Overview
The article highlights the critical importance of selecting HPLC waste containers, underscoring the necessity for laboratory compliance and safety. It asserts that adherence to proper selection criteria—such as material compatibility, effective sealing mechanisms, and regulatory compliance—is essential for the effective management of hazardous byproducts. This careful selection minimizes environmental risks and mitigates potential legal complications that arise from improper waste disposal. By prioritizing these factors, laboratories can ensure a safer working environment while adhering to industry standards.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) waste management is essential for maintaining a safe and compliant laboratory environment. The generation of hazardous byproducts during HPLC processes necessitates a thorough understanding of the selection criteria for waste containers. How can laboratories ensure they meet regulatory standards while also protecting their staff and the environment from potential dangers? This article delves into the intricacies of HPLC waste container selection, offering insights on best practices and compliance guidelines that every lab should follow.
Understand HPLC Waste Management Basics
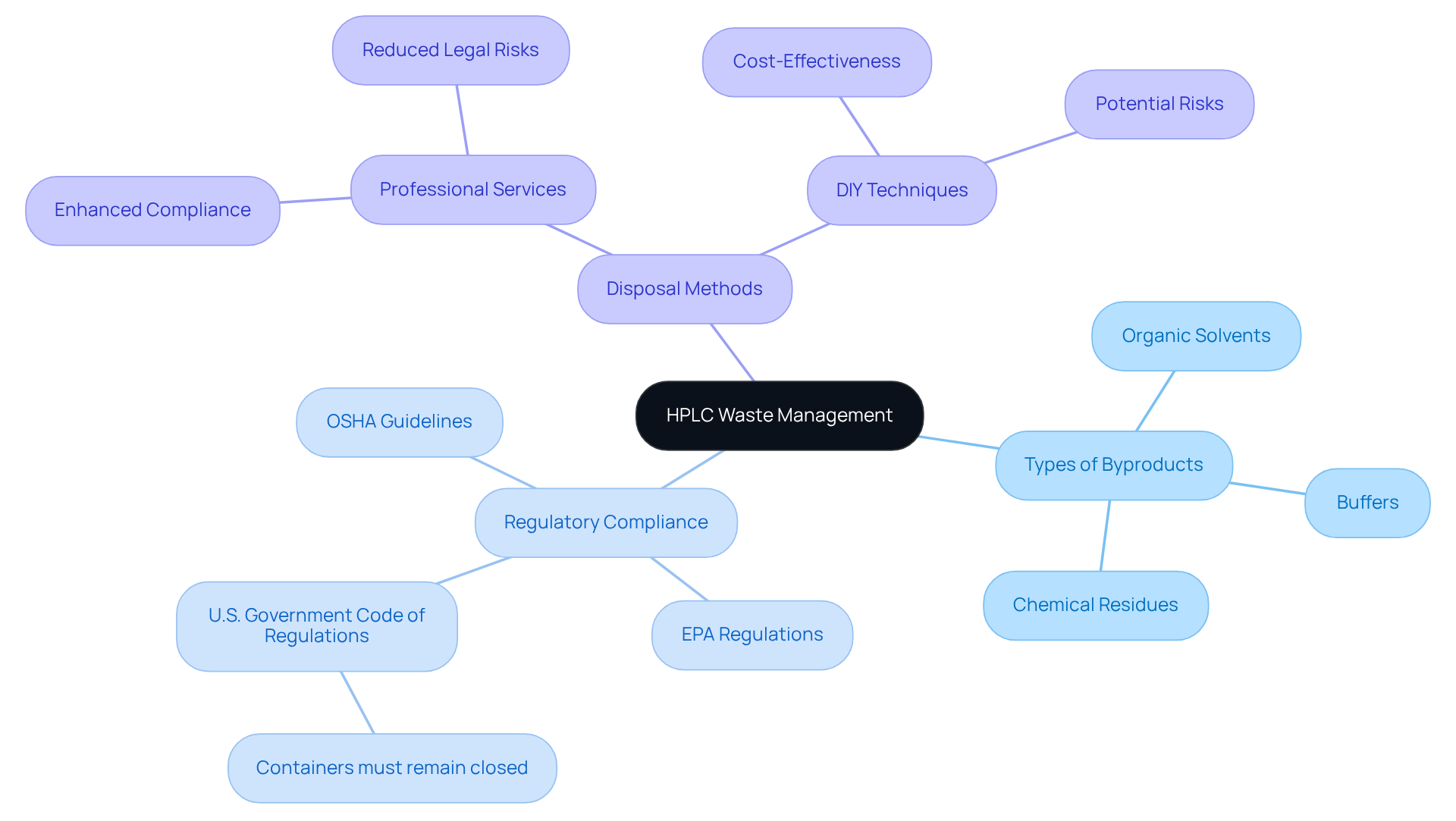
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) generates a range of byproducts, including solvents, buffers, and chemical residues, which are often classified as hazardous due to their flammable, toxic, or reactive properties. Effective management of this refuse in an HPLC waste container is imperative, not only for compliance with regulations such as OSHA and EPA but also for ensuring a safe laboratory environment. For instance, the U.S. Government Code of Regulations mandates that containers holding hazardous materials must remain closed during storage, except during the addition or removal of substances.
Understanding the specific categories of is vital. Common refuse includes organic solvents, which can pose significant health risks if not managed appropriately. Recent studies underscore that improper disposal methods can lead to legal complications and environmental hazards, reinforcing the necessity for adherence to best practices in refuse management.
Case studies reveal that while DIY disposal techniques may appear cost-effective, professional services often ensure enhanced compliance with regulations and reduce risks associated with hazardous materials. For example, research on hazardous material management in educational settings emphasizes the importance of an HPLC waste container for the accurate identification and classification of refuse to bolster security and regulatory adherence.
By comprehending the categories of HPLC refuse, their associated dangers, and the regulatory obligations for disposal, you can make informed decisions regarding suitable disposal methods and the use of HPLC waste containers. This foundational knowledge is crucial for maintaining laboratory security and compliance.
Identify Key Selection Criteria for HPLC Waste Containers
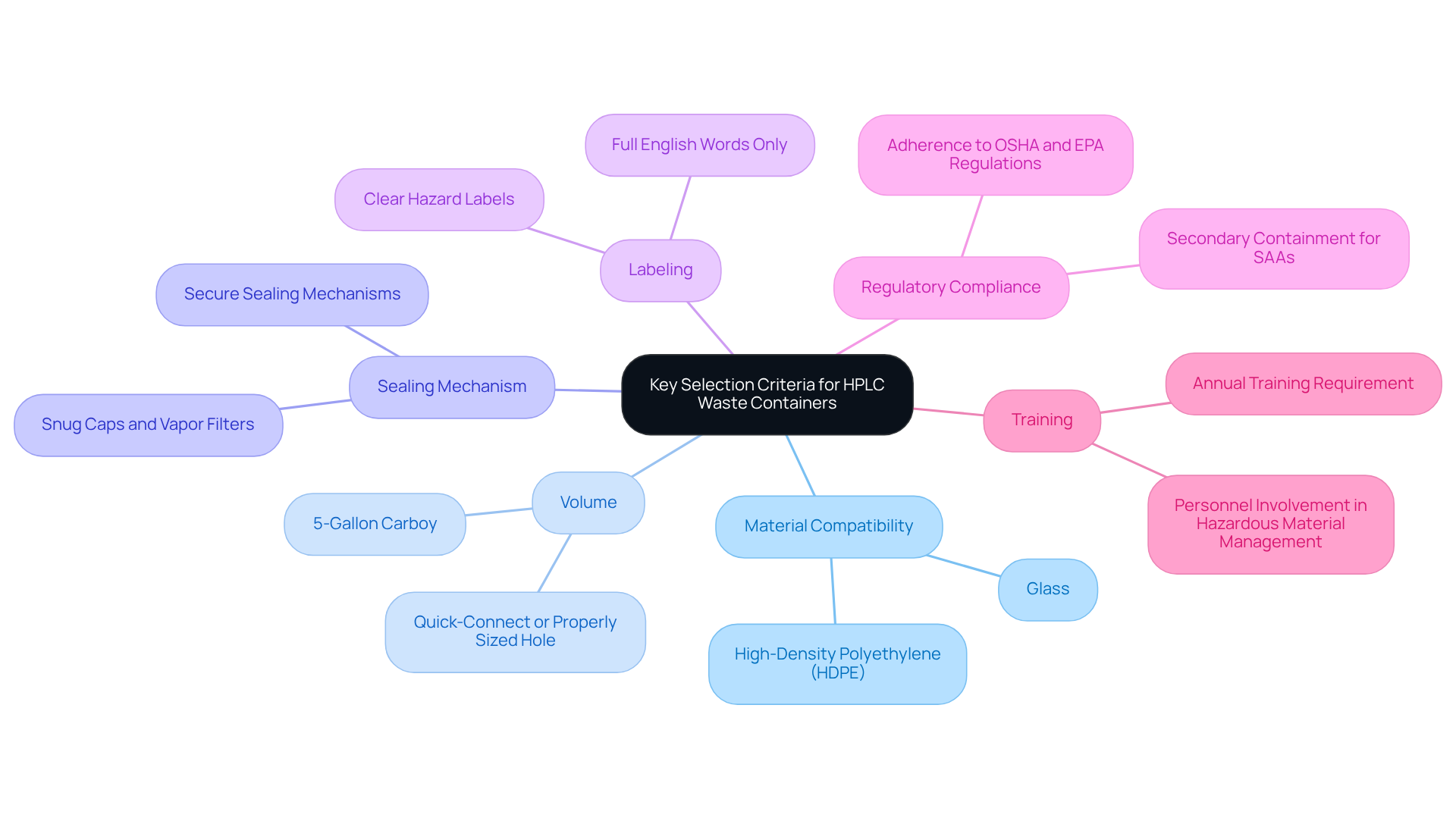
When selecting an [HPLC waste container](https://jmscience.com/products/test-capcell-pak-c-18-mg-ii-hplc-column-35x1-5mm-pore-size-100a-particle-size-3um?srsltid=AfmBOopFF9q1JI0nzl4p0Hwo6jPtl8hczf4WFToIvrd0NJI8Bm3sODP8), several key criteria must be considered to ensure safety and compliance.
- Material Compatibility: The receptacle should be made from substances that withstand the solvents and chemicals being disposed of. High-density polyethylene (HDPE) and glass are commonly recommended due to their durability and chemical resistance.
- Volume: It is essential to select a size that corresponds with the amount of refuse produced in your laboratory. HPLC waste should be collected in a 5-gallon carboy with a quick-connect or a properly sized hole in the cap to prevent frequent changes and minimize the risk of overflows, which can lead to hazardous spills.
- Sealing Mechanism: Opt for containers equipped with secure sealing mechanisms to prevent leaks and vapor release. Containers should have snug caps and, where applicable, vapor filters to improve protection.
- Labeling: Proper labeling is essential. Containers must be clearly labeled with the type of material they hold, including hazard warnings, to facilitate safe handling and ensure compliance with hazardous material regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Confirm that the receptacle adheres to all relevant safety and environmental regulations, including those established by OSHA and the EPA. This includes ensuring that the receptacle is . Additionally, secondary containment must be used for all liquid chemical disposal containers in Satellite Accumulation Areas (SAAs).
- Training: Ensure that all personnel involved in hazardous material management have completed training at least once every 12 months, as this is essential for maintaining adherence to regulations and security in laboratory operations.
By following these criteria, laboratories can effectively manage HPLC materials and their disposal in an HPLC waste container, ensuring both safety and adherence to regulatory standards. The significance of appropriate disposal management practices is further highlighted in the case study titled "HPLC Disposal Management," which discusses the safe collection and elimination of HPLC byproducts.
Explore Different Types of HPLC Waste Containers
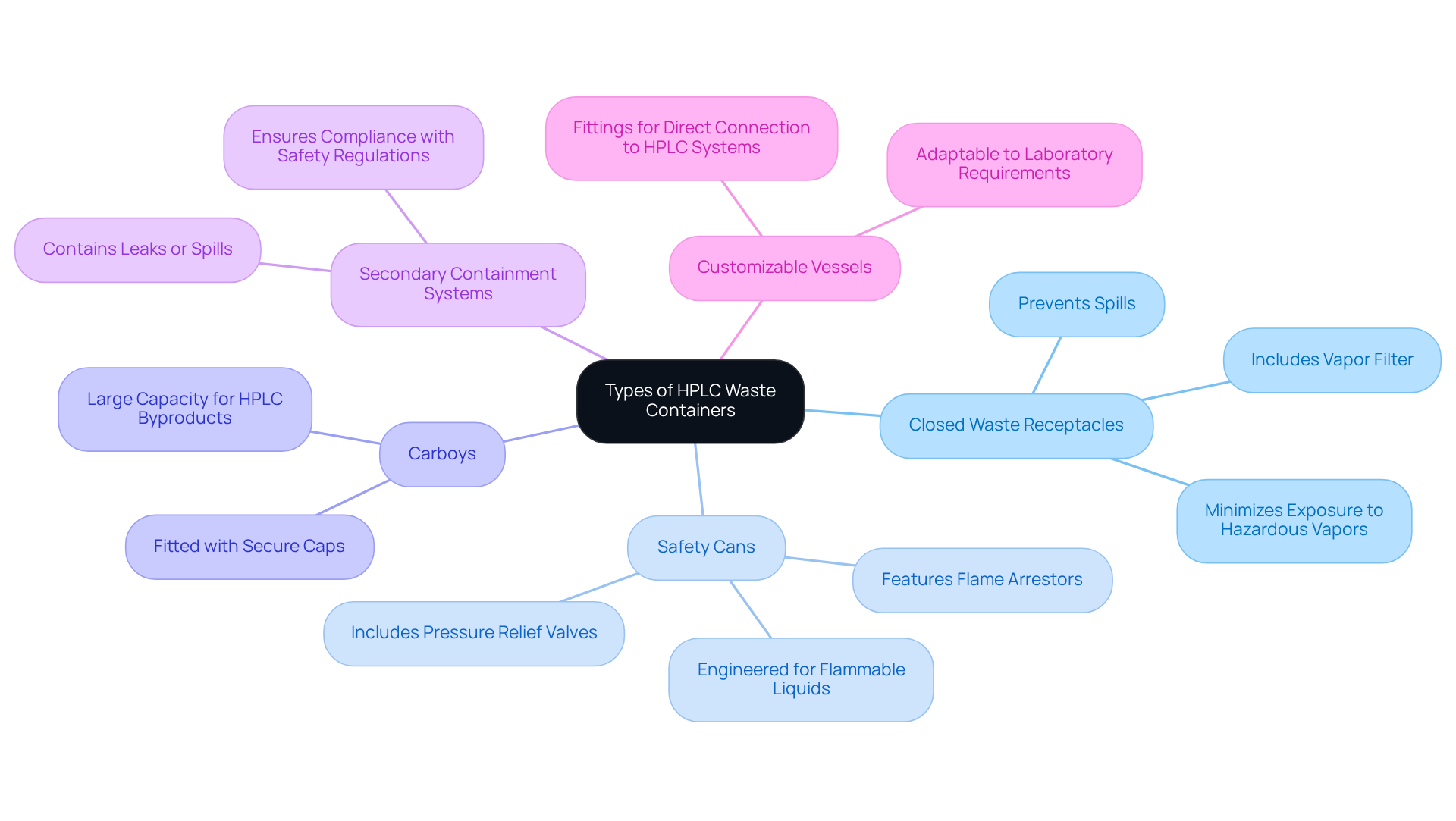
There are several types of [hplc waste containers](https://chromtech.com/how-do-you-dispose-of-hplc-waste) available, each meticulously designed for specific applications.
- Closed Waste Receptacles serve to minimize exposure to hazardous vapors and prevent spills. These receptacles often feature a secure cap and may include a vapor filter, ensuring maximum safety in laboratory environments.
- Safety Cans are specially engineered for flammable liquids, incorporating essential features such as flame arrestors and pressure relief valves. These design elements significantly enhance safety, making them indispensable in chemical handling.
- Carboys, often referred to as HPLC waste containers, are large vessels capable of holding considerable amounts of refuse, frequently utilized in laboratories that produce substantial quantities of HPLC byproducts. It is crucial that the hplc waste container is fitted with secure caps to prevent accidental leaks.
- Secondary Containment Systems provide an additional layer of protection by containing any leaks or spills from the primary storage unit. This feature is vital for ensuring adherence to safety regulations and maintaining a secure laboratory environment.
- Lastly, Customizable Vessels are offered by some manufacturers, allowing adaptation to particular laboratory requirements, including fittings for direct connection to HPLC systems. This flexibility ensures that laboratories can effectively.
Implement Best Practices for HPLC Waste Container Usage
To ensure the safe and compliant usage of HPLC waste containers, it is imperative to adhere to the following best practices:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct periodic checks on refuse bins for leaks, cracks, or signs of deterioration. Ensure that caps are secure and fittings are intact to prevent hazardous spills. Frequent assessments can significantly lower the chance of incidents and enhance adherence to regulations.
- Proper Labeling: Clearly label all waste containers with the type of waste they contain, including appropriate hazard symbols and the date of accumulation. This practice not only aids in compliance but also improves protection by informing personnel of potential risks. As noted by Justrite, proper labeling of the hplc waste container is essential for effective chemical management and safety.
- Maintain a Refuse Disposal Schedule: Establish a routine for emptying and disposing of refuse containers to prevent overfilling, which can lead to dangerous situations. Compliance rates improve significantly when a structured schedule is in place, ensuring timely disposal and reducing liability. For instance, the University of Delaware's policies highlight the significance of routine refuse disposal to mitigate long-term liability and environmental consequences.
- Training and Awareness: Ensure that all laboratory personnel receive comprehensive training in proper disposal procedures. Understanding the significance of is vital for preserving a secure laboratory environment. Training programs should encompass the latest guidelines and best practices in waste management.
- Emergency Preparedness: Equip the laboratory with spill kits and establish emergency procedures for accidental spills or leaks. Regularly review and practice these procedures to ensure that all personnel are prepared to respond effectively in the event of an incident. Having a well-defined emergency response plan is crucial for minimizing risks associated with hazardous materials.
By implementing these best practices, laboratories can significantly enhance their compliance with safety regulations and improve overall waste management efficiency.
Conclusion
Effective management of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) waste transcends regulatory requirements; it is a cornerstone of laboratory safety and environmental stewardship. The selection of appropriate HPLC waste containers is vital for ensuring compliance with safety standards, thereby protecting both personnel and the environment from hazardous materials.
This article outlines crucial considerations for selecting HPLC waste containers, such as:
- Material compatibility
- Volume
- Sealing mechanisms
- Proper labeling
A thorough understanding of the types of waste generated, adherence to regulatory requirements, and the implementation of best practices for container usage are emphasized. By adhering to these guidelines, laboratories can significantly mitigate the risks associated with hazardous waste management.
In conclusion, the significance of rigorous HPLC waste management cannot be overstated. Laboratories must prioritize compliance and safety through informed container selection and adherence to best practices. A proactive approach not only safeguards the health of laboratory personnel but also fosters a sustainable environment. By committing to these standards, laboratories can lead the way in responsible waste management, establishing a benchmark for safety and regulatory compliance within their field.




