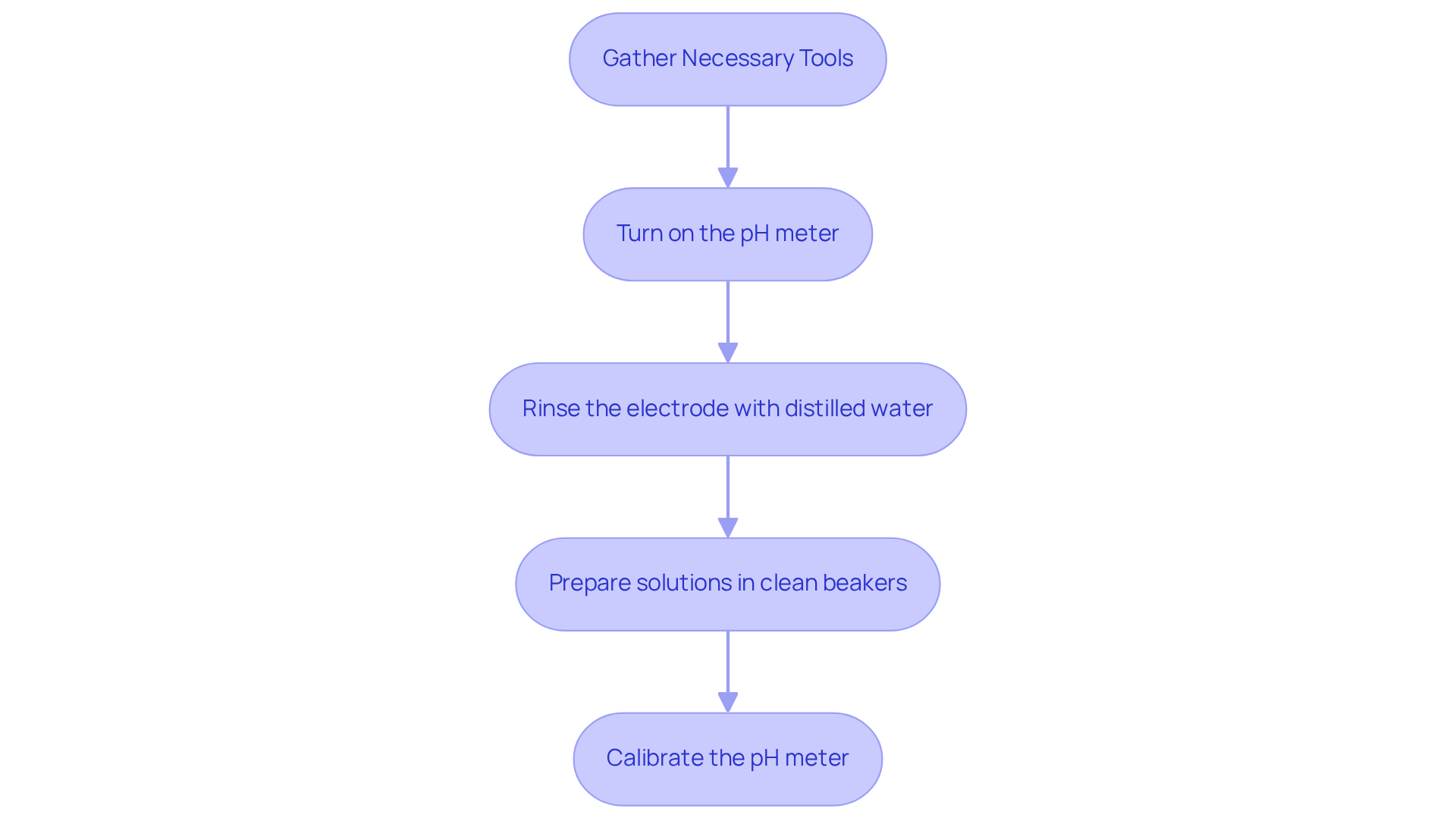
Before initiating the calibration process, it is imperative to have the following tools prepared:
- pH Meter: Ensure it is clean and functioning properly. As noted by Brandon Schaefer, 'For the meter to be precise, it must be calibrated using supports.'
- Standard Solutions: Acquire at least two reference liquids, typically pH 4.00 and pH 7.00, with the option of pH 10.00 for a three-point adjustment. The precision of pH readings hinges on the quality of these uncontaminated reagents.
- Distilled Water: Necessary for rinsing the probe between liquid mixtures.
- Clean Beakers: Utilize separate beakers for each buffer solution to prevent cross-contamination.
- Paper Towels or Lint-Free Cloth: Essential for drying the sensor.
Setup Steps:
- Turn on the pH meter and allow it to warm up if necessary.
- Rinse the electrode with distilled water to eliminate any contaminants.
- Prepare the solutions in clean beakers, ensuring they are at room temperature for precise readings. To guarantee accuracy, it is important to know how to at the same temperature as the measurements.
To ensure reliable pH measurements, using high-quality, uncontaminated buffers is crucial. Routine adjustments are necessary, as all electrodes deteriorate over time, which can impact measurement precision. The results of these adjustments should include slope and offset values, which must be verified for accuracy following the adjustment. Adhering to these best practices will not only uphold the integrity of your calibration process but also provide guidance on how to calibrate pH probe to guarantee precise pH readings in pharmaceutical labs.
Follow Step-by-Step Calibration Procedures
To effectively calibrate your pH meter, follow this step-by-step procedure, ensuring accuracy and reliability in your measurements:
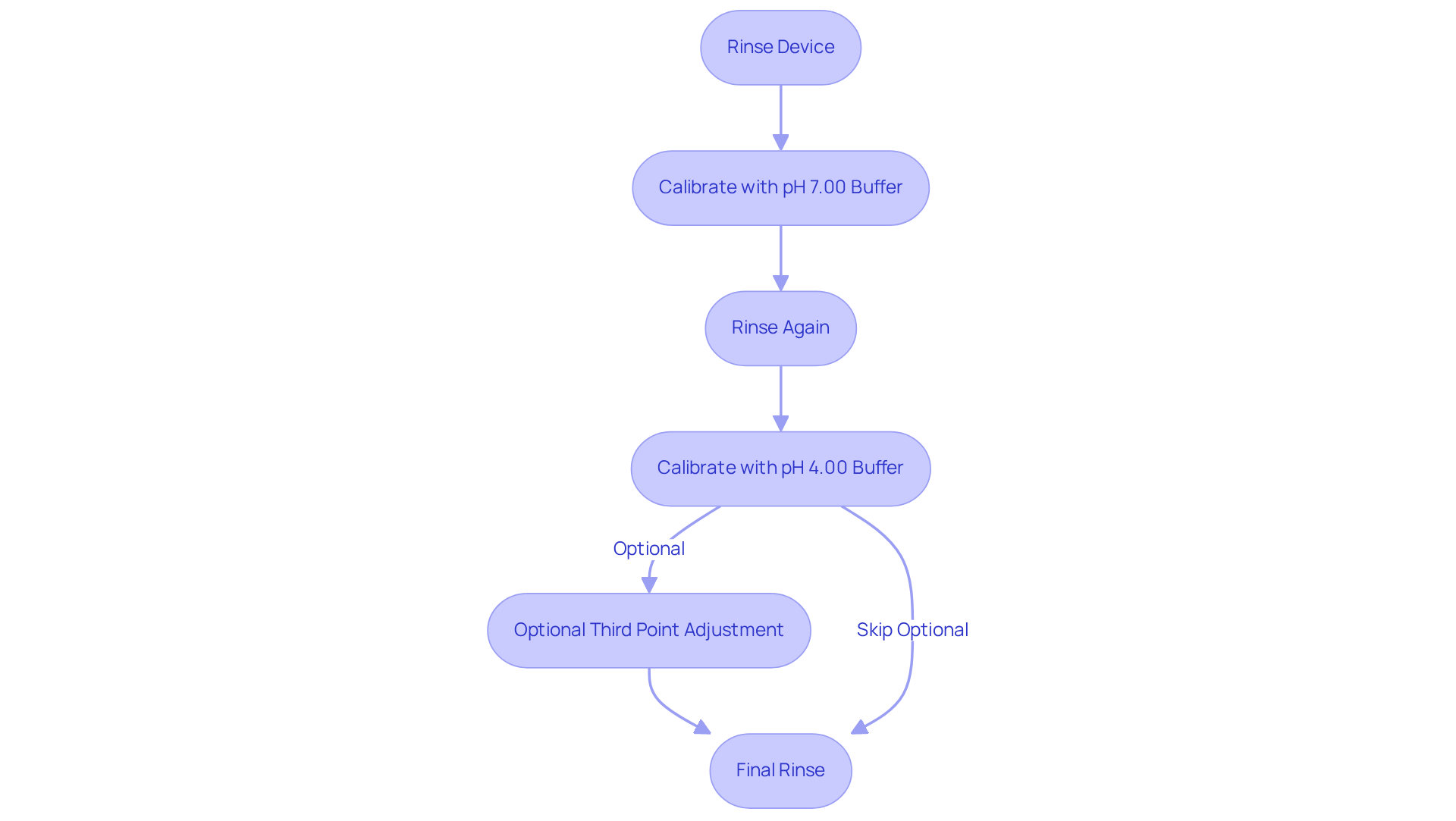
- Rinse the device: Immerse the component in distilled water and gently shake off any excess.
- Calibrate with pH 7.00 Buffer: Submerge the electrode in the pH 7.00 buffer solution. Stir gently and allow the reading to stabilize, which typically takes about 1 minute. If necessary, adjust the meter to display pH 7.00.
- Rinse Again: Rinse the device with distilled water to prevent contamination.
- Calibrate with pH 4.00 Buffer: Place the electrode in the pH 4.00 buffer solution. Stir gently and wait for stabilization. Adjust the meter to read pH 4.00.
- Optional Third Point Adjustment: For improved precision, particularly in vital applications, repeat the adjustment process using a pH 10.00 solution.
- Final Rinse: Rinse the component one last time with distilled water and store it according to the manufacturer's guidelines.
This adjustment procedure usually requires about 5 to 10 minutes, depending on the number of points utilized and the stabilization duration needed for each buffer solution. Routine adjustment, preferably a minimum of , is essential for understanding how to calibrate pH probe to preserve measurement precision, especially as sensors deteriorate and their effectiveness may fluctuate. Calibration frequency may need to be adjusted based on usage and contamination levels. Additionally, ensure that the adjustment is conducted at a temperature near 25°C for optimal accuracy. New or dry electrodes must be immersed in additive fluid for a minimum of 4 hours prior to use, and measuring fluids should be utilized within 20 minutes of being opened to maintain their precision.
Troubleshoot Common Calibration Issues
When facing calibration challenges, it is essential to consider effective troubleshooting strategies, such as .
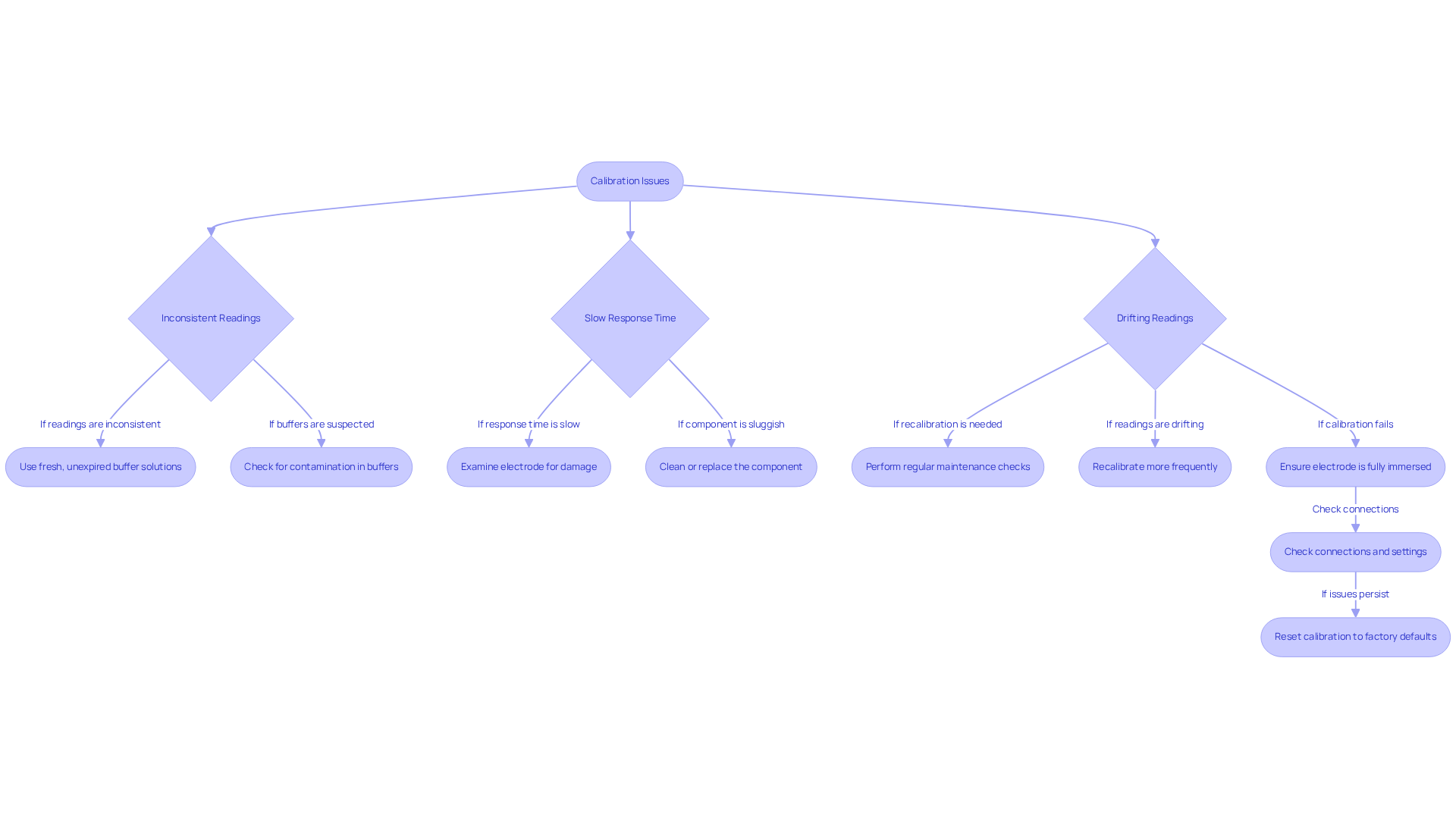
Inconsistent Readings: Always utilize fresh, unexpired buffer solutions. Contaminated or expired buffers can significantly compromise accuracy. Studies indicate that up to 15% of calcium measurements may be biased due to calibration errors, leading to potential economic impacts estimated between 60 million to 199 million USD per year. Ensuring the integrity of your buffers is crucial for reliable results.
Slow Response Time: A sluggish component may necessitate cleaning or replacement. Examine the component for visible damage, as older parts typically last 12-18 months and should respond within 60 seconds. Slow response times are often indicative of the need for maintenance, highlighting the importance of regular checks to sustain optimal performance.
Drifting Readings: If readings fluctuate, it may suggest that the sensor is aging or that more frequent recalibration is required. Regular adjustments, specifically how to calibrate pH probe, are often recommended for pH meters that are used frequently, and routine maintenance checks are vital to ensure consistent performance over time.
When learning how to calibrate pH probe, if the meter fails to calibrate, confirm that the electrode is fully immersed in the buffer solution and that all connections are secure. Additionally, ensure that the meter settings align with the adjustment type being performed. If difficulties persist, consider resetting the calibration to factory defaults, if the instrument permits such action.
Implementing these troubleshooting steps is essential for maintaining the accuracy and reliability of your pH meter, thereby ensuring optimal performance in your laboratory operations.
Conclusion
Understanding how to calibrate a pH probe is fundamental for maintaining the accuracy and reliability of measurements in laboratory settings, particularly within the pharmaceutical industry. Proper calibration ensures that results reflect the true pH of solutions and upholds the integrity of research and development processes. By prioritizing regular calibration, laboratories can mitigate risks associated with inaccurate readings, ultimately safeguarding both product quality and patient safety.
Throughout this article, key procedures for effective pH meter calibration have been outlined, emphasizing the importance of using fresh buffers, maintaining clean equipment, and adhering to a systematic calibration process. The step-by-step guidance provided reinforces the necessity of routine checks and troubleshooting common issues that may arise during calibration. These practices are integral to achieving precise measurements and ensuring compliance with strict regulatory standards.
In conclusion, the significance of mastering pH probe calibration cannot be overstated. By implementing the discussed techniques and remaining vigilant about potential calibration challenges, laboratory managers can enhance the reliability of their pH measurements. This commitment to precision not only contributes to the success of scientific endeavors but also plays a critical role in maintaining the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Embracing these best practices will ultimately lead to better outcomes in laboratory operations and a stronger foundation for future research.




