Overview
The article emphasizes essential selection strategies for pipette tubes in laboratories, underscoring the necessity of choosing the appropriate type based on specific laboratory requirements. It systematically outlines various types of pipette tubes along with their applications. Key factors such as liquid properties, volume needs, and quality evaluation are discussed to enhance experimental precision and reliability. This comprehensive approach not only informs but also guides laboratory professionals in making informed decisions, ultimately contributing to the integrity of their experimental outcomes.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of laboratory work, the selection of pipette tubes plays a pivotal role in determining the accuracy and reliability of experimental outcomes. With a diverse array of options available, ranging from standard to specialized tubes, it is essential for laboratory personnel to comprehend their unique features in order to optimize liquid handling processes. As technological advancements continue to transform laboratory practices, the careful selection of pipette tubes emerges as a critical step in safeguarding the integrity of scientific research. This article explores the various types of pipette tubes, outlines key selection criteria, discusses quality evaluation methods, and presents best practices for their usage, empowering laboratories to enhance efficiency and achieve precise results.
Understand Different Types of Pipette Tubes
A variety of pipette tubes are available, with each meticulously designed for specific applications and liquid handling requirements. consistently enhances its product offerings to elevate scientific practices, ensuring that pharmaceutical lab managers have access to the latest innovations. The most prevalent types include:
- : Typically crafted from polypropylene, these tubes are ideal for general laboratory use. They perform effectively with most dropper tools and are perfectly suited for transferring non-viscous liquids.
- Filter Transfer Vessels: These containers are equipped with a filter that prevents contamination of the transfer device and the sample. They are particularly advantageous when working with sensitive assays or hazardous materials.
- Low Retention Pipette Containers: Designed to minimize liquid retention, these containers are essential for applications requiring precise volume measurements, such as PCR or cell culture.
- Sterile pipette tubes: Critical for microbiological applications where contamination must be strictly avoided, as they come pre-sterilized.
- Specialized Cylinders: Certain applications may require cylinders with unique features, such as extended lengths for accessing deep containers or specialized shapes for distinct liquid handling tasks.
By understanding these types, laboratory personnel can select the appropriate cylinders for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and precision in their experiments. Choosing the right sample containers not only enhances workspace efficiency but also contributes to advancements in research and healthcare, aligning with JM Science's mission to support scientific progress.
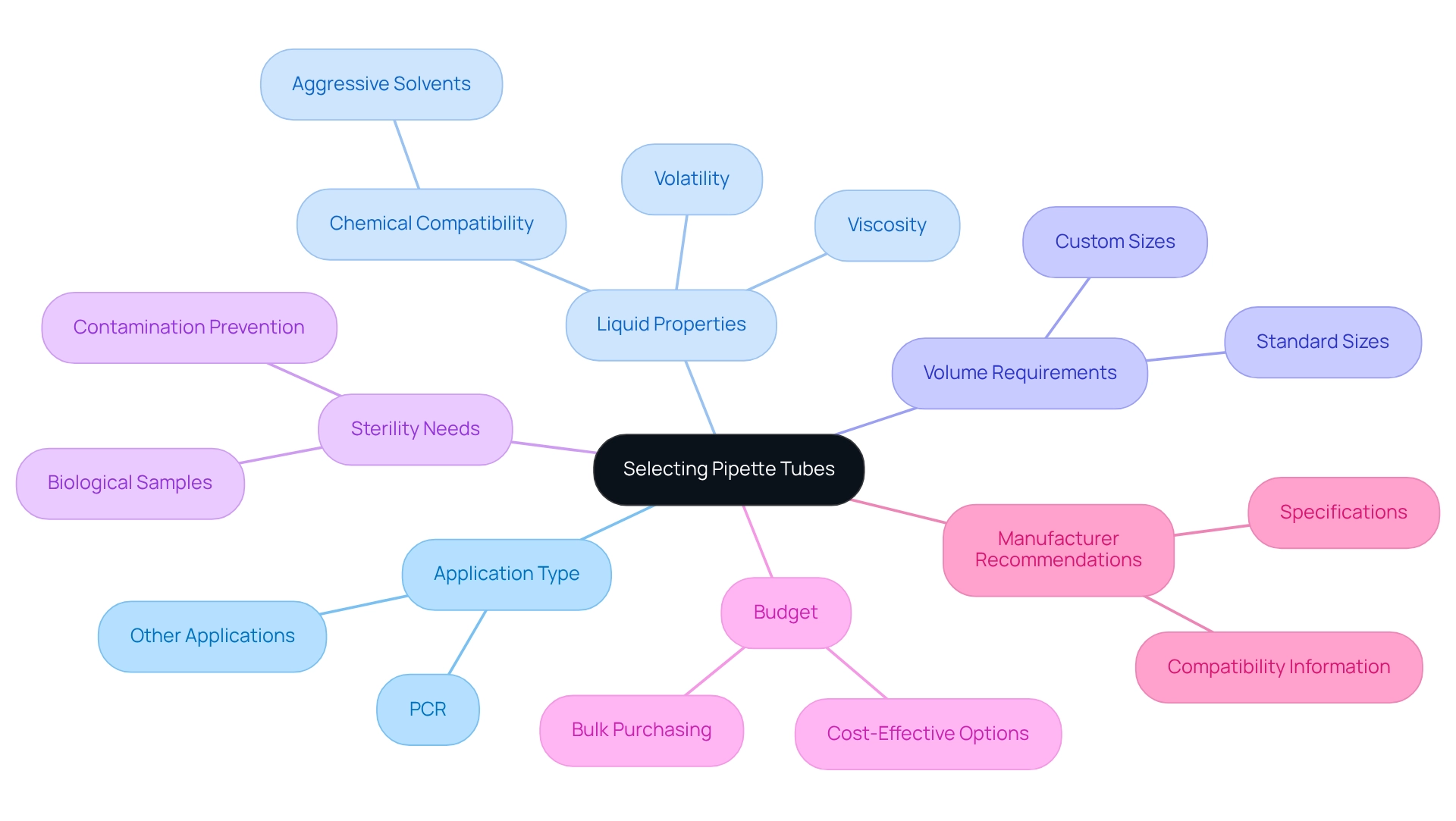
Select Pipette Tubes Based on Laboratory Requirements
When selecting pipette tubes, it is essential to consider several factors to ensure they meet the specific requirements of your laboratory.
- Application Type: First, identify the type of experiments you will conduct. For instance, if you are performing PCR, low retention containers are advisable to prevent sample loss. This consideration is vital for maintaining the integrity of your results.
- Liquid Properties: Next, assess the viscosity, volatility, and chemical compatibility of the liquids you will be handling. For aggressive solvents, ensure that the material of the container is resistant to chemical degradation. This will safeguard your samples and enhance the reliability of your experiments.
- Volume Requirements: It is also important to select containers that fit the volume ranges you will be working with. Standard containers are available in various sizes, so choose those that align with your pipetting needs. This ensures efficiency in your laboratory processes. Sterility needs dictate that if your work involves biological samples, using sterile pipette tubes is essential to prevent contamination. Maintaining sterility is critical for accurate experimental outcomes. Additionally, assess your budget and the cost and availability of the pipette tubes. Bulk purchasing options may prove to be more cost-effective for high-volume research facilities. This consideration can lead to significant savings without compromising quality.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Finally, consult with manufacturers or suppliers for guidance on the best transfer devices for your specific applications. They often provide detailed specifications and compatibility information that can aid in your decision-making process.
By thoughtfully evaluating these factors, laboratory staff can select the most appropriate sample containers, thereby improving the dependability and precision of their experimental findings.
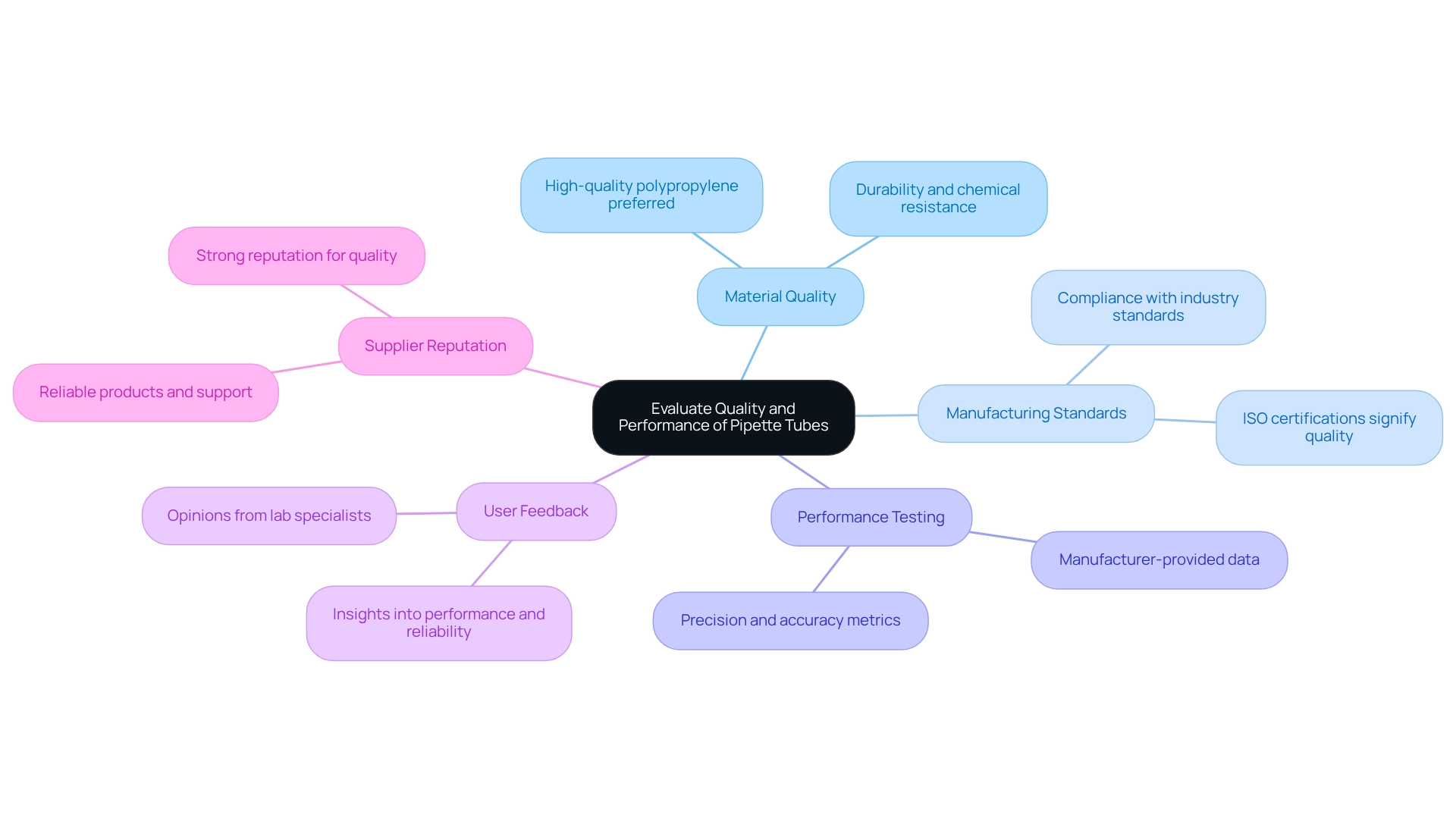
Evaluate Quality and Performance of Pipette Tubes
To ensure that the necessary quality standards are met, it is essential to evaluate several key criteria for pipette tubes.
- Material Quality is paramount; assess the substance used in the fabrication of measurement cylinders. High-quality polypropylene is preferred for pipette tubes due to its durability and chemical resistance, which are critical for reliable performance.
- Next, consider Manufacturing Standards. It is vital to ensure that the pipes are produced in accordance with applicable industry standards, such as ISO certifications. These certifications signify conformity to rigorous quality management systems, reinforcing the reliability of the products.
- Performance Testing is another crucial factor. Seek data on performance testing for pipette tubes, including precision and accuracy metrics. Manufacturers often provide this information to demonstrate the reliability of their products, allowing for informed decision-making.
- Furthermore, User Feedback plays a significant role. Collect opinions from other lab specialists regarding their experiences with specific brands or categories of transfer devices. This feedback can provide valuable insights into performance and reliability in real-world applications, enhancing your understanding of the products available.
- Lastly, prioritize Supplier Reputation. Select suppliers with a strong reputation for quality and customer service. Established suppliers are more likely to provide reliable products and support, ensuring a smoother procurement process.
By thoroughly assessing these factors, research facilities can guarantee the utilization of high-quality sample containers, ultimately improving the precision and dependability of their experimental outcomes.
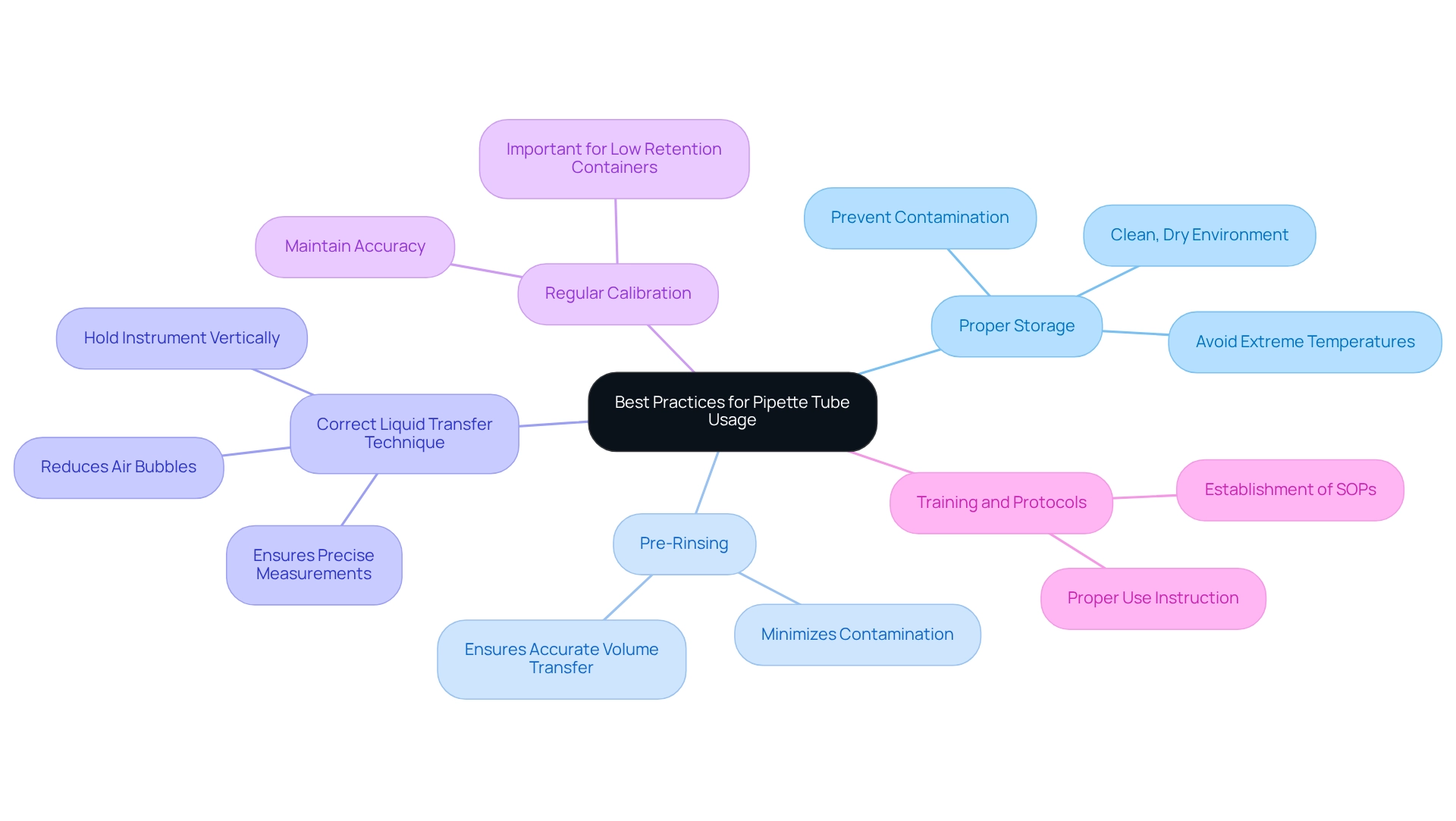
Implement Best Practices for Pipette Tube Usage
To optimize the efficiency and accuracy in laboratory settings, it is essential to implement best practices for the use of pipette tubes.
- Proper Storage is paramount. Laboratory instruments should be kept in a clean, dry environment to prevent contamination and deterioration. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures or direct sunlight, as these factors can compromise the integrity of the equipment.
- Pre-Rinsing is a critical step for essential applications. Pre-rinsing the pipette tubes with the liquid to be transferred minimizes contamination and guarantees accurate volume transfer, which is vital for reliable results.
- Utilizing the Correct Liquid Transfer Technique is also crucial. Hold the instrument vertically while aspirating and dispensing liquids to reduce the risk of air bubbles and ensure precise measurements. This method enhances the overall reliability of the pipetting process.
- Regular Calibration of liquid handling devices is necessary to maintain accuracy. This practice is especially important when using low retention or specialized containers, as even minor discrepancies can lead to significant errors in experimental outcomes.
- Finally, providing Training and Protocols for laboratory personnel is essential. Instruction on the proper use of pipette tubes, coupled with the establishment of standard operating procedures (SOPs), ensures consistency and reliability in pipetting practices.
By implementing these best practices, laboratories can significantly enhance their operational efficiency and improve the quality of their experimental results.
Conclusion
The careful selection and effective use of pipette tubes are crucial for achieving reliable and accurate results in laboratory experiments. Understanding the various types of pipette tubes—ranging from standard and filter tubes to low retention and sterile options—enables laboratory personnel to choose the most appropriate tools for their specific applications. This knowledge not only enhances efficiency but also supports advancements in research and healthcare.
Selecting the right pipette tubes involves a thorough consideration of several factors, including the type of experiments, liquid properties, volume requirements, and sterility needs. By evaluating these criteria, laboratories can ensure they are equipped with the best tools to maintain the integrity of their work. Additionally, assessing the quality and performance of pipette tubes through material evaluation, manufacturing standards, and user feedback further reinforces the reliability of experimental outcomes.
Finally, implementing best practices for pipette tube usage—such as proper storage, pre-rinsing, and regular calibration—can significantly enhance laboratory operations. By adhering to these guidelines, laboratories not only improve their accuracy and reliability but also foster an environment conducive to scientific progress. The commitment to selecting and utilizing the right pipette tubes is an investment in the future of research and innovation, ensuring that scientific endeavors yield meaningful and trustworthy results.




