Overview
The article delineates four essential practices for the effective use of aspirating pipettes:
- Understanding the types of pipettes
- Implementing best pipetting techniques
- Maintaining and calibrating the devices
- Troubleshooting common issues
These practices are critical as they enhance precision and ensure reliable measurements. Furthermore, they uphold the integrity of laboratory results, which in turn optimizes overall laboratory efficiency and accuracy. By adhering to these practices, laboratory professionals can significantly improve their operational effectiveness.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of laboratory work, aspirating pipettes emerge as indispensable instruments, each type fulfilling distinct functions tailored to a variety of scientific needs. From the versatile serological pipette, ideal for cell culture, to the precision-driven volumetric pipette, comprehending these tools is essential for any researcher striving for reliable results.
As advancements in pipette technology continue to unfold, including electronic options that enhance accuracy and control, the significance of selecting the appropriate pipette for specific tasks cannot be overstated.
This article explores the diverse types of aspirating pipettes, best practices for effective usage, maintenance tips for optimal performance, and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring that laboratory professionals are equipped with the knowledge to maximize their pipetting efficiency.
Understand Aspirating Pipette Types and Their Applications
Aspirating pipettes are indispensable tools in laboratory environments, available in various types, including serological, volumetric, and transfer instruments, each tailored for specific applications.
- Serological instruments, typically constructed from 100% virgin polystyrene, excel in transferring larger volumes of liquid and are preferred for their clarity, alongside adjustable aspiration and dispensing speeds. This versatility renders them ideal for cell and tissue culture tasks, where sterility and precision are crucial. A recent case study underscored that these devices not only enhance clarity but also allow for adjustable aspiration and dispensing rates, accommodating diverse tasks and liquid varieties.
- Conversely, volumetric instruments are designed to deliver precise measurements, making them essential for applications that demand high precision. Utilizing a serological tool for tasks requiring precision can lead to significant inaccuracies, underscoring the importance of selecting the appropriate type based on the specific needs of the experiment.
- Furthermore, the choice between can impact chemical compatibility with the liquids being handled, thereby influencing experimental integrity. Recent advancements in aspirating pipettes technology have introduced features that enhance usability and accuracy, such as electronic devices that provide greater control and consistency in liquid handling.
- As research facilities increasingly adopt these innovations, understanding the distinctions between liquid handling devices becomes critical for optimizing efficiency and ensuring reliable outcomes. Moreover, with the upcoming SETAC Europe conference on May 11, 2025, in Vienna, Austria, discussions surrounding the latest liquid handling technologies will be particularly relevant.
- Research facilities also have the opportunity to participate in the latest prize draw from INTEGRA Biosciences for a chance to win the MINI 96 Portable Electronic Pipette, highlighting ongoing innovations in this field. Statistics reveal that serological tools are widely utilized in laboratories, yet comprehending their specific applications in comparison to volumetric instruments is vital for effective laboratory practices.
Implement Best Practices for Effective Pipetting Techniques
To achieve optimal results when using aspirating pipettes, it is imperative to adhere to the following best practices:
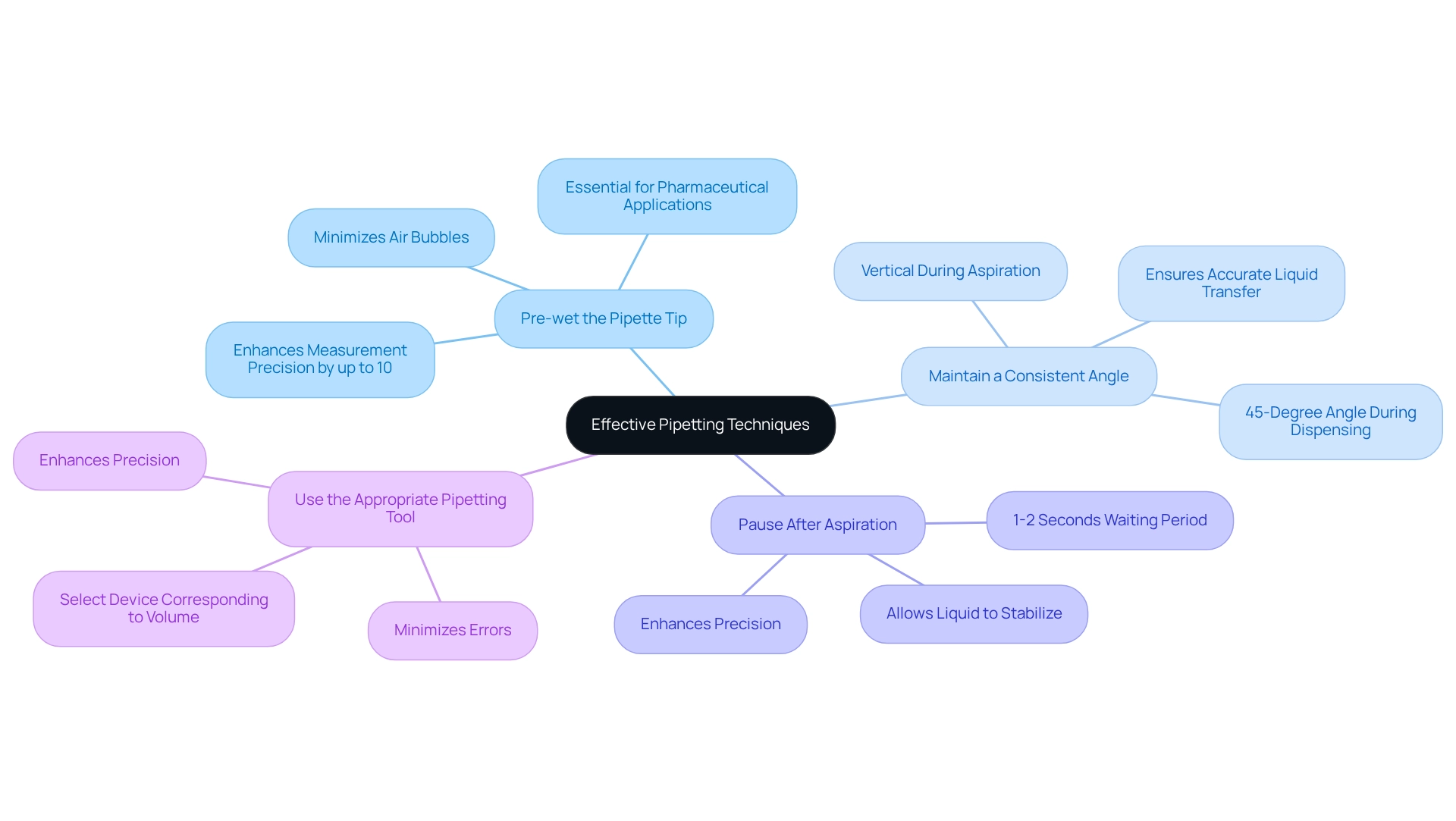
- Pre-wet the pipette tip: Aspirate and dispense the liquid several times before taking your measurement. This method moistens the tip and significantly minimizes the risk of air bubbles, which can adversely affect precision. Studies indicate that pre-wetting can enhance measurement precision by up to 10%. For instance, a stock solution with a concentration of 1000 mg/L diluted to 10 mg/L results in of 100, underscoring the essential need for precision in pipetting, particularly in pharmaceutical applications.
- Maintain a consistent angle: It is crucial to hold the device vertically during aspiration and at a 45-degree angle during dispensing. This positioning ensures accurate liquid transfer while minimizing the potential for errors.
- Pause after aspiration: Allow a brief pause of 1-2 seconds after aspirating. This waiting period is vital for allowing the liquid to stabilize in the tip, enhancing precision and ensuring that the liquid is fully drawn into the tip before dispensing.
- Use the appropriate pipetting tool: Always select a device that corresponds with the volume you are working with. Utilizing the appropriate size minimizes errors and enhances precision, as improper sizing can lead to significant inaccuracies in measurements.
Integrating these practices not only enhances pipetting accuracy but also fosters a culture of precision within the workspace. A case study examining user manuals for liquid handling devices emphasizes that knowledge of these instructions leads to improved accuracy in measurements. Furthermore, lab supervisors underscore the significance of pre-wetting tips for aspirating pipettes, noting that it is a fundamental practice for preserving the integrity of experiments. As JM Science Inc. states, "In scientific research, it is crucial to avoid any unintended transfer of substances between samples, as this can introduce unwanted variables and compromise the integrity of the experiment." By implementing these best practices and ensuring ongoing training for laboratory staff, laboratories can significantly reduce the incidence of inadequate pipetting habits, ultimately leading to more efficient operations. Additionally, a well-organized lab is essential for efficient operations and minimizing inadequate pipetting habits.
Maintain and Calibrate Pipettes for Optimal Performance
To ensure the reliability and precision of aspirating pipettes at peak performance, it is crucial to adhere to essential practices in laboratory settings.
- Regular Calibration: Adjusting measuring devices at least once every three months—or more frequently based on usage intensity—is essential. Regular calibration is vital for ensuring accurate volume dispensation, which directly impacts the reproducibility of experimental results. Research indicates that creating a calibration timetable based on usage can significantly enhance compliance and precision in laboratory environments. With over 30,000 customers relying on , the importance of proper calibration practices cannot be overstated.
- Routine Cleaning: Maintaining cleanliness is imperative. Regularly wipe the exterior of the device with a lint-free cloth and a suitable cleaning solution, such as 70% ethanol. This practice helps prevent contamination and preserves the integrity of samples.
- Inspect for Wear: Conduct regular inspections for signs of wear or damage, particularly on seals and O-rings. These components are essential for maintaining the precision of the device. Promptly replacing any worn parts is crucial to uphold performance standards.
- Expert Recommendations: Laboratory professionals emphasize that routine cleaning and maintenance not only prolong the lifespan of these instruments but also enhance their accuracy. According to Kristen Emata, the Qualer asset management software offers exceptional data management, which simplifies and enhances the calibration process with us. Implementing these best practices can lead to improved outcomes in pharmaceutical labs, where precision is paramount. Additionally, the frequency of calibration for the device should be tailored based on usage intensity, with recommendations ranging from annually to every few months, as highlighted in the case study titled 'Frequency of Calibration.'
By adhering to these guidelines, laboratories can ensure that their aspirating pipettes remain dependable tools for precise measurements, ultimately aiding in the success of their scientific efforts. For additional assistance, consider utilizing calibration services from Pipette.com to maintain your instruments effectively.
Address Challenges and Troubleshoot Common Issues
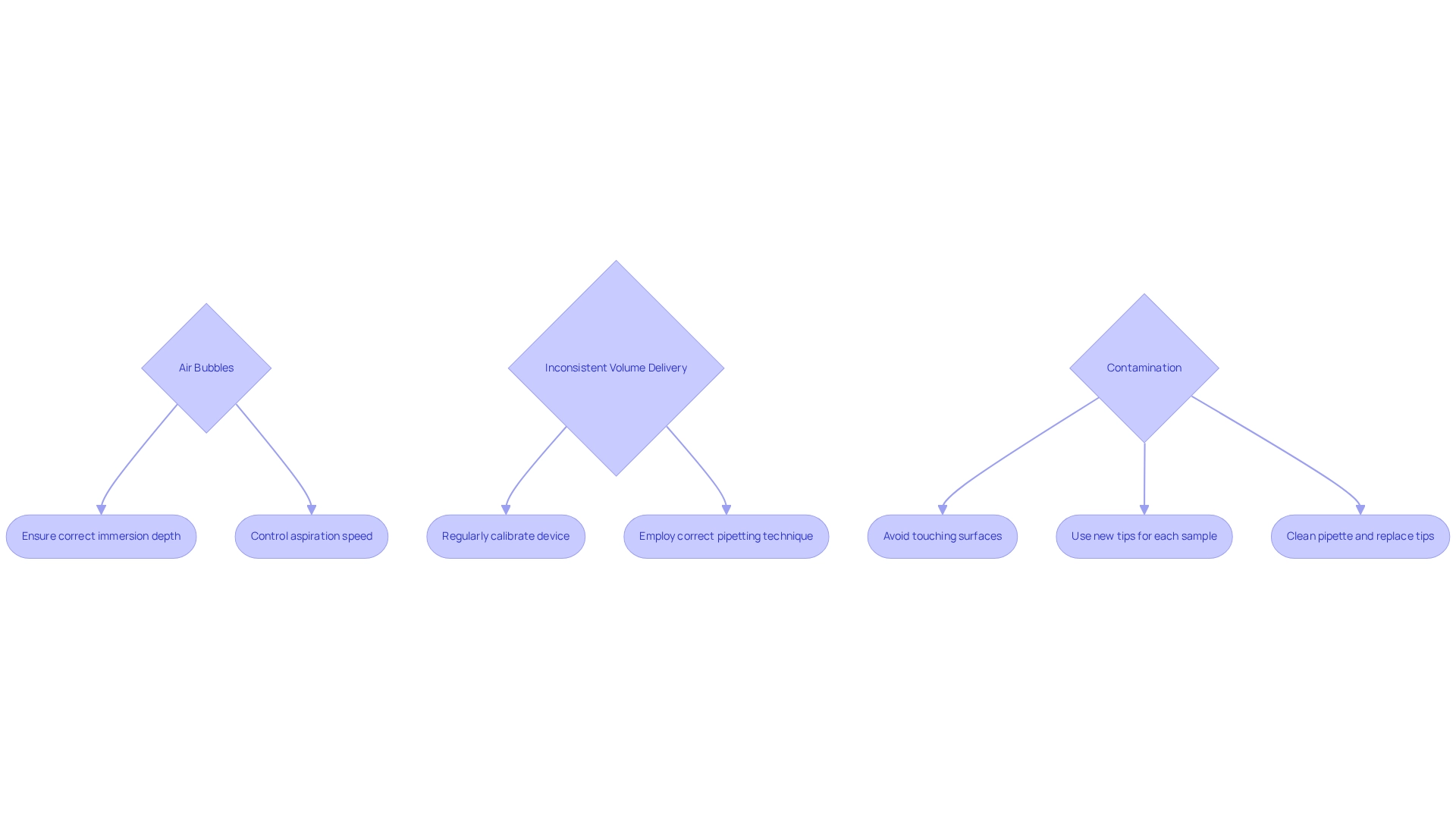
Common challenges encountered when utilizing aspirating pipettes include air bubbles, inconsistent volume delivery, and contamination. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring accurate results and maintaining the integrity of laboratory work.
Air bubbles can be a significant concern. If air bubbles are present in the transfer tip, it is essential to ensure that the tip is immersed to the correct depth during aspiration and that aspiration occurs at a controlled speed. This practice minimizes the introduction of air into the sample, thereby enhancing accuracy.
Inconsistent volume delivery often stems from improper calibration or technique. To resolve this, regularly calibrate your liquid handling device and employ the correct pipetting technique, such as pausing briefly after aspiration. These steps are vital in achieving reliable and precise measurements.
Contamination poses another serious risk. To prevent this, avoid allowing the instrument's end to touch any surfaces and always utilize new ends for each sample. Should contamination occur, it is imperative to clean the pipette thoroughly and replace any affected tips to uphold the quality of your work. By implementing these troubleshooting tips, you can significantly enhance the performance of your aspirating pipettes.
Conclusion
Aspirating pipettes are indispensable instruments in laboratory work, meticulously crafted for specific tasks that enhance precision and reliability in scientific research. From the versatile serological pipettes, which are ideal for cell culture, to the accuracy-focused volumetric pipettes, comprehending the unique applications of these tools is essential for any researcher striving to achieve valid results. As advancements in pipette technology continue to evolve, including the incorporation of electronic options that enhance accuracy and control, the need for selecting the appropriate pipette for specific laboratory requirements becomes increasingly critical.
Implementing best practices for pipetting techniques—such as:
- Pre-wetting tips
- Maintaining the correct angle
- Conducting regular calibration
substantially improves measurement accuracy and cultivates a culture of precision within laboratory environments. Furthermore, addressing common challenges through effective troubleshooting can avert errors that jeopardize experimental integrity.
Ultimately, the collective understanding and application of these principles not only optimize laboratory efficiency but also strengthen the reliability of scientific outcomes. By prioritizing the selection, maintenance, and proper usage of aspirating pipettes, researchers can ensure their findings are both accurate and replicable, thereby paving the way for advancements in scientific knowledge and innovation.




