Overview
This article delineates effective strategies for organizing a pipette tips box, highlighting the critical role of:
- Clear labeling
- Color-coding
- Accessibility
- Regular inventory checks
- The use of refillable boxes
By implementing these methods, laboratories can significantly enhance efficiency and reliability. Ensuring that the right tools are readily available and properly maintained reduces the risk of errors in liquid handling tasks. In turn, this fosters a more productive and error-free laboratory environment, prompting laboratories to adopt these essential practices.
Introduction
In the intricate realm of laboratory work, the selection of pipette tips is pivotal, often determining the success or failure of experiments. With an array of tip types available, each tailored for specific applications, comprehending their distinct features is essential for any researcher striving for precise and reliable results.
From standard tips that cater to general purposes to specialized variants such as filter and low retention tips, the right choice can markedly improve both accuracy and efficiency in pipetting tasks.
As laboratories increasingly acknowledge the critical role these tools play, this article explores the various pipette tip types, their applications, and vital criteria for selection, providing insights that can enhance laboratory practices and outcomes.
Understand Pipette Tip Types and Their Applications
A pipette tips box contains indispensable tools in laboratory environments, with various types meticulously designed for specific applications.
- Standard Recommendations: The most commonly utilized options, these tools are versatile and suitable for a range of general tasks, delivering consistent performance across diverse uses.
- Filter Suggestions: Featuring a built-in barrier that prevents aerosols from contaminating the pipette, these tips are ideal for sensitive applications like PCR and cell culture, where contamination can compromise results. Recent market analysis reveals a significant increase in the popularity of filter ends, underscoring a heightened awareness of contamination risks in sensitive laboratory settings.
- Low Retention Techniques: Tailored to minimize liquid retention, low retention tips are perfect for handling viscous or valuable samples, ensuring maximum recovery and enhancing measurement accuracy.
- Sterile Instruments: Gamma-irradiated to eliminate biological contaminants, sterile tips are crucial for microbiological tasks and any process requiring aseptic conditions, thereby safeguarding experimental integrity.
- Wide Bore Nozzles: Designed for managing larger particles or thick liquids, these nozzles facilitate smooth aspiration and dispensing, particularly beneficial in scenarios involving cell suspensions or dense reagents.
Understanding the distinct features and applications of is vital for selecting the appropriate type to meet specific research needs. This choice not only enhances accuracy and efficiency in pipetting tasks but also bolsters the overall reliability of experimental outcomes. Expert opinions emphasize that selecting the right tip is crucial for achieving optimal results, highlighting the importance of this decision in scientific practices. As noted by laboratory experts, "Choosing the appropriate tip can greatly influence the precision of your outcomes and the effectiveness of your processes." Additionally, case studies indicate that laboratories prioritizing filter tips in sensitive applications experience fewer contamination incidents, leading to more reliable data. Furthermore, projections for 2025 indicate a substantial increase in the market share of various disposable tips, particularly low retention and filter varieties, showcasing their growing importance in modern research practices. Continuous advancements in tip technology are evolving, offering enhanced features that cater to the specific needs of laboratory professionals.
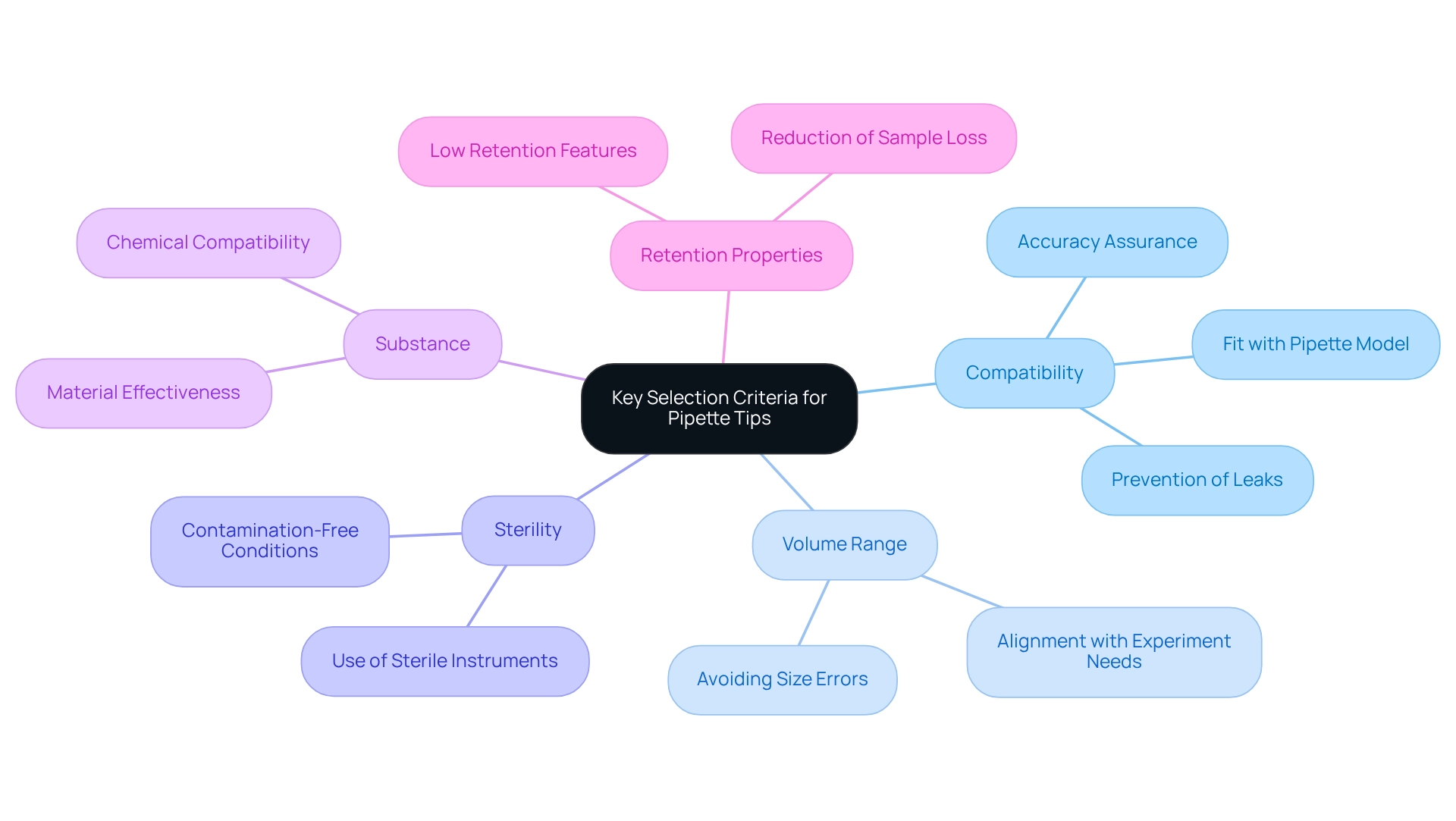
Evaluate Key Selection Criteria for Pipette Tips
When selecting a pipette tips box, it is crucial to consider several key criteria that ensure optimal performance in laboratory settings.
- Compatibility is essential; ensure the components fit your pipette model securely to prevent leaks and inaccuracies.
- The volume range must align with the specific needs of your experiments, as utilizing the incorrect size can lead to significant errors.
- Sterility is paramount for applications requiring contamination-free conditions, so choosing sterile instruments is advisable.
- The substance of the tips is also important, as certain materials are designed for specific chemical compatibility, enhancing their effectiveness.
- Evaluate the retention properties; if low retention features are necessary for your application, they can significantly reduce sample loss.
By thoroughly evaluating these standards, you can confidently select the most suitable laboratory accessories, such as a pipette tips box, tailored to your requirements.
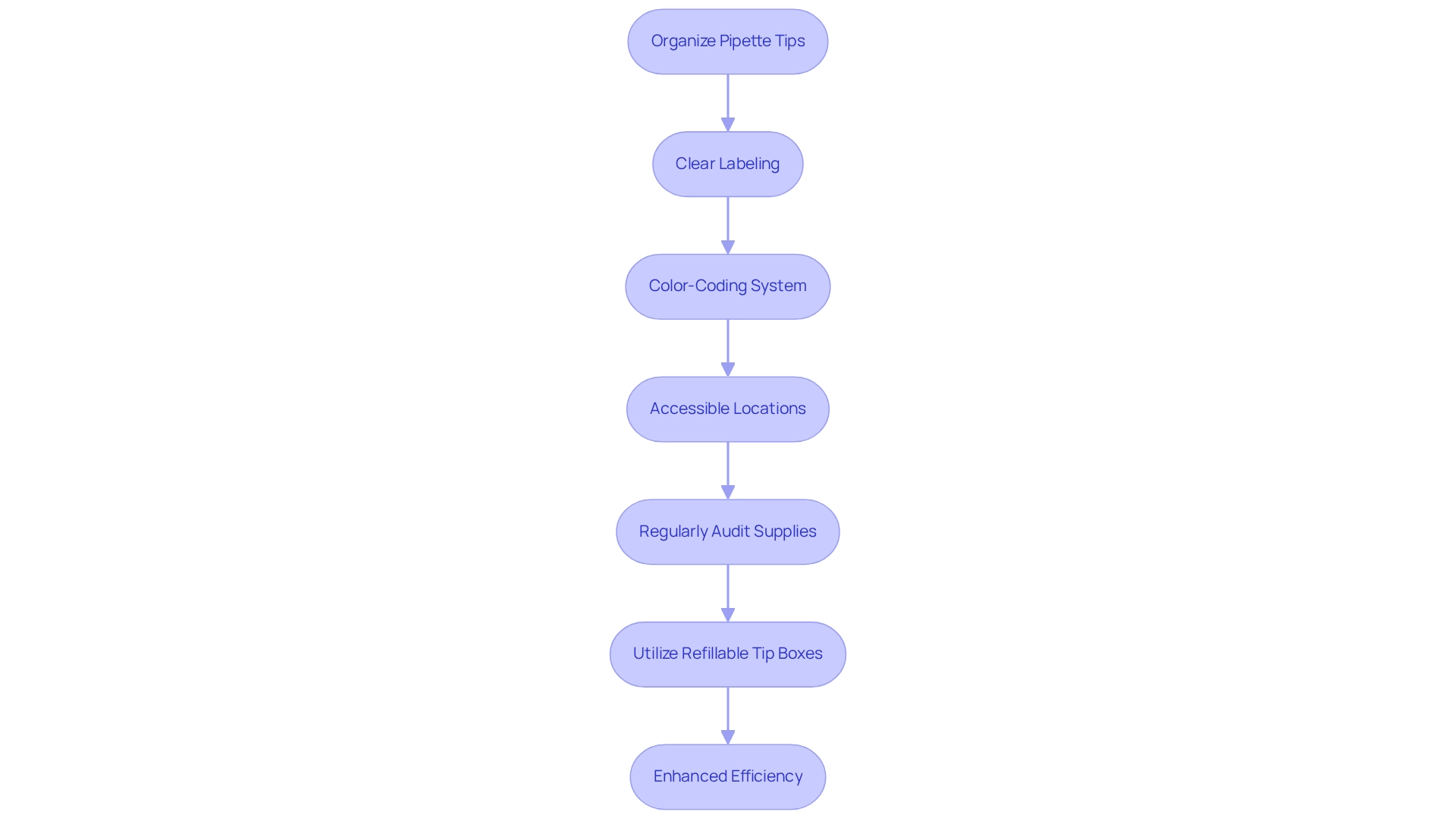
Organize and Manage Your Pipette Tips Efficiently
To effectively organize and manage your pipette tips box, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Use Clear Labeling: Clearly mark each box or rack with the type and size of tools. This practice enables rapid recognition, significantly decreasing the time spent searching for the appropriate items.
- Implement a Color-Coding System: Utilize color-coded racks for various types of attachments. This visual distinction enhances visibility and organization, facilitating faster access during experiments.
- Store in Accessible Locations: Position frequently used tips within easy reach. Streamlining your workflow in this manner minimizes disruptions and enhances overall efficiency in the lab.
- Regularly Audit Supplies: Conduct periodic inventory checks to ensure adequate supplies. Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining the reliability of liquid handling devices in research environments, guaranteeing that all calibration levels are precisely prepared and assessed. This method aids in removing outdated or compromised items, thus preserving the quality of your scientific work.
- Utilize Refillable Tip Boxes: Consider adopting refillable boxes to reduce waste. This approach not only keeps your supply organized but also supports sustainability efforts within the lab.
By applying these optimal methods, you can establish for managing your disposable instruments, ultimately resulting in enhanced efficiency and dependability in your operational processes. Furthermore, understanding the solubility traits of analytes, as emphasized in the case study 'Analyte Solubility and Calibration Challenges,' can prevent calibration issues, ensuring that your measuring devices are employed effectively for precise measurements. Remember, if a liquid transfer device passes the routine check, it is confirmed to be functioning as intended, further enhancing your facility's efficiency.
Troubleshoot Common Pipette Tip Issues
Frequent problems with laboratory tools can significantly impact results; however, understanding their solutions can enhance precision and productivity. Addressing prevalent challenges with effective strategies is essential for laboratory success.
Inconsistent Volume Dispensing: This issue often stems from improper tip attachment or calibration errors. are crucial, as studies show that precision can vary, with discrepancies as low as 0.05% in pipetting measurements. Ensuring tips are securely attached mitigates this problem. Moreover, utilizing E1-ClipTip Electronic pipettes allows for separate adjustments of aspiration and dispensing speeds, facilitating optimal and consistent liquid dispensing.
Dripping Tips: Dripping can occur if the tip is not firmly attached. To combat this, consider employing low retention methods, particularly when handling viscous liquids, as they minimize liquid loss and enhance dispensing precision.
Air Bubbles: Air pockets can lead to inaccurate measurements. To eliminate this issue, pre-wet the tip by aspirating and dispensing the liquid prior to taking the actual measurement. This practice ensures a more reliable volume.
Contamination: For sensitive applications, using sterile instruments is imperative. Avoid touching the tip with bare hands to prevent contamination, which can compromise the integrity of experiments.
Tip Ejection Issues: If tips are not ejecting properly, verify that the device is clean and that the ejector mechanism functions correctly. Regular maintenance can prevent these issues and ensure smooth operation.
By proactively addressing these common issues related to the pipette tips box, laboratory staff can maintain the quality of their liquid handling tasks, ultimately enhancing overall efficiency and reliability. As noted, "With their unmatched versatility, these instruments remain essential tools that significantly contribute to the success and progress of scientific research and experiments." Furthermore, multichannel pipettes are invaluable for laboratories aiming to boost throughput while ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate pipette tips is a fundamental aspect of laboratory work that significantly influences the success of experiments. This article has explored the various types of pipette tips available—from standard to specialized options like filter and low retention tips—each tailored for specific applications. Understanding the unique features and benefits of these tips is essential for enhancing accuracy and efficiency in pipetting tasks, ultimately leading to more reliable experimental outcomes.
Moreover, the criteria for selecting pipette tips, including compatibility, volume range, and sterility, are critical considerations that determine the effectiveness of laboratory procedures. Implementing organized management strategies, such as clear labeling and regular inventory checks, can significantly streamline laboratory workflows and minimize the risk of errors.
Addressing common pipette tip issues is also vital for maintaining optimal performance. By recognizing potential problems like inconsistent volume dispensing or contamination, laboratory personnel can take proactive measures to ensure precision in their work.
In conclusion, the careful selection, organization, and maintenance of pipette tips are integral to achieving high standards in laboratory practices. By prioritizing these factors, researchers can enhance their experimental accuracy and contribute to the overall reliability of scientific data. As laboratories continue to evolve, the importance of these seemingly small tools will only grow, underscoring the need for informed decision-making in their use.




